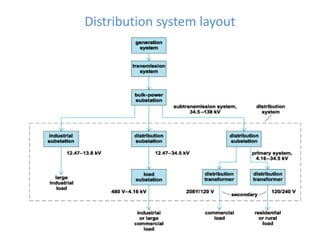
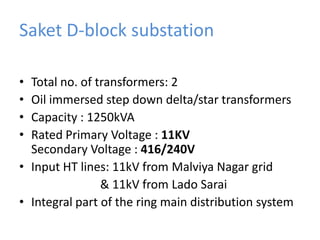
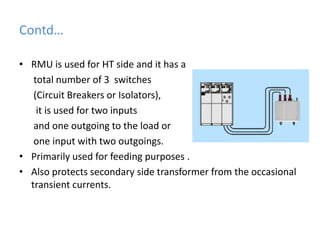
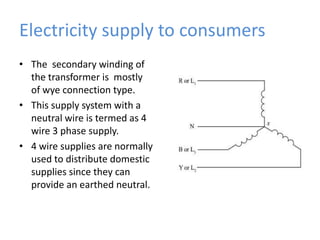
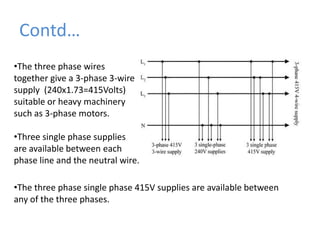
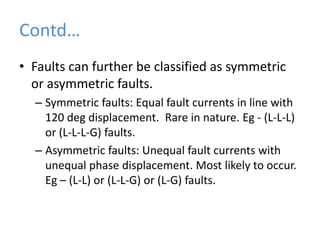
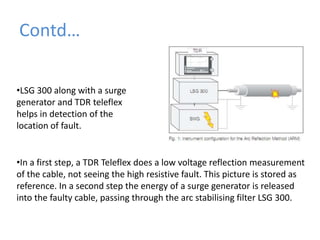
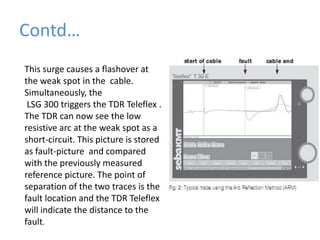
BRPL distributes power to over 12.2 lakh customers across 19 districts in South and West Delhi. Power is generated at medium voltages and stepped up to high or extra high voltages for transmission, then stepped down at distribution stations to 415/240V for customers. The Saket D-block substation has 2 transformers with a capacity of 1250kVA each that step down 11kV power from feeders to 416/240V. Ring Main Units are used at the high voltage side for feeding and protection, with 3 switches for 2 inputs and 1 output. Power is distributed through overhead or underground lines, with underground being more expensive. Faults can be transient from temporary contacts or persistent from cable damage, and can