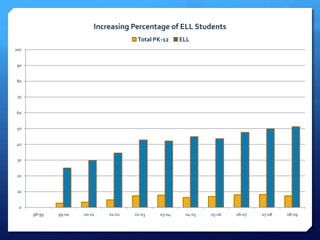
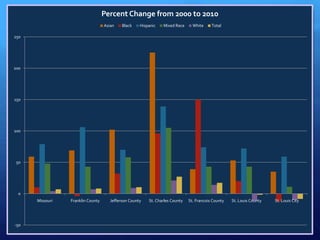
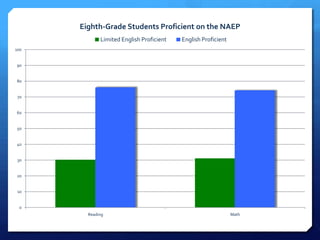
The document discusses diversity and English language learners (ELLs) in US schools. It notes that the NCATE defines diversity to include differences based on various demographic factors. It also states that the number of ELLs in US schools has risen 57% in the past decade and that ELLs now represent the fastest growing student population. ELL students lag behind English-proficient students in academic achievement and high school graduation rates. Additionally, most mainstream teachers have ELL students but only 29% feel adequately trained to teach them effectively.