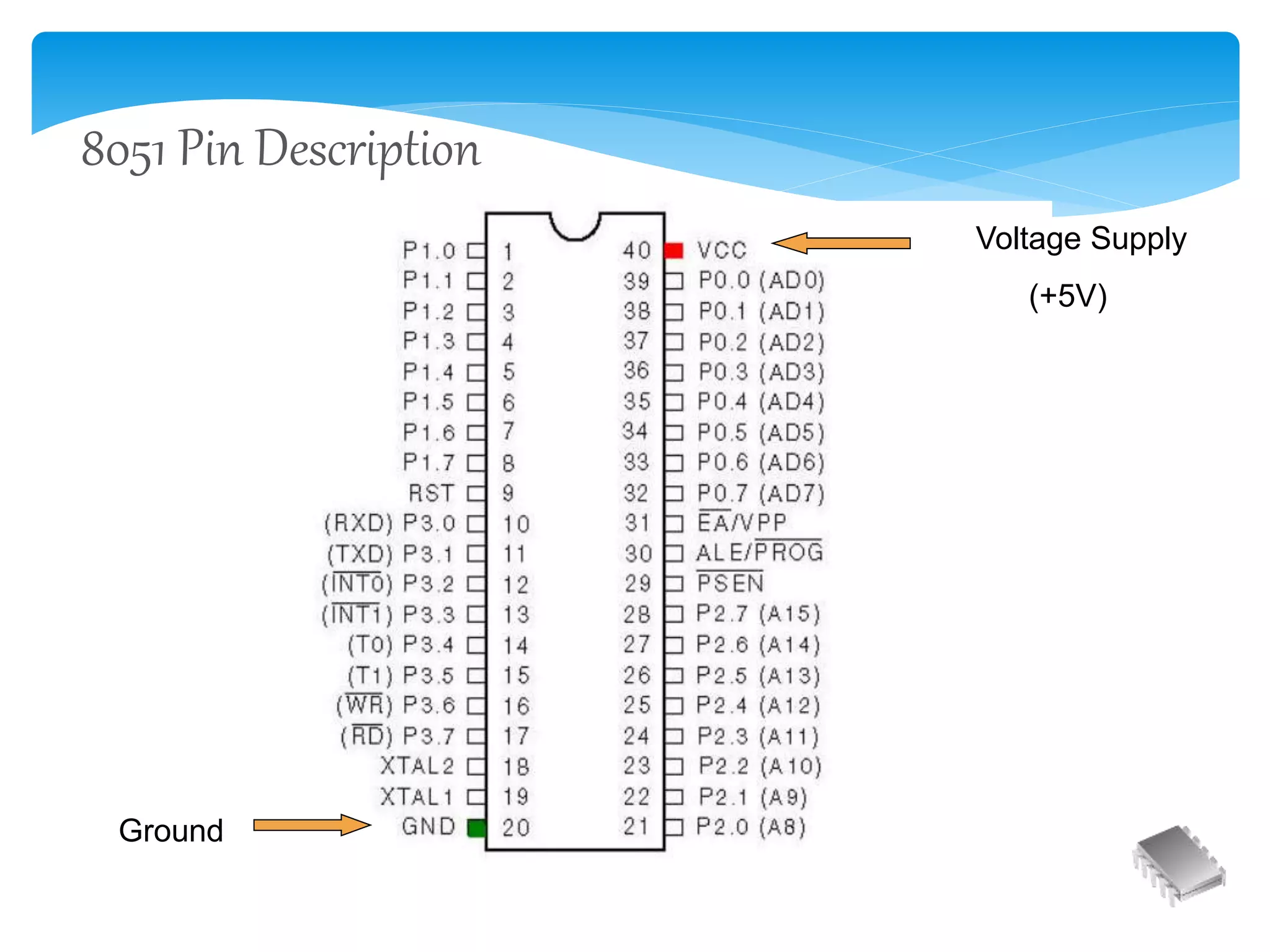
The document is a presentation on embedded systems covering their definition, components, characteristics, and various application areas such as telecommunication and automotive. It also discusses the 8051 microcontroller, its features, and development tools, highlighting challenges and future trends in embedded systems. Ultimately, it emphasizes the increasing integration of microprocessors in everyday devices, making them 'smart'.