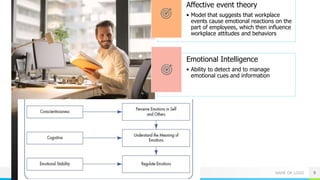
The document explores the differences between emotions and moods, highlighting that emotions are short-lived responses to specific events, while moods are longer-lasting and more generalized. It discusses the impact of emotional labor on employees and presents affective events theory, emotional intelligence, and strategies for emotion regulation. Additionally, it addresses how emotions influence workplace dynamics, including job attitudes and behaviors.