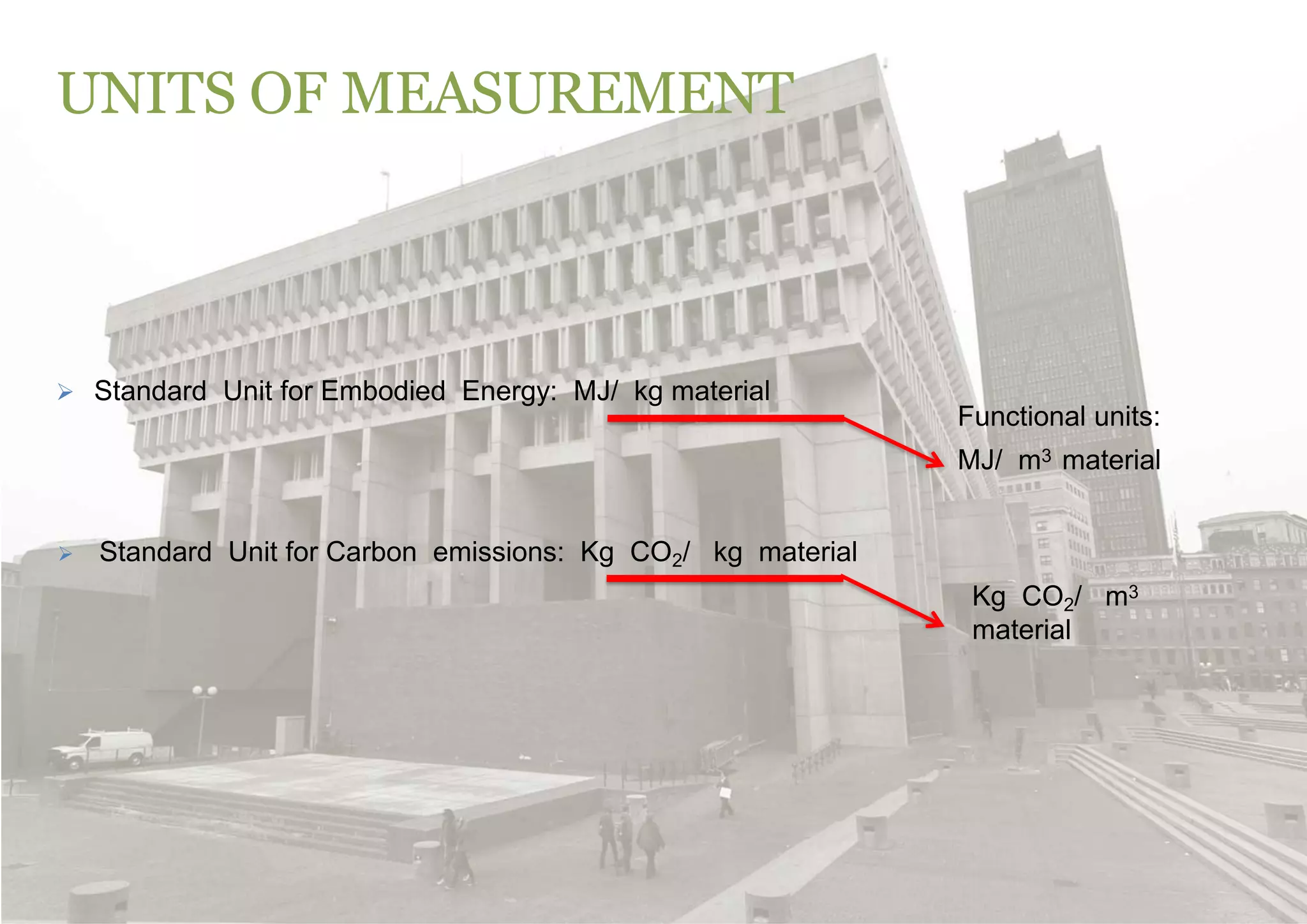
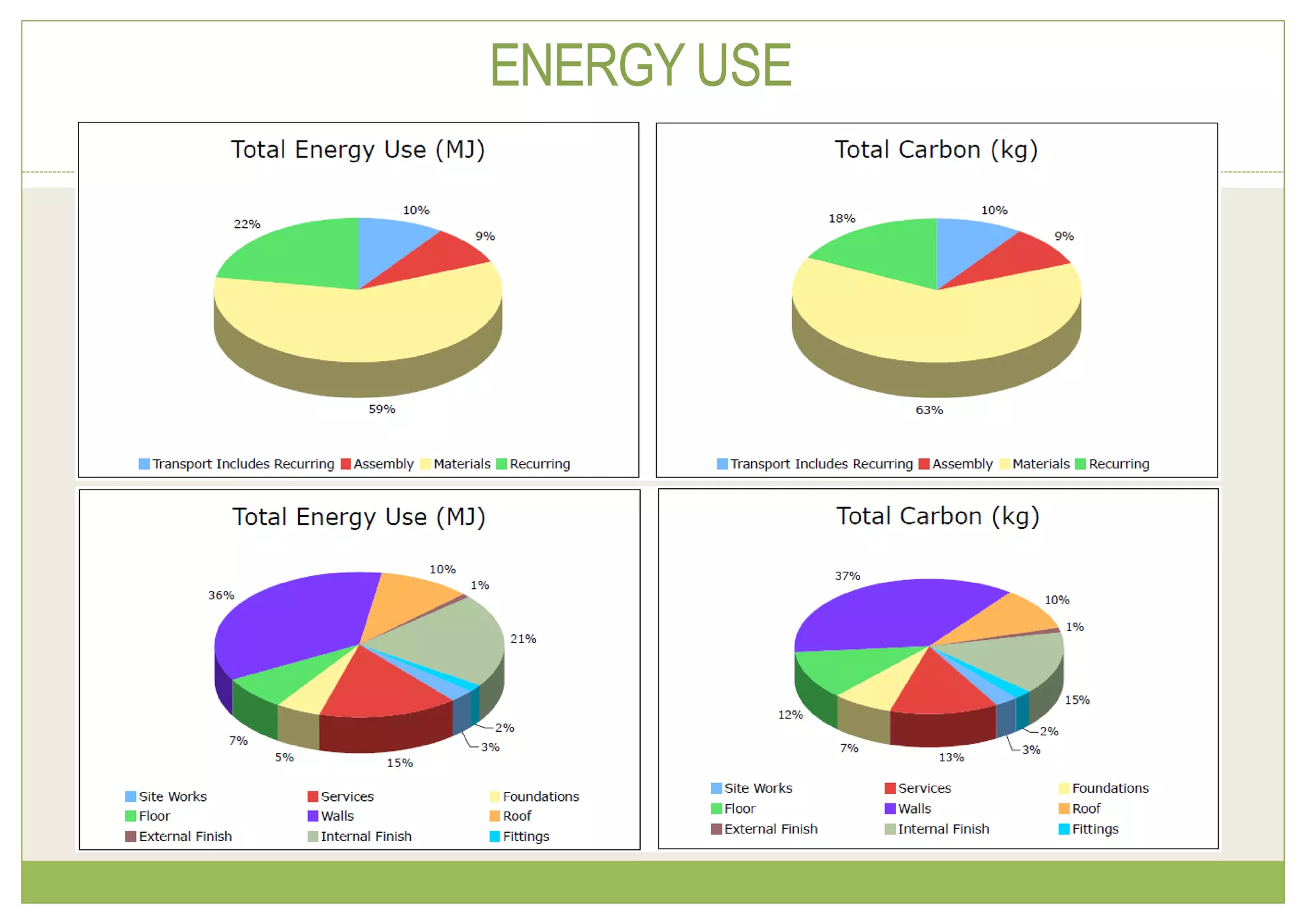
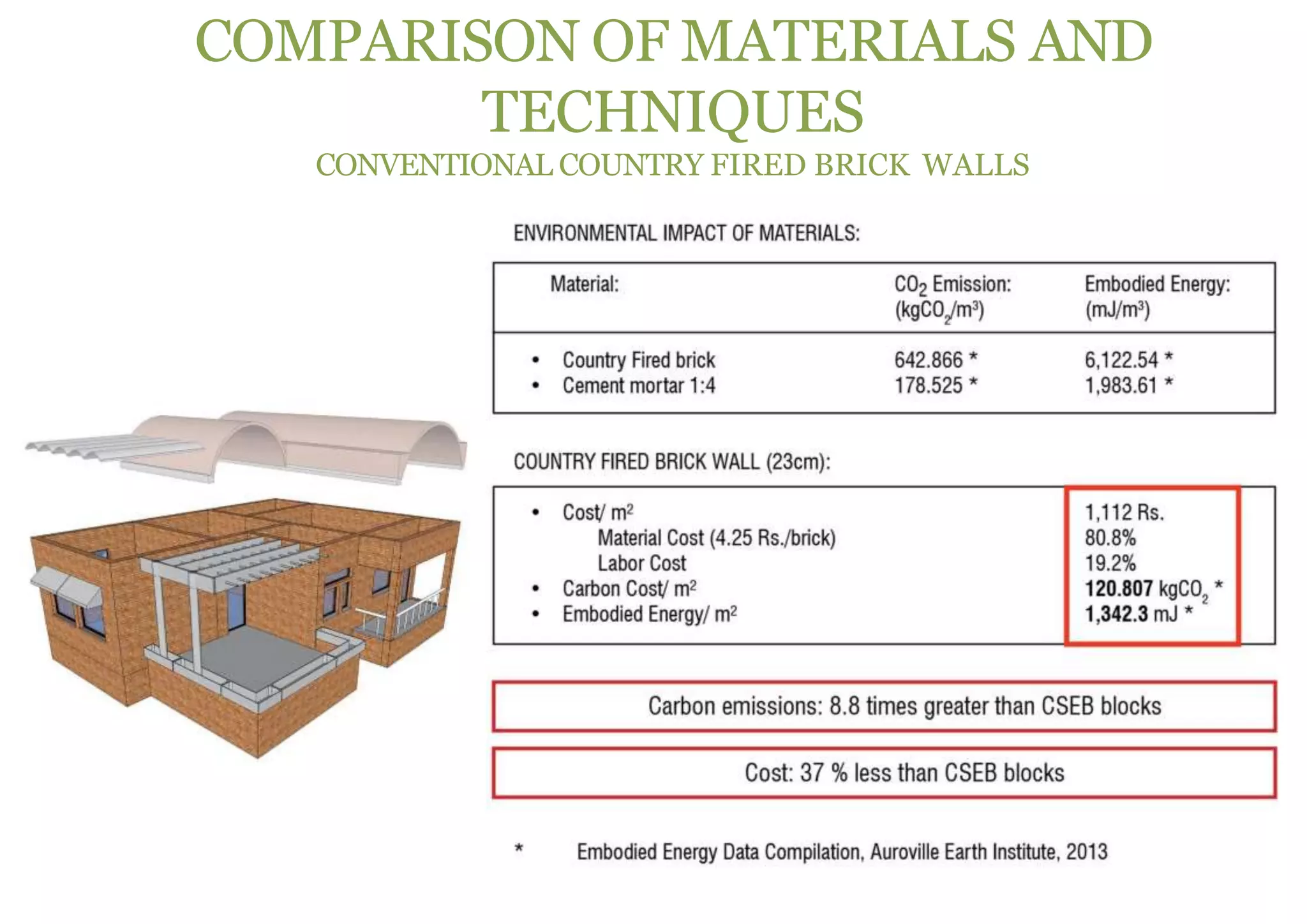
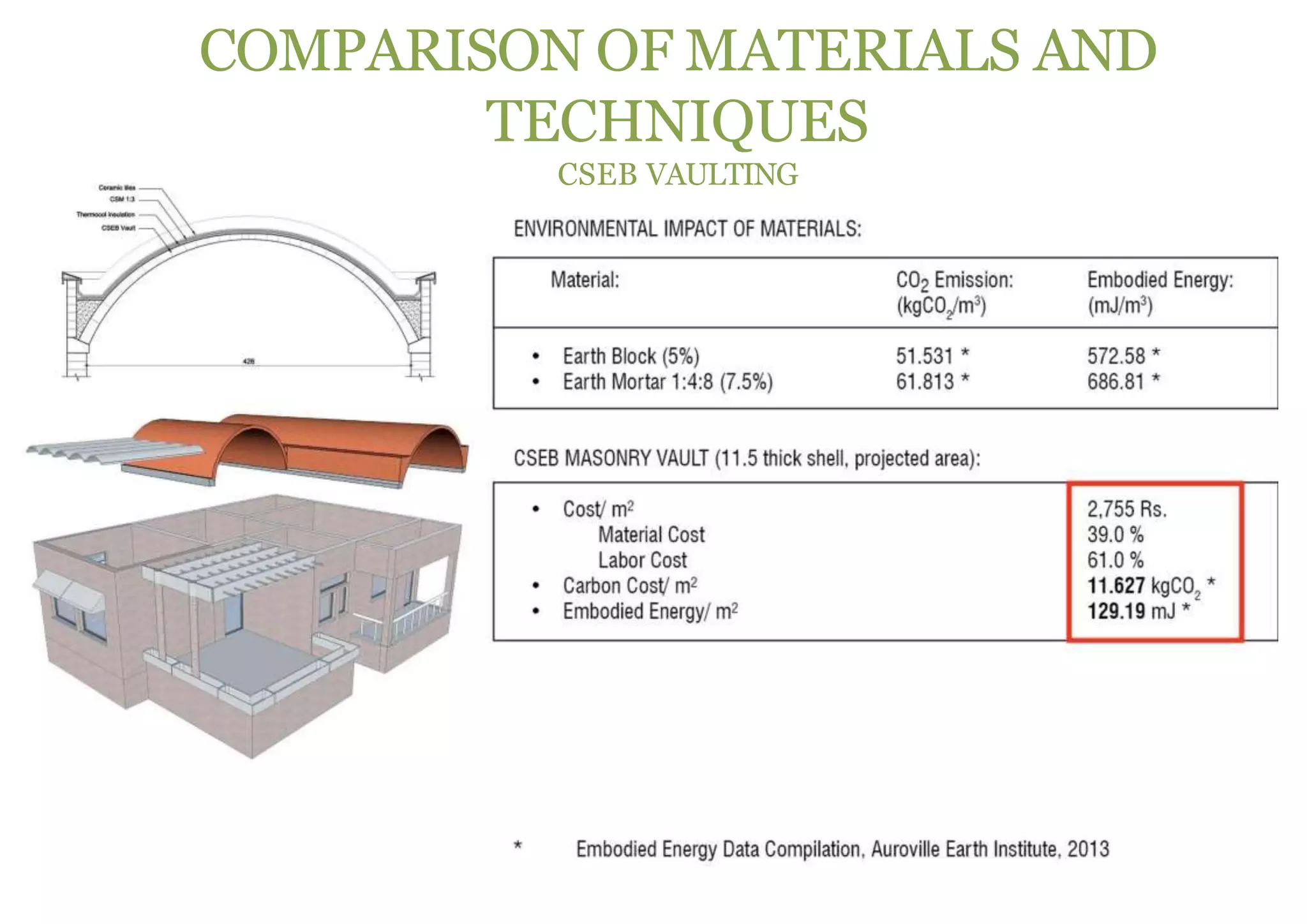
The document discusses embodied energy in sustainable building materials, defining it as the total primary energy consumed throughout a material's life cycle, including extraction, manufacturing, and transport. It emphasizes the importance of selecting materials with low embodied energy and provides guidelines for reducing energy consumption in construction through durability, local sourcing, and recycling practices. The document also highlights the environmental impact of the building industry, noting that buildings account for 30-40% of global energy use and are significant contributors to CO2 emissions and waste.