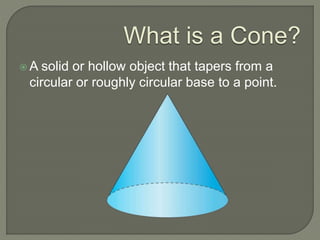
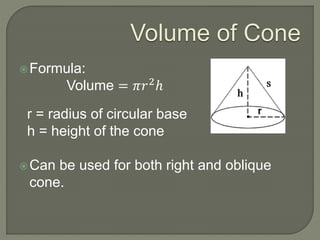
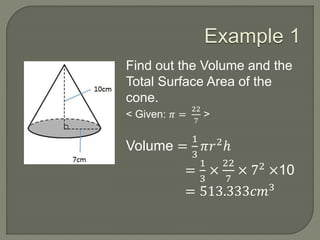
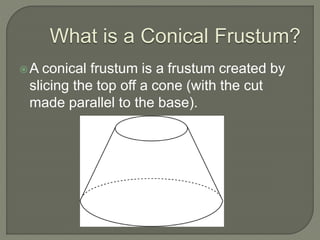
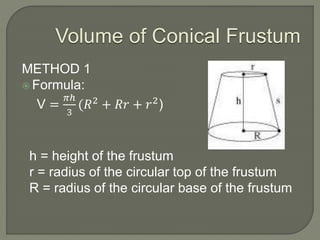
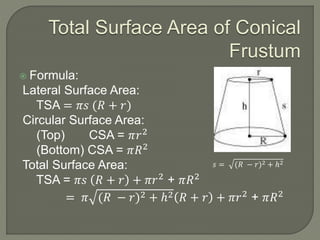
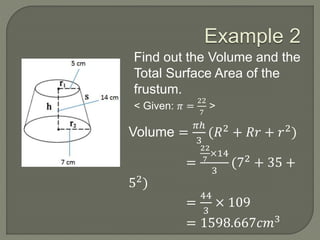
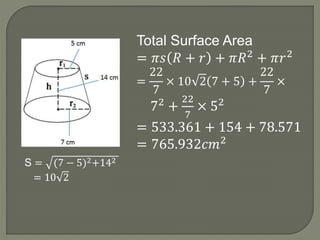
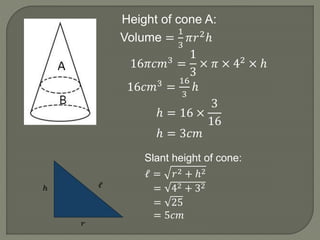
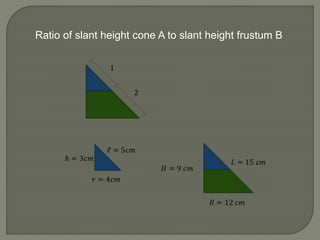
The document defines and provides information about cones, conical frustums, and how to calculate their volume and total surface area. It explains that a cone tapers from a circular base to a point, and can be a right cone or oblique cone. Formulas are given for calculating the volume and total surface area of cones and conical frustums. Examples are worked through applying the formulas to calculate volume and surface area of different cone and frustum shapes.