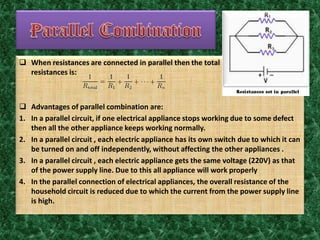
The document discusses electric circuits and some key concepts:
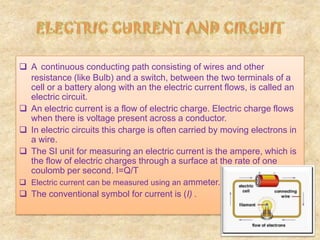
1. An electric circuit is a continuous conducting path that allows electric current to flow between the terminals of a battery or cell. Current is the flow of electric charge, often carried by electrons in a wire.
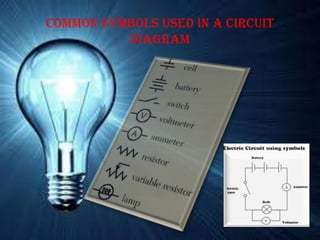
2. Potential difference (p.d.) is the work done to move a unit charge between two points in a circuit. It is measured in volts using a voltmeter.
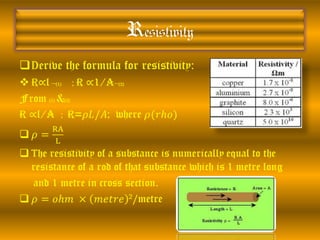
3. Ohm's law states that current is directly proportional to potential difference and inversely proportional to resistance. Resistance depends on the material and dimensions of the conductor as well as temperature.