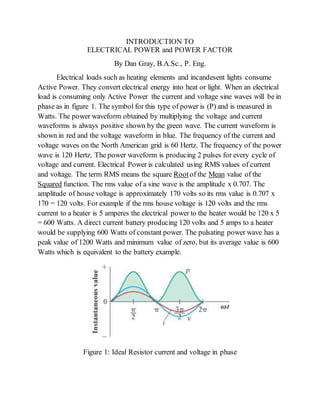
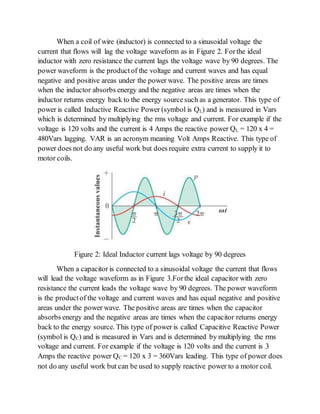
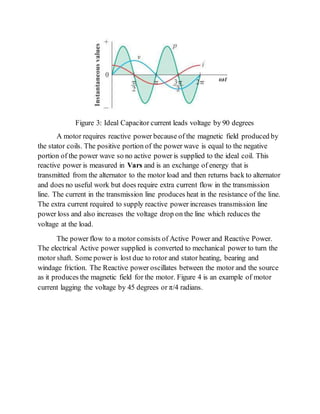
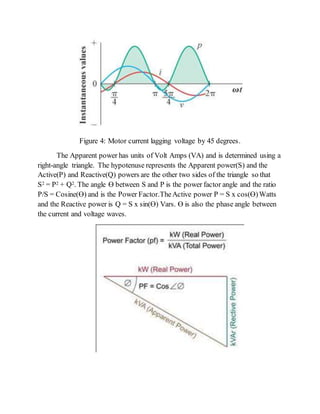
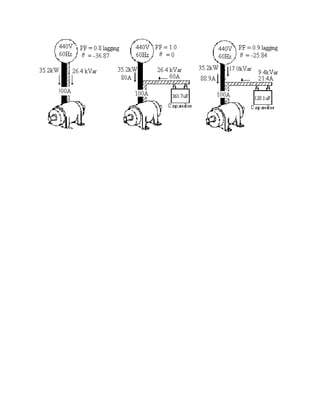
1) Electrical loads that consume only active power have current and voltage waves that are in phase. Loads that consume reactive power have current and voltage waves that are out of phase.
2) Reactive power is measured in vars and is supplied by inductive and capacitive loads. It does not do useful work but requires extra current.
3) Connecting a capacitor of the correct size in parallel with an inductive motor can supply the motor's reactive power needs, improving the power factor to 1.