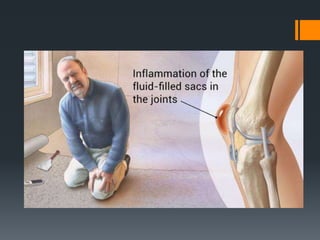
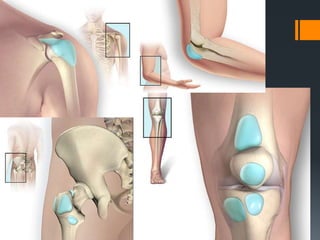
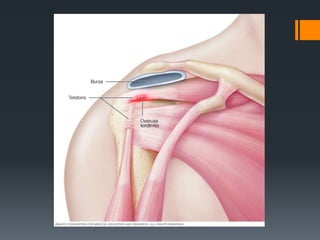
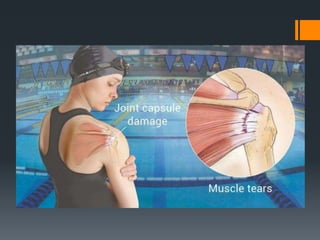
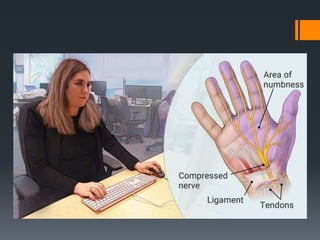
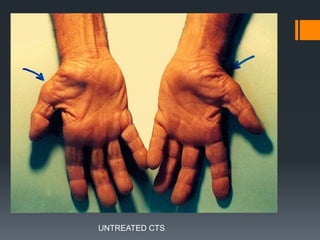
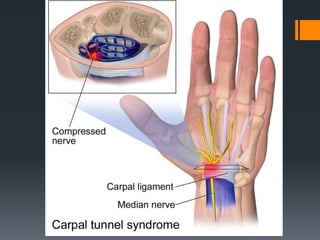
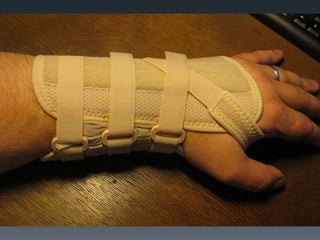
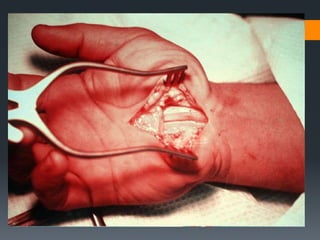
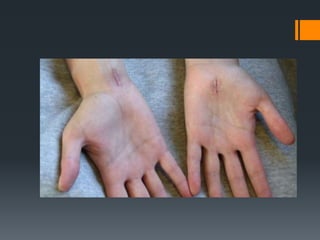
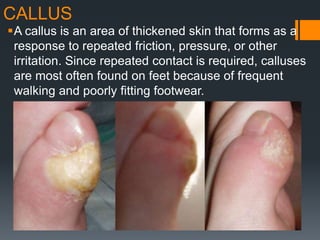
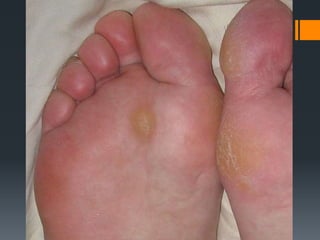
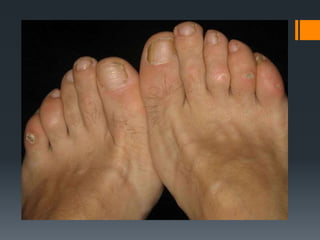
The document outlines common upper and lower extremity disorders including bursitis, tendonitis, impingement syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome, ganglion cysts, Dupuytren's contracture, calluses, and corns. Each condition is defined, with symptoms, common locations, risk factors, and treatment options discussed. The information highlights the importance of proper care and preventative measures for these disorders.