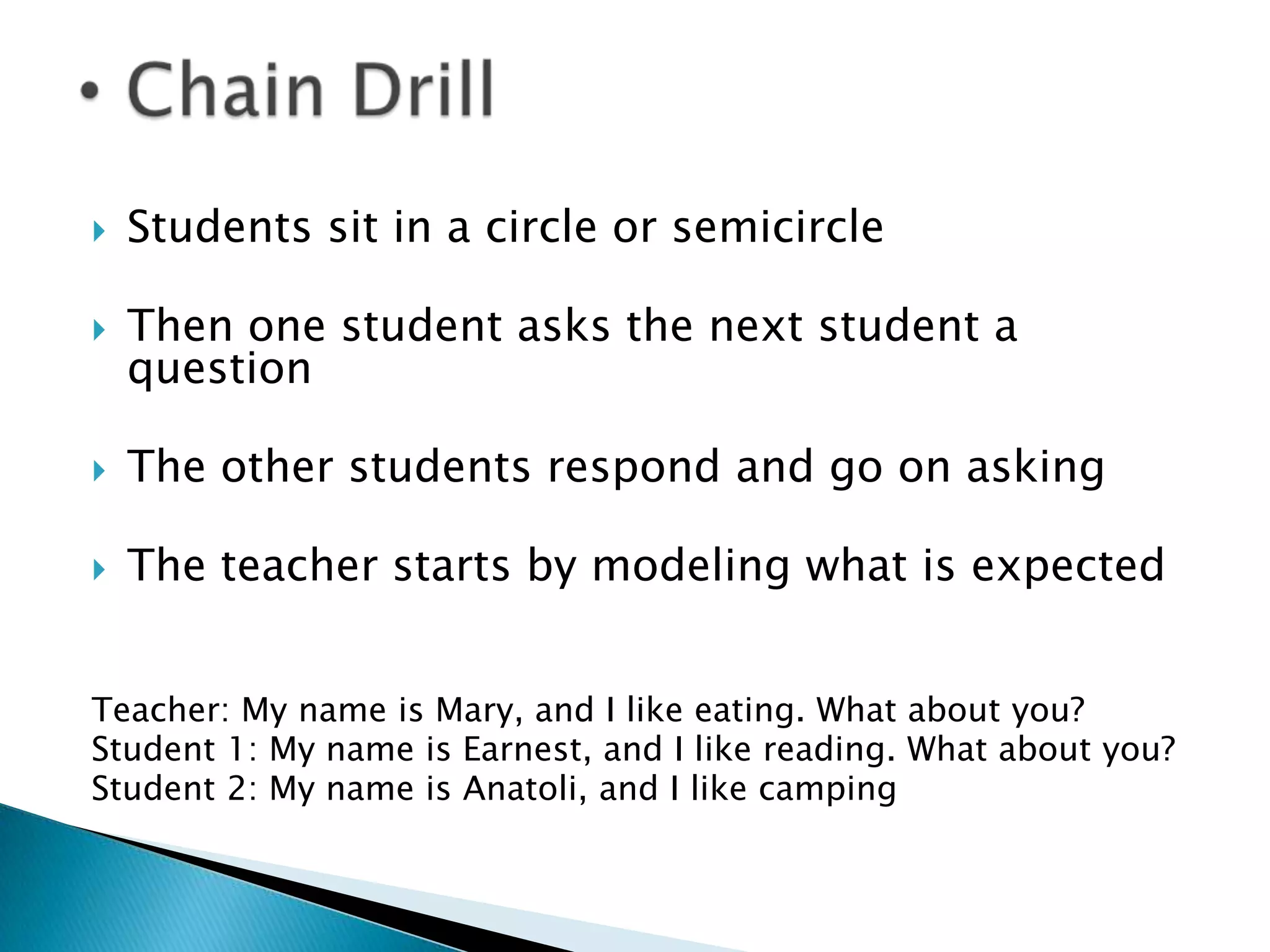
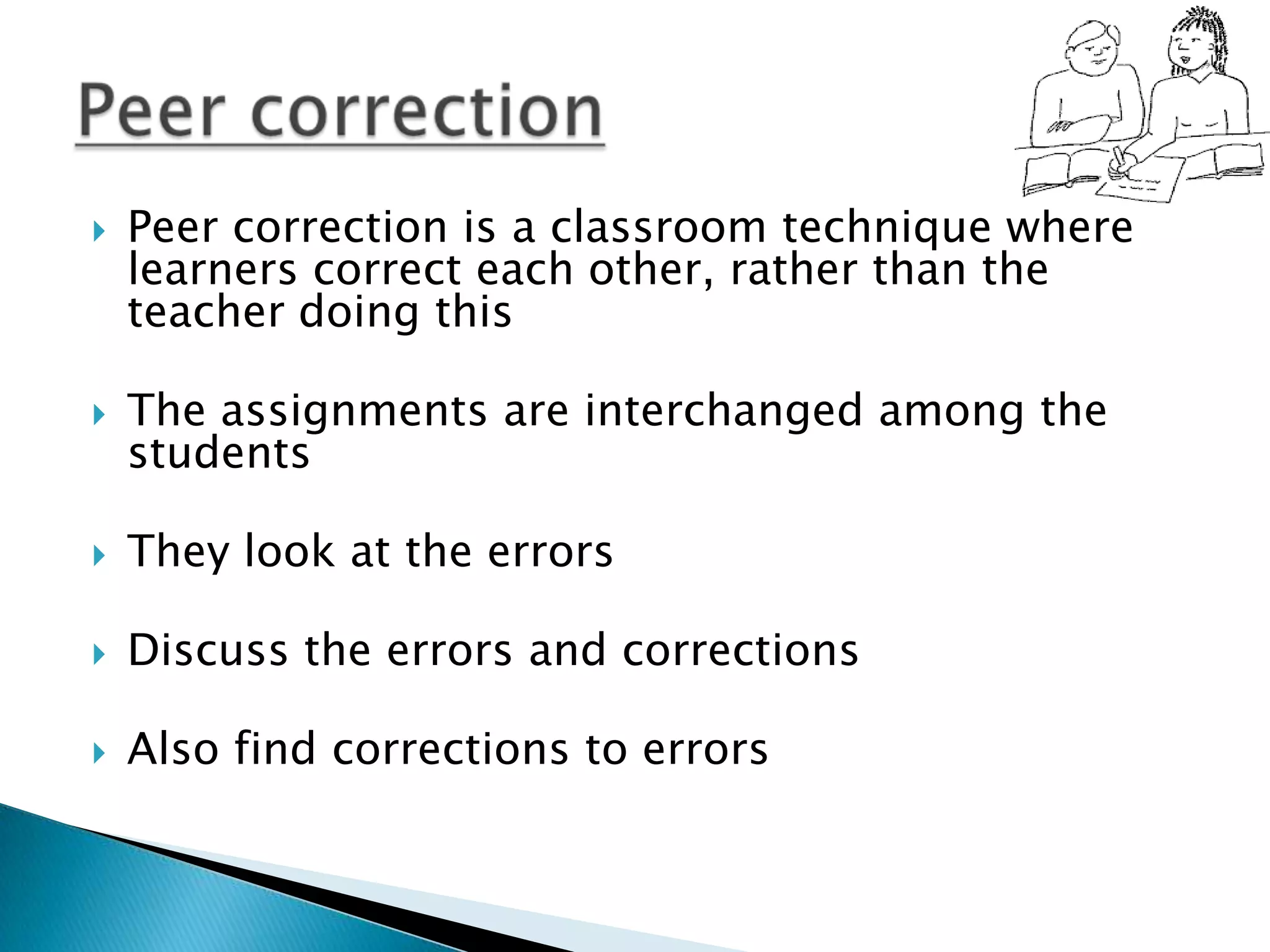
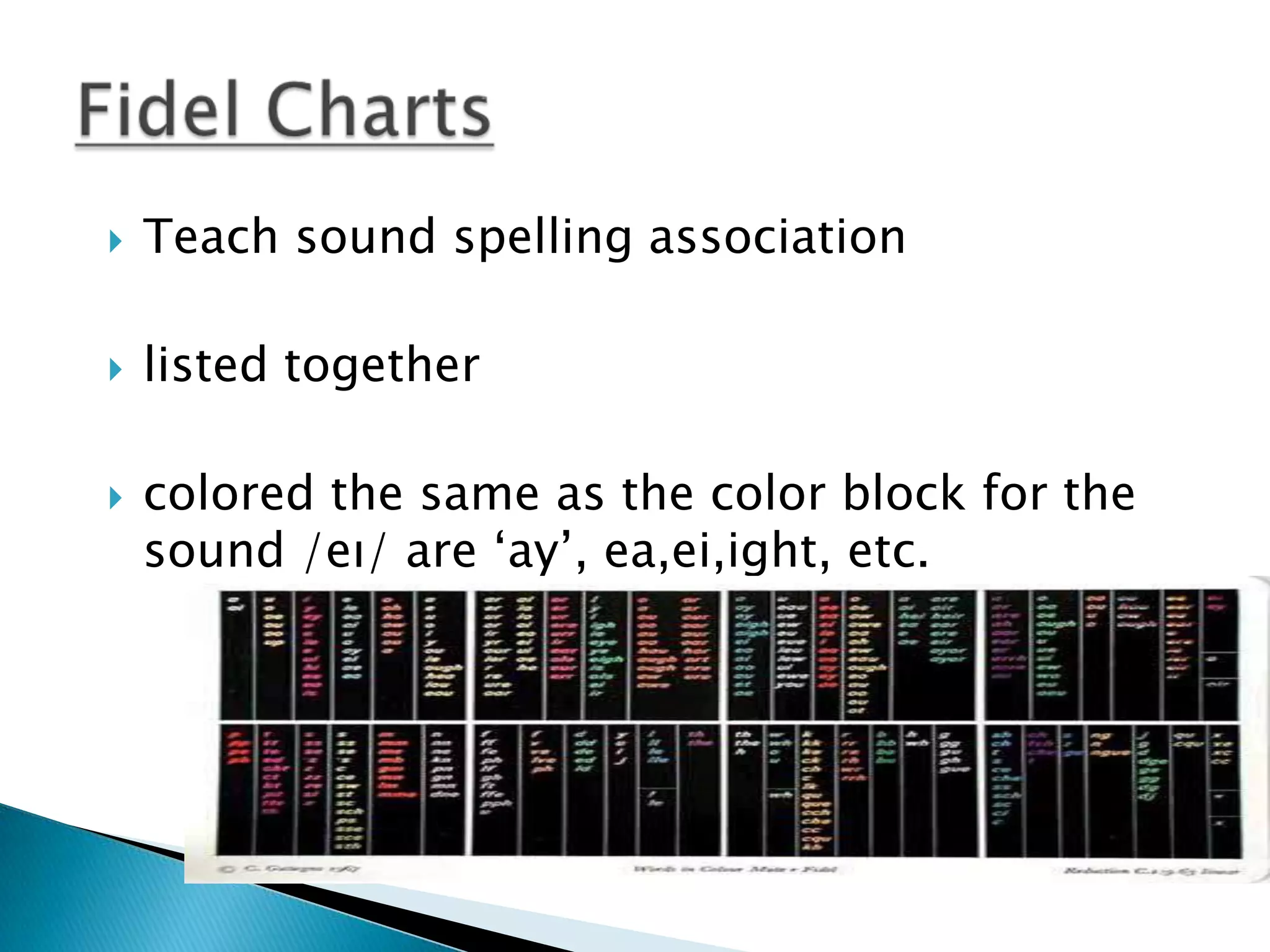
The document describes various classroom activities used in different language teaching methods, including grammar translation, audio-lingualism, and the silent way. Some common activities across methods are translation exercises, question-and-answer drills, fill-in-the-blank exercises, dictation, and memorization of vocabulary and grammar rules. The audio-lingual method focuses on dialogue memorization and mechanical drills. The silent way emphasizes visual aids like sound-color charts and color rods to teach pronunciation and grammar concepts. Peer correction and structured feedback are also characteristics of the silent way.















![ A minimal pair is a pair of words that differ in a
single phoneme
Minimal pairs are often used to show that two sounds
contrast in a language
For example, we can demonstrate that [s] and [z] contrast
in English by adducing minimal pairs
such as sip and zip, or bus and buzz
Do you repairclocks/clogs?“
It will help the students with pronunciation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theclassroomactivitiesinlanguageteaching-130325174250-phpapp01/75/The-classroom-activities-in-language-teaching-17-2048.jpg)