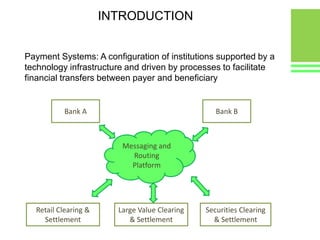
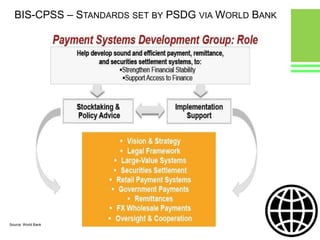
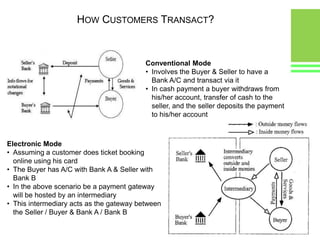
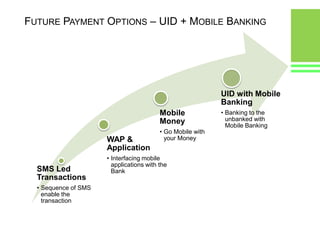
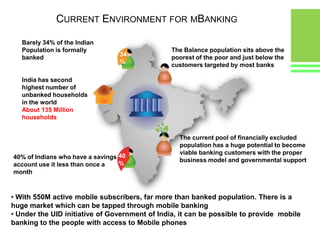
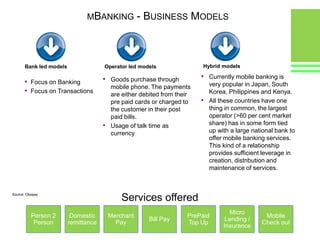
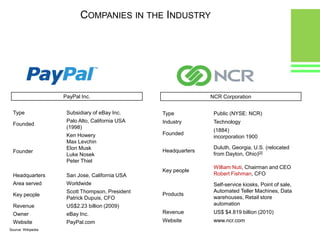
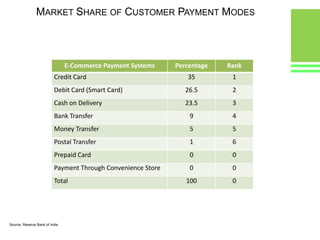
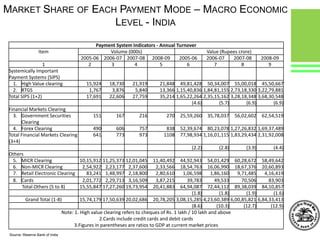
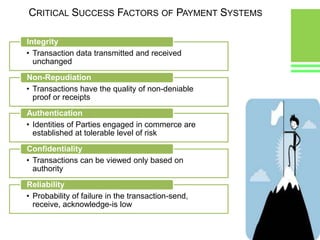
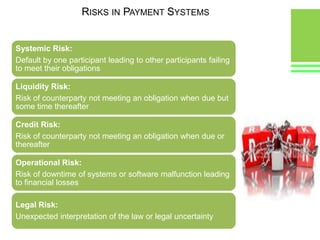
This document provides an overview of global and Indian payment and transaction processing systems. It discusses the global regulatory framework established by the Bank for International Settlements and the regulatory framework in India established by the Reserve Bank of India. It describes how banks transact with each other using real-time gross settlement systems like RTGS and net settlement systems like NEFT. It also outlines how customers transact through conventional and electronic modes like mobile banking. Specialized companies operating in various areas of the industry are discussed as well as the market share and critical success factors of different payment modes. Risks to payment systems are also addressed.