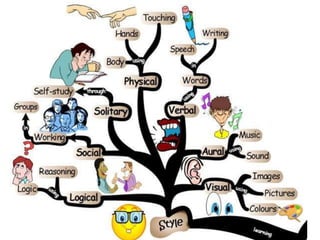
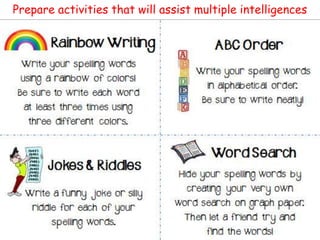
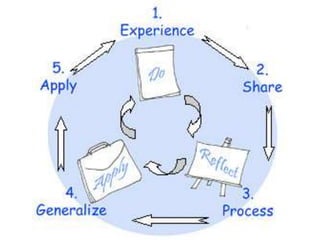
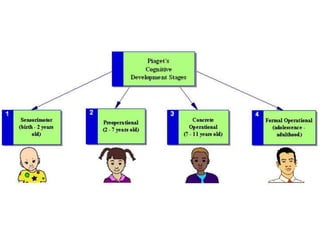
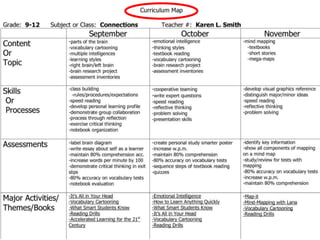
This document outlines the objectives and tasks for a 6-episode field study course. The objectives are to observe students' development, teaching approaches, and how instruction should consider development. Episode 1 focuses on the learning environment and having students observe a school. Episode 2 is on diversity among learners and having students interview peers. Episode 3 looks at classroom management and how it affects learning. Episode 4 examines individual differences and matching activities. Episode 5 analyzes the learning process in relation to diversity. Episode 6 considers home-school links. The document provides guidance and resources to help students complete tasks and evidence for each episode.