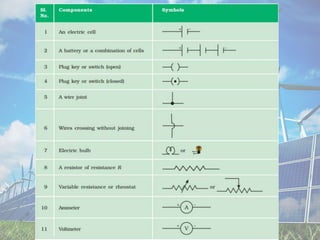
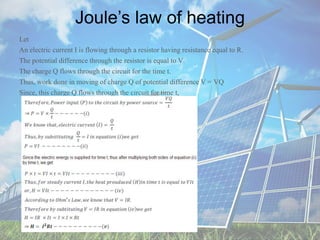
There are three types of electrical charges: positive charges consist of protons, negative charges consist of electrons, and the SI unit of charge is the coulomb. Conductors contain free or loosely bound electrons that allow them to conduct electricity, while insulators do not have free electrons and obstruct electricity flow. Potential difference is defined as the work required to move a unit positive charge between two points in an electric field. Common measuring instruments include the voltmeter, which measures potential difference, and the ammeter, which measures electric current in amperes. Resistors can be connected in series, where the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances, or parallel, where the total resistance is lower than the lowest individual resistance.