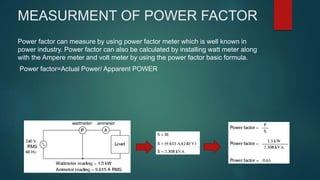
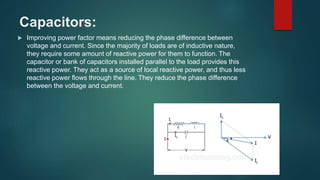
This document discusses the power factor, including its definition as the ratio of actual power to apparent power, measurement, types of loads and their effect on power factor, disadvantages of a poor power factor, and methods to improve it. Some key points covered are: the power factor is the cosine of the phase angle between voltage and current; resistive loads have a power factor of 1 while inductive loads have a lagging power factor; a poor power factor increases losses and costs; and power factor can be improved by using capacitors, static VAR compensators, or synchronous condensers.