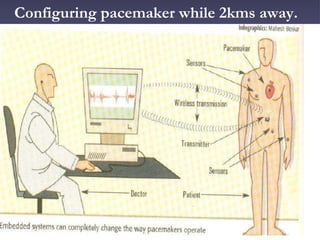
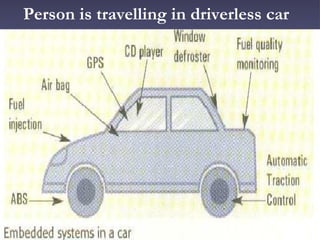
1. Embedded systems allow for controlling devices remotely such as driving a car from 2km away. Real-time operating systems and embedded systems allow for these advanced capabilities.
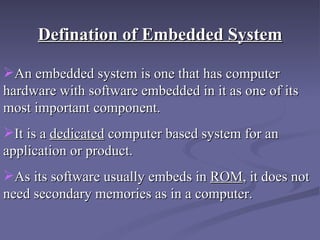
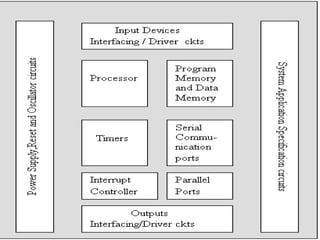
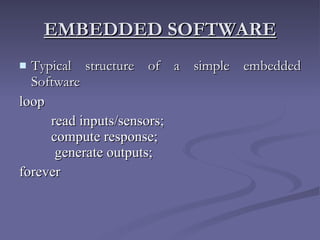
2. An embedded system is a computer system with dedicated functions within a larger mechanical or electrical system, often with real-time computing constraints. It usually has software programmed into read-only memory.
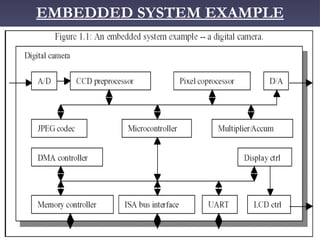
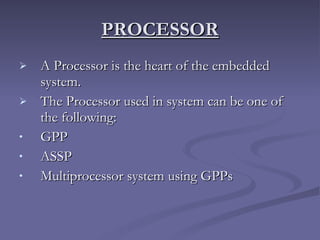
3. Examples of embedded systems include processors in consumer electronics, appliances, aircraft control systems, and medical equipment. Processors must be selected based on specifications like instruction set and clock frequency.