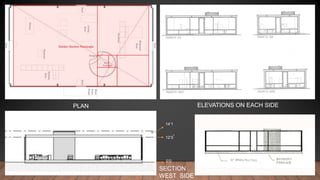
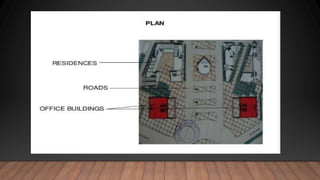
Philip Johnson was an American architect known for experimenting with glass facades. Some of his most notable works include the Glass House (1949) and Puerta de Europa office towers in Madrid, Spain (1996). The Glass House was Johnson's personal residence made of steel and glass with no interior supports. It influenced the use of all-glass buildings. Puerta de Europa featured twin towers at a 15 degree angle clad in stainless steel and red metal, breaking conventions of typical skyscrapers. Johnson believed in drawing from others and not pursuing originality for its own sake.