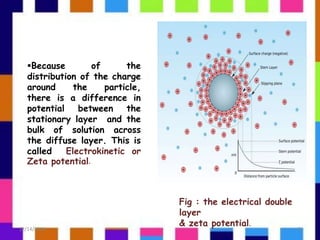
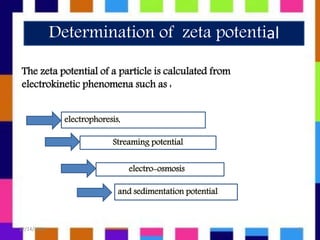
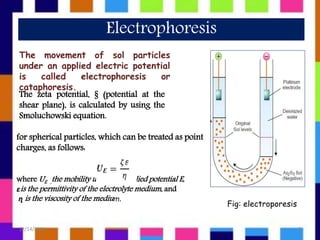
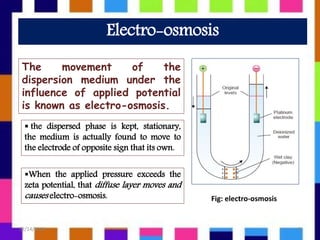
This presentation discusses zeta potential and its determination. Zeta potential is defined as the potential difference between the dispersion medium and stationary layer of fluid attached to dispersed particles. There are several methods to determine zeta potential including electrophoresis, streaming potential, and electro-osmosis. Zeta potential is a key indicator of stability in colloidal dispersions - higher zeta potential leads to more electrostatic repulsion and stability against aggregation. Zeta potential has applications in areas like water purification, minerals processing, emulsions, and pharmaceuticals.