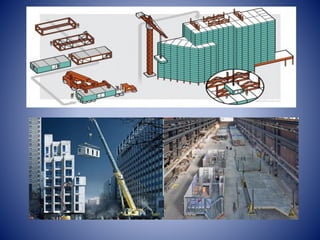
This document discusses modular construction. It defines modular construction as structures made off-site from prefabricated components that are assembled on-site. It covers the application of modular construction in housing, education, and healthcare. It describes the types as permanent modular construction and relocatable buildings. The benefits are listed as reduced costs, improved quality, sustainability, and reduced construction time. The limitations include transportation challenges and need for skilled labor. A case study of modular apartments in San Jose, California is presented.