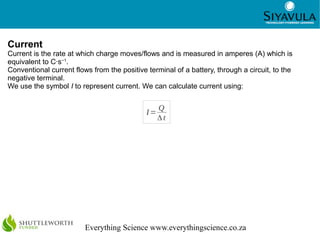
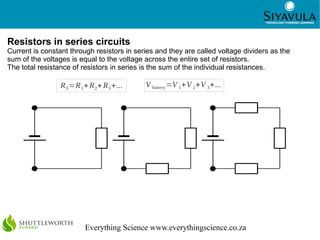
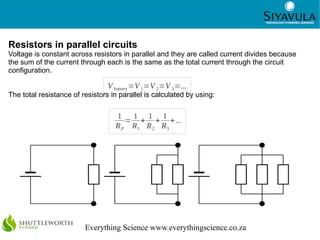
This document discusses key concepts in electric circuits including potential difference, electromotive force (emf), current, resistance, and how these concepts relate to different circuit configurations. It defines potential difference and emf as the voltage across battery terminals when not or in a complete circuit. Current is defined as the rate of charge flow measured in amperes. Resistance depends on the material and physical characteristics of a circuit element and is measured in ohms. Resistors in series have the same current but their voltages add up, while resistors in parallel have the same voltage but their currents add up. Measuring devices like voltmeters and ammeters must be connected appropriately.