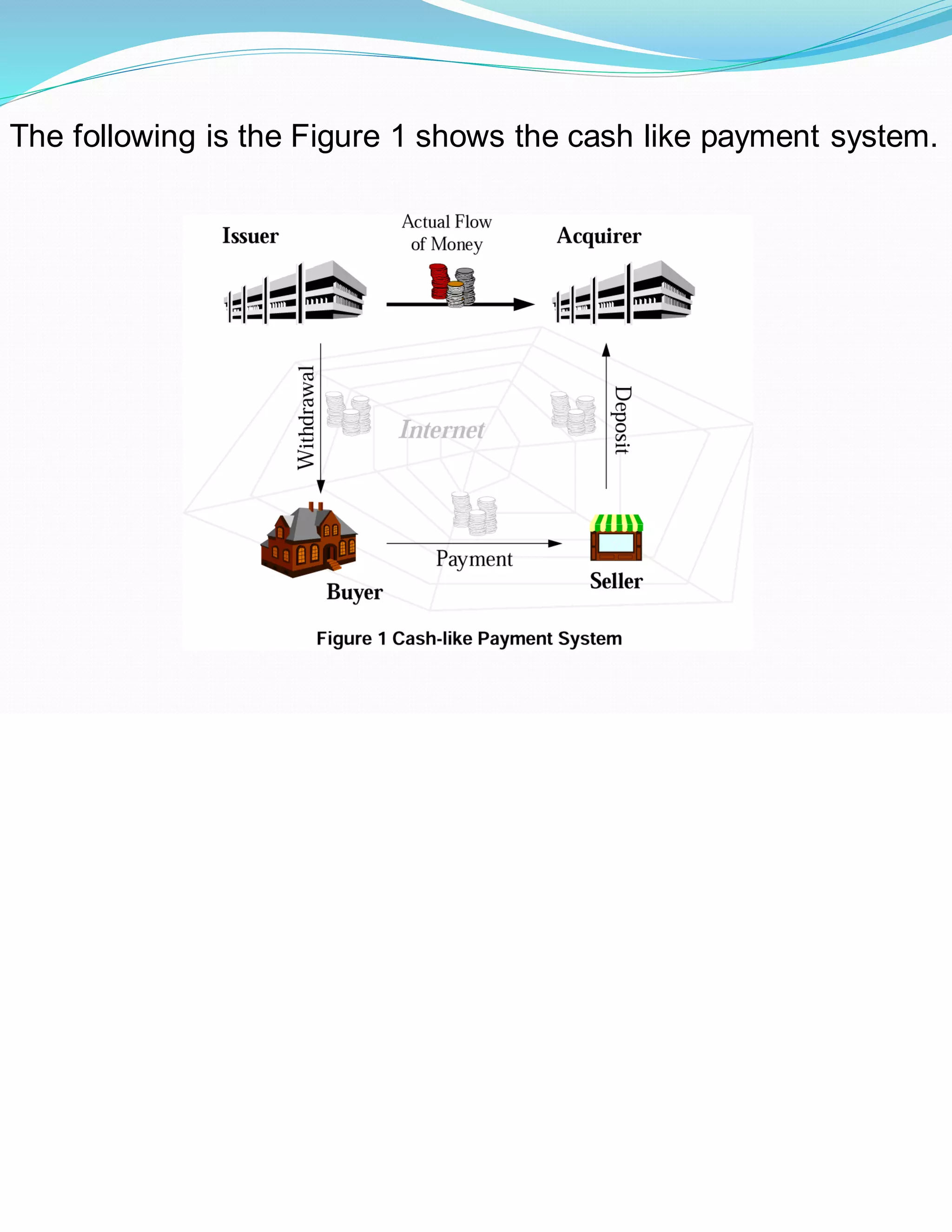
The document discusses digital payment systems and their security requirements. It outlines different digital payment models including prepaid cash-like systems and pay-now versus pay-later systems. The key security requirements for digital payments are integrity, privacy, and confidentiality. Both online and offline payment systems are discussed and compared, with the conclusion being that online payment systems provide advantages in terms of speed and accessibility. Secure digital payment technology already exists but must ensure security for all parties.