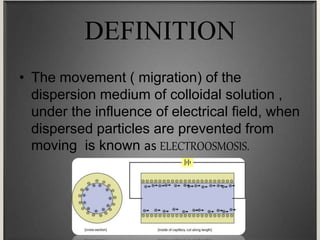
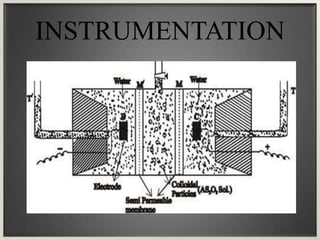
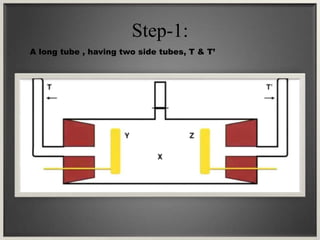
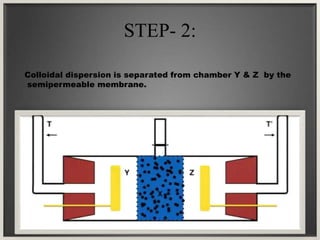
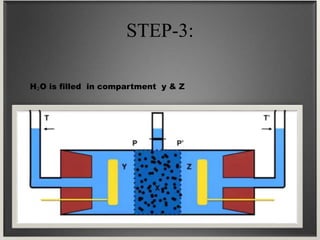
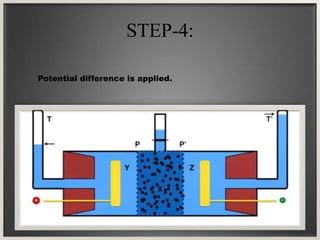
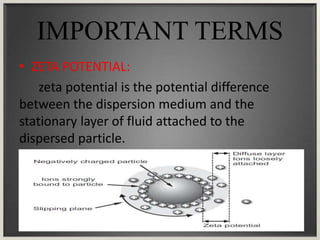
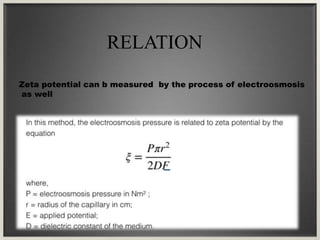
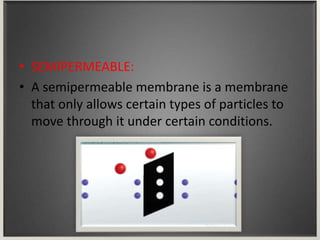
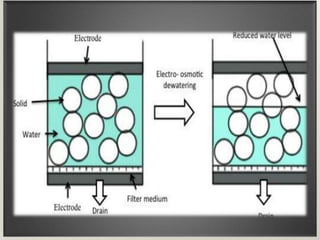
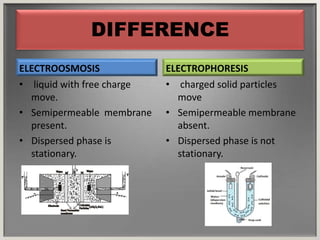
Electroosmosis is the movement of the dispersion medium in a colloidal solution under an electrical field when the dispersed particles are stationary, first reported in 1807. It serves as a drying technique for dewatering substances like clay and involves a specially designed apparatus with semi-permeable membranes. Key applications include the dewatering of moist clay, removal of water from peat, and drying of dye paste.