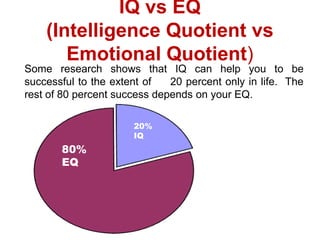
This document defines emotional intelligence and its importance. It discusses the domains of EI, including intrapersonal skills like self-awareness and interpersonal skills like empathy. Experts note that EI predicts life success better than IQ. While traditional views see emotions as distracting, high performers view emotions as motivating. The document advocates teaching with EI by acknowledging learners' feelings to create an environment conducive to learning. In conclusion, EI involves self-awareness, managing distressing moods, empathy, and social skills to embrace life.