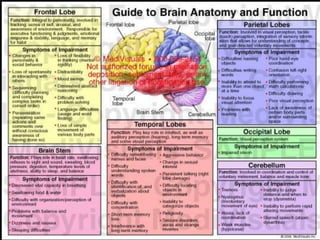
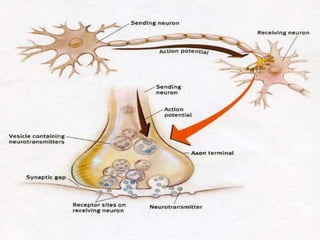
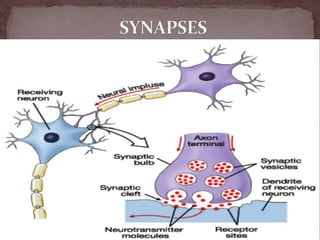
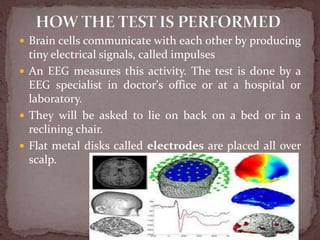
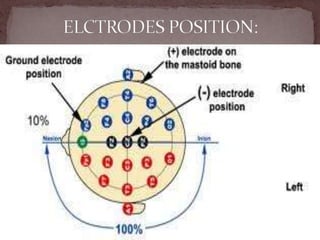
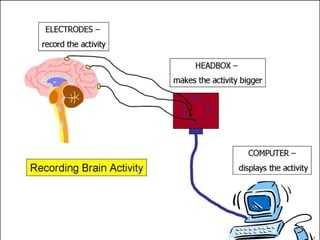
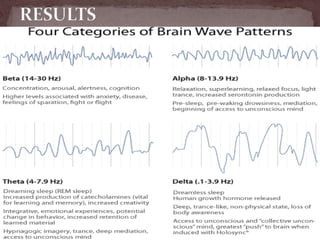
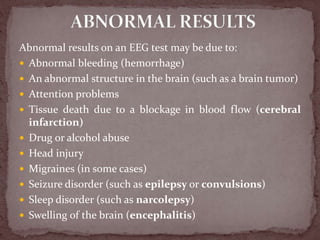
The document summarizes the electroencephalogram (EEG) test, which measures and records the electrical activity of the brain. An EEG is performed by placing electrodes on the scalp that detect brain waves produced when neurons fire. Abnormal EEG results can help diagnose conditions like epilepsy, sleep disorders, brain tumors, and head injuries by showing irregular wave patterns. The test is painless and safe, though flashing lights may trigger seizures in some patients.