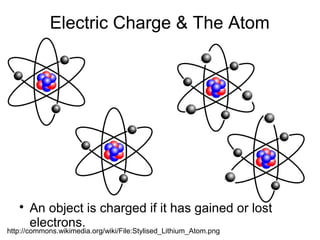
This document provides information about electric charge and the atom. It discusses how objects become charged by gaining or losing electrons and how like charges repel and opposite charges attract. It also describes electric fields as regions of space where electrical forces act and how charged particles like electrons create electric fields. Additional topics covered include lightning, lightning rods, current, resistance, circuits and power. Key points are made about charge being measured in coulombs and current in amps. Series and parallel circuits are explained in terms of how voltage and current are distributed.