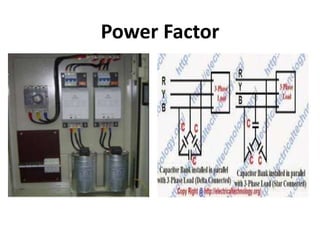
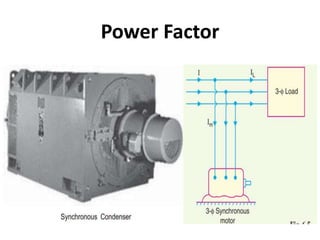
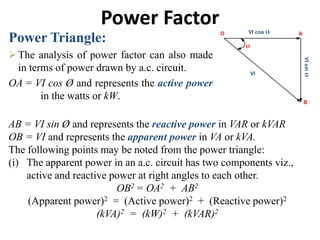
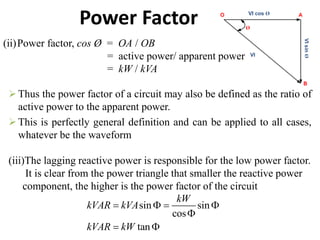
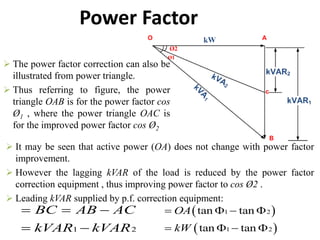
This document discusses power factor in electrical circuits. It defines power factor as the cosine of the angle between the voltage and current. A lagging power factor occurs when the current lags the voltage in an inductive circuit, while a leading power factor occurs when the current leads the voltage in a capacitive circuit. Low power factors can be caused by inductive loads like motors and have negative effects like increased line losses. Common methods to improve power factor include adding static capacitors, using phase advancers for motors, or installing synchronous condensers. The power triangle diagram is also used to illustrate the relationships between active power, reactive power, and apparent power as it relates to power factor.