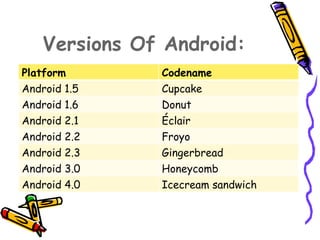
This document provides an introduction and overview of the Android platform. It discusses that Android is an open-source software platform based on Linux, developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance. It allows developing applications through the Java programming language. The document then covers Android's software development, versions released so far, advantages like customization abilities, and limitations like some Bluetooth functions. Overall, it presents the key aspects of the Android platform.