This document provides an overview of the electronic system components of a robot and the wiring process. It includes:
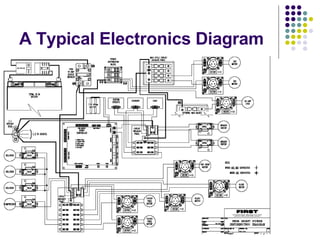
1) The main electronic system components of a robot which include the computer, circuit breakers, power controllers like victors and spikes, batteries, main power switch, grounding stud, power distribution block, and sensors.
2) Descriptions of each component and their functions in the robot's power and control system.
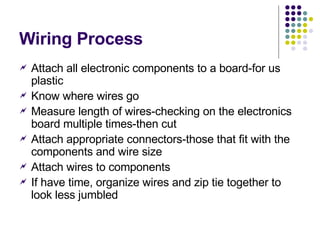
3) Guidelines for the wiring process which involve attaching components, measuring and cutting wires, connecting with the proper connectors, organizing wires, and basic wiring rules around wire sizes, connections, and safety.