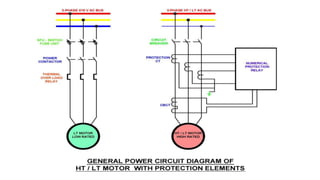
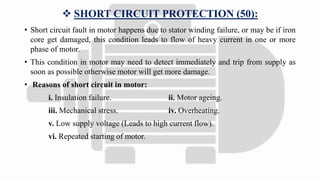
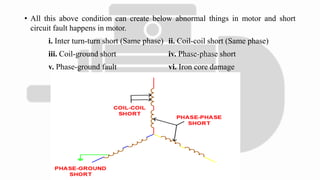
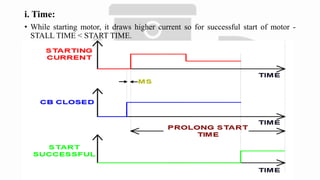
The document discusses various protection mechanisms for electrical motors including thermal overload, short circuit, stall detection, under and over voltage protection, and negative phase sequence protection. Each protection method is crucial for preventing damage to the motor due to conditions such as overheating, electrical faults, and mechanical failures. Numerical relays are highlighted as key devices used to monitor and protect motors under different operating conditions.