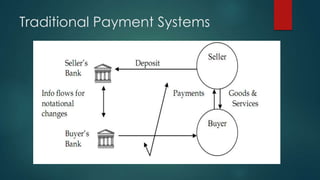
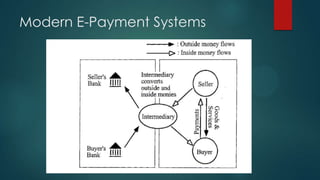
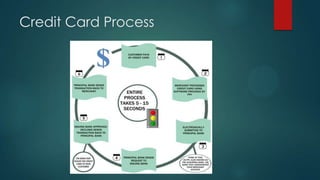
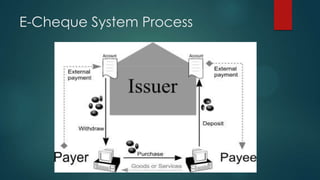
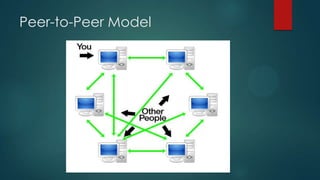
This document discusses electronic payment systems. It begins by defining electronic payment systems and how they can be modern versions of traditional systems like checks and credit cards or based on digital currency. It then discusses traditional payment systems and some of their limitations. The document goes on to describe various modern electronic payment systems like credit cards, smart cards, debit cards, electronic checks, and peer-to-peer payments. For each system it provides details of how they work and their advantages and disadvantages. It concludes by discussing the benefits of electronic payment systems and some disadvantages.