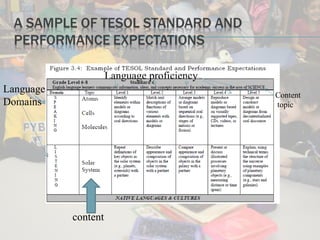
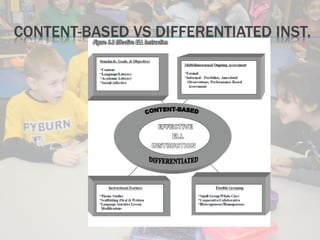
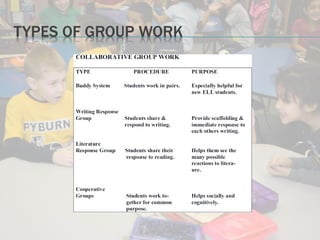
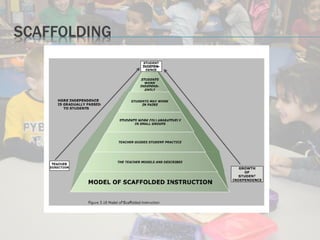
This document discusses standards-based instructional practices for English learners. It outlines that standards consist of content, benchmarks, and performance standards. It also emphasizes using differentiated instruction and content-based instruction to create meaningful learning experiences for English learners that align language development with grade-level content standards. The document recommends using thematic instruction and ongoing informal assessment to support English learners in developing both language skills and academic content knowledge.