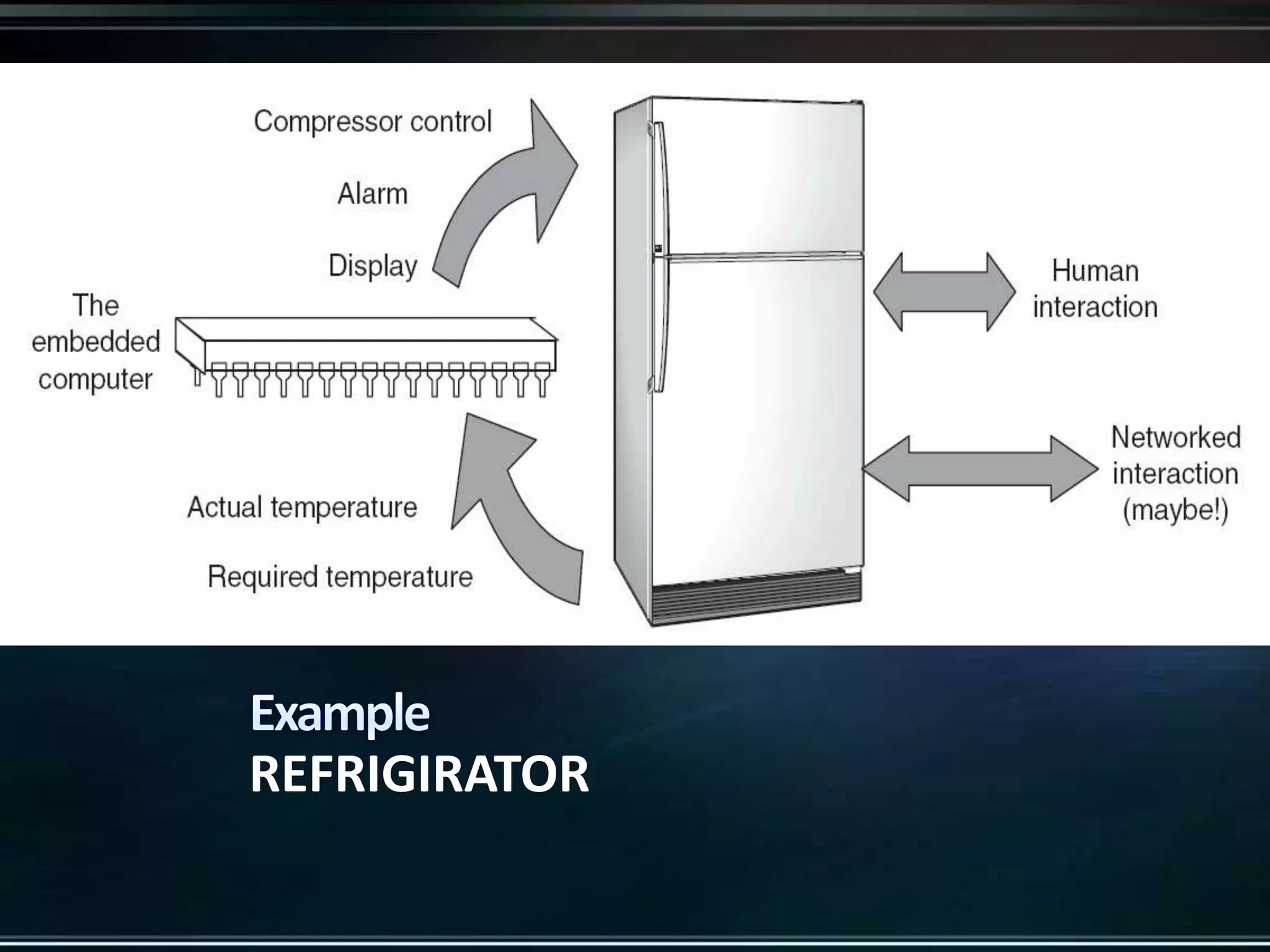
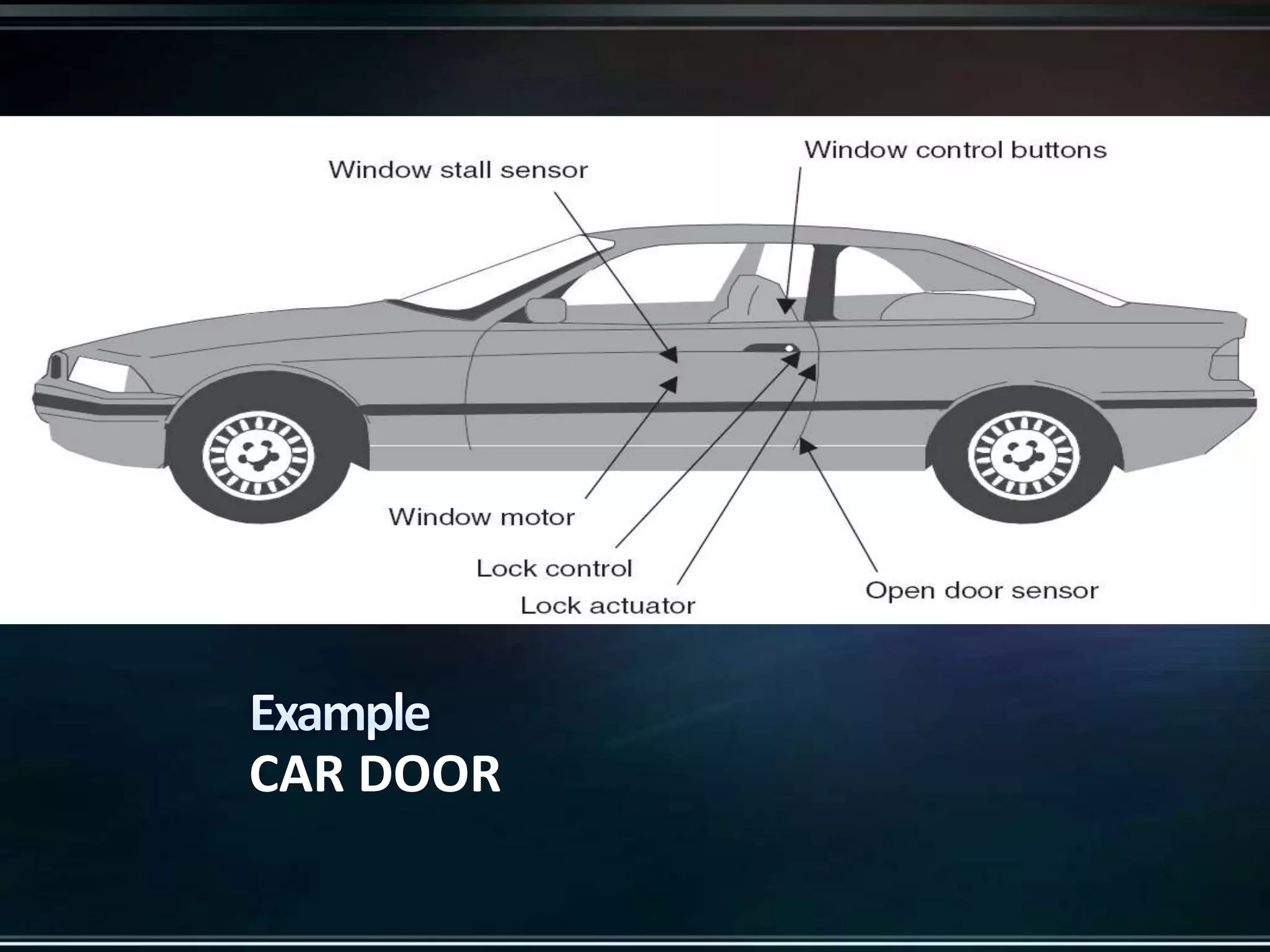
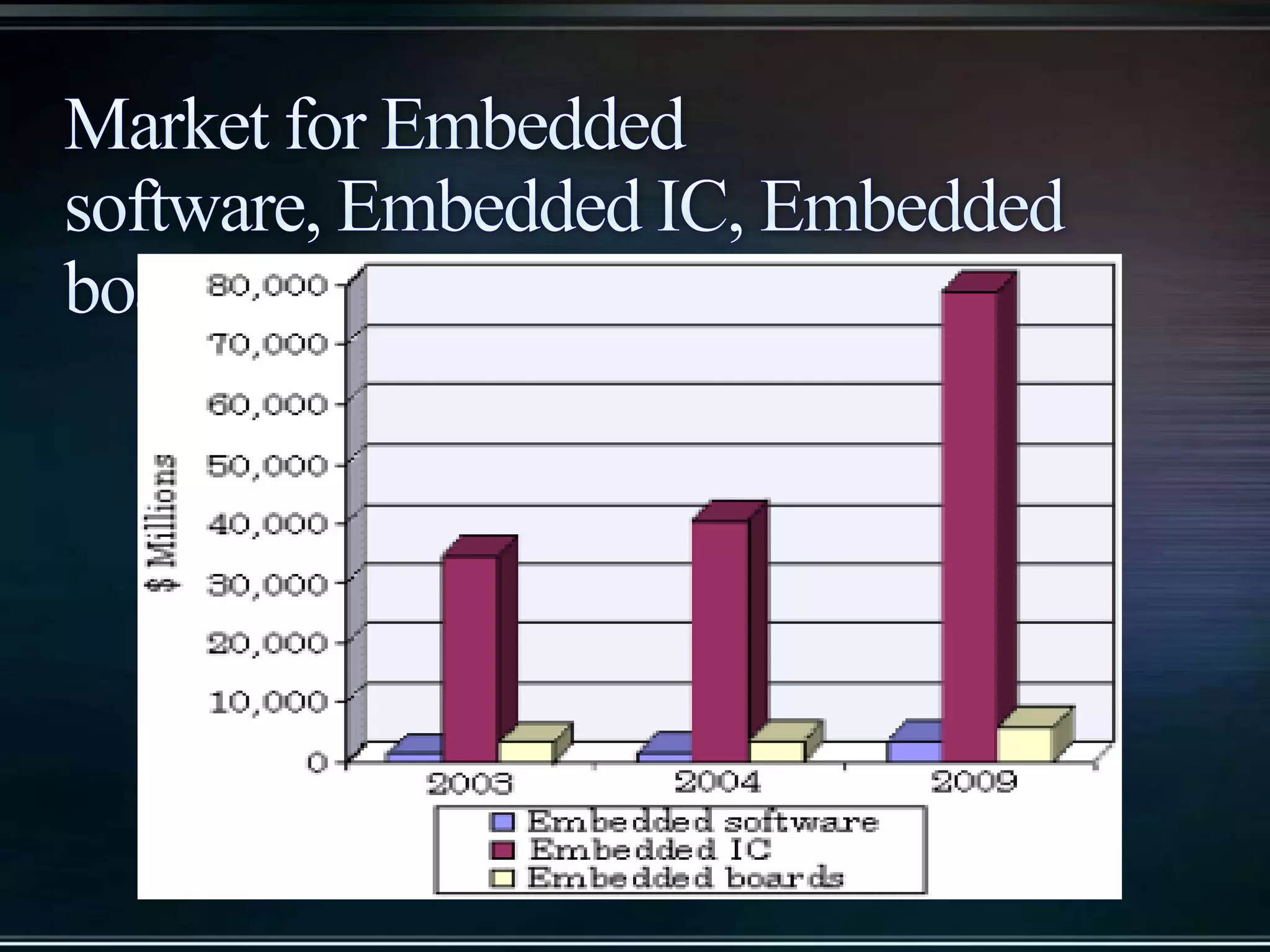
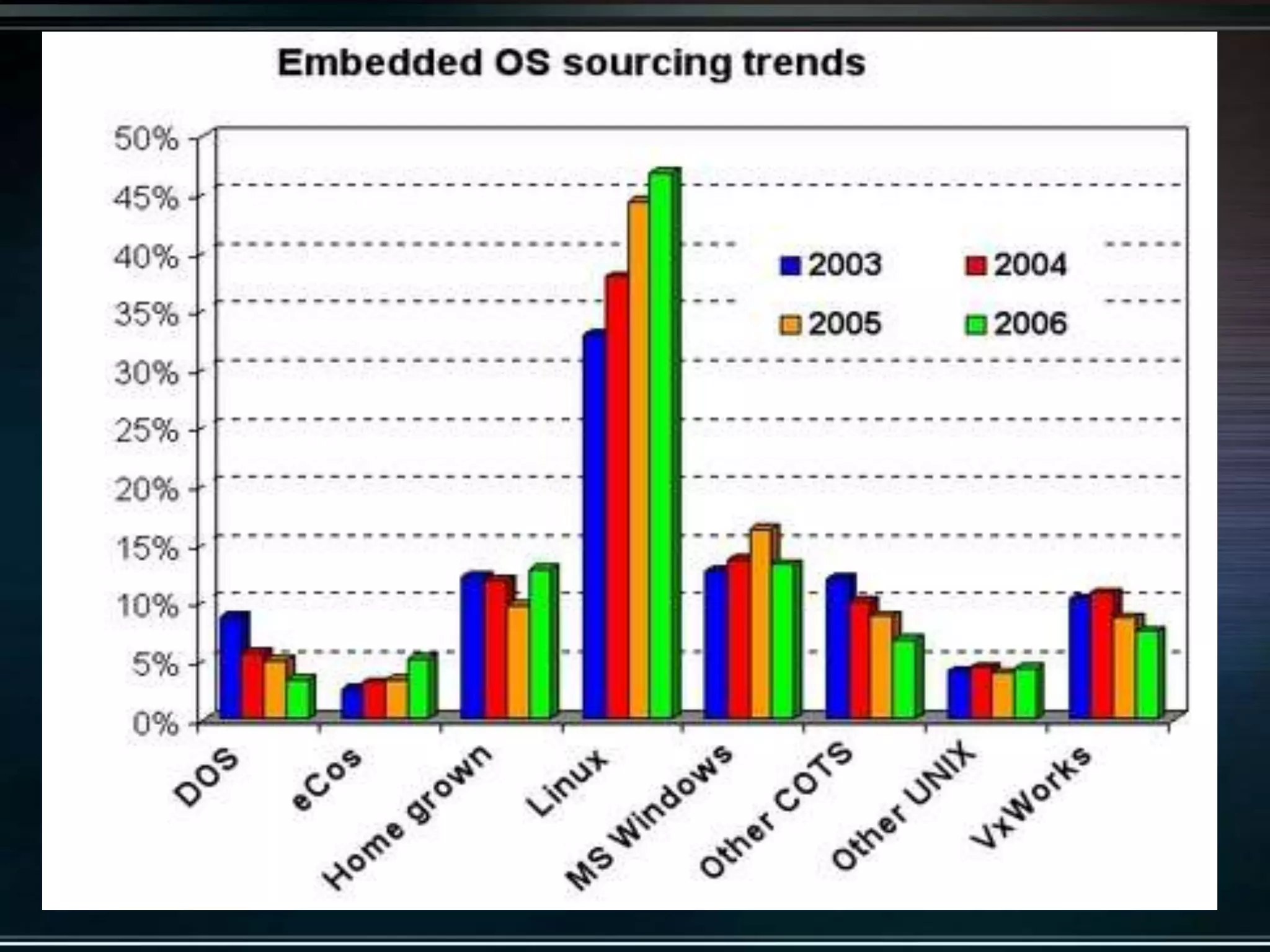
The document provides an introduction to embedded systems, including a definition and key characteristics. It discusses how embedded systems contain microcontrollers or digital signal processors and are designed to perform specific control functions within larger systems. Examples of embedded systems include appliances, vehicles, and electronic devices. The document highlights how embedded systems are specialized for particular tasks, constrained in terms of components and costs, and must perform functions in real-time.