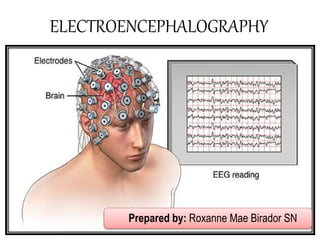
Hans Berger, a German psychiatrist, published the first paper on the human electroencephalogram (EEG) in 1924 after placing electrodes on the scalps of patients who had undergone brain surgery. An EEG detects and records the brain's electrical activity through electrodes attached to the scalp. It can help diagnose conditions like epilepsy, brain tumors, strokes, and sleep disorders. An EEG is a painless and safe test, but may cause minor scalp irritation in some cases. Proper preparation is important to get accurate results.