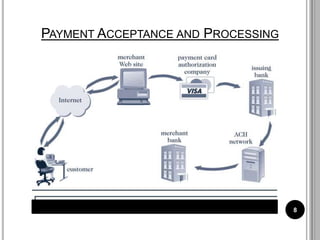
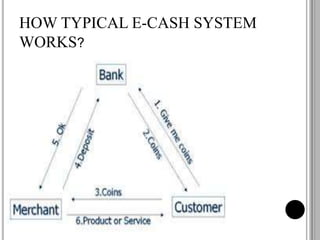
This document discusses various electronic payment systems. It describes methods of electronic payment such as electronic cash, software wallets, smart cards, and credit/debit cards. It also outlines requirements for e-payments like atomicity and non-repudiation. Several modes of e-payment are explained in detail, including payment cards, electronic cash, check free, check share, internet cash, wallets, and smart cards. Benefits and drawbacks of different systems are provided.