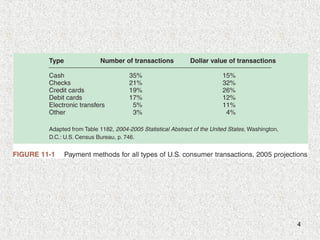
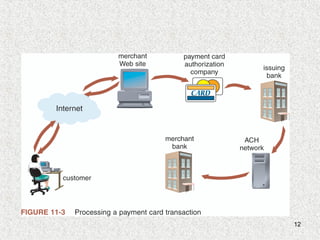
This document discusses various forms of online payment systems including payment cards, electronic cash, electronic wallets, and smart cards. It outlines the basic functions of online payment systems and how payment cards, electronic cash, and stored-value cards work. It also discusses technologies like electronic wallets, smart cards, and security issues like phishing attacks that threaten online financial institutions.