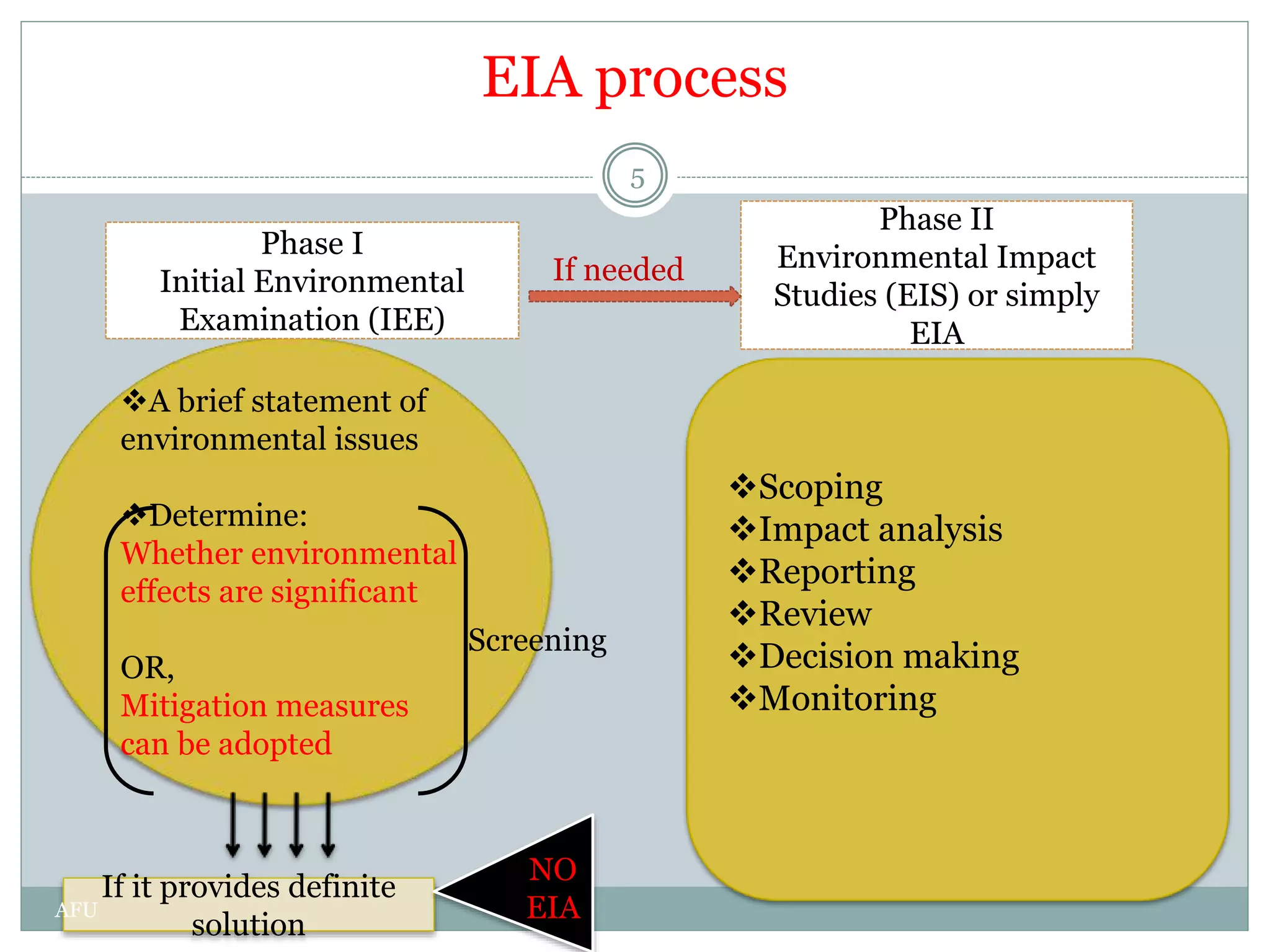
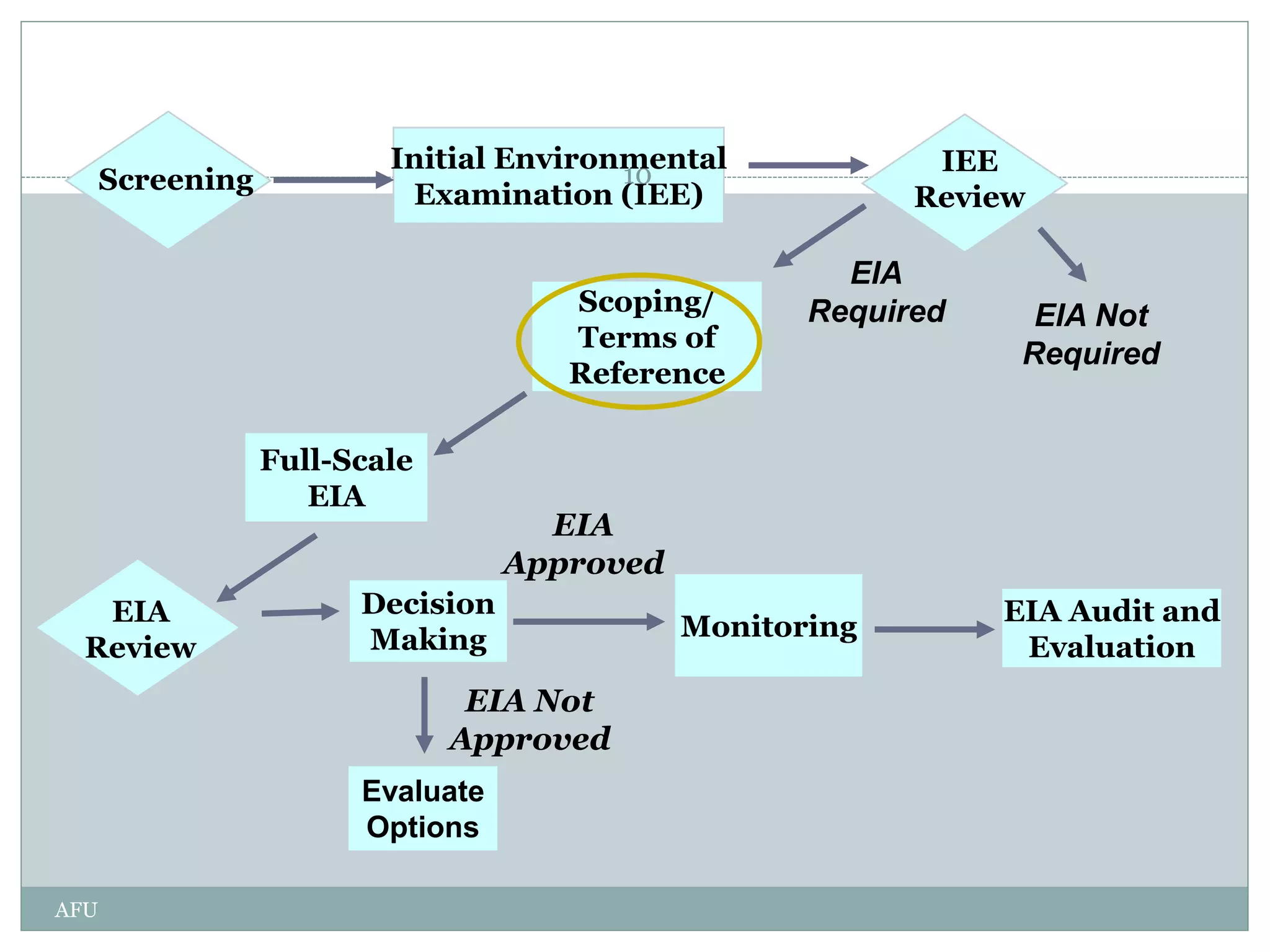
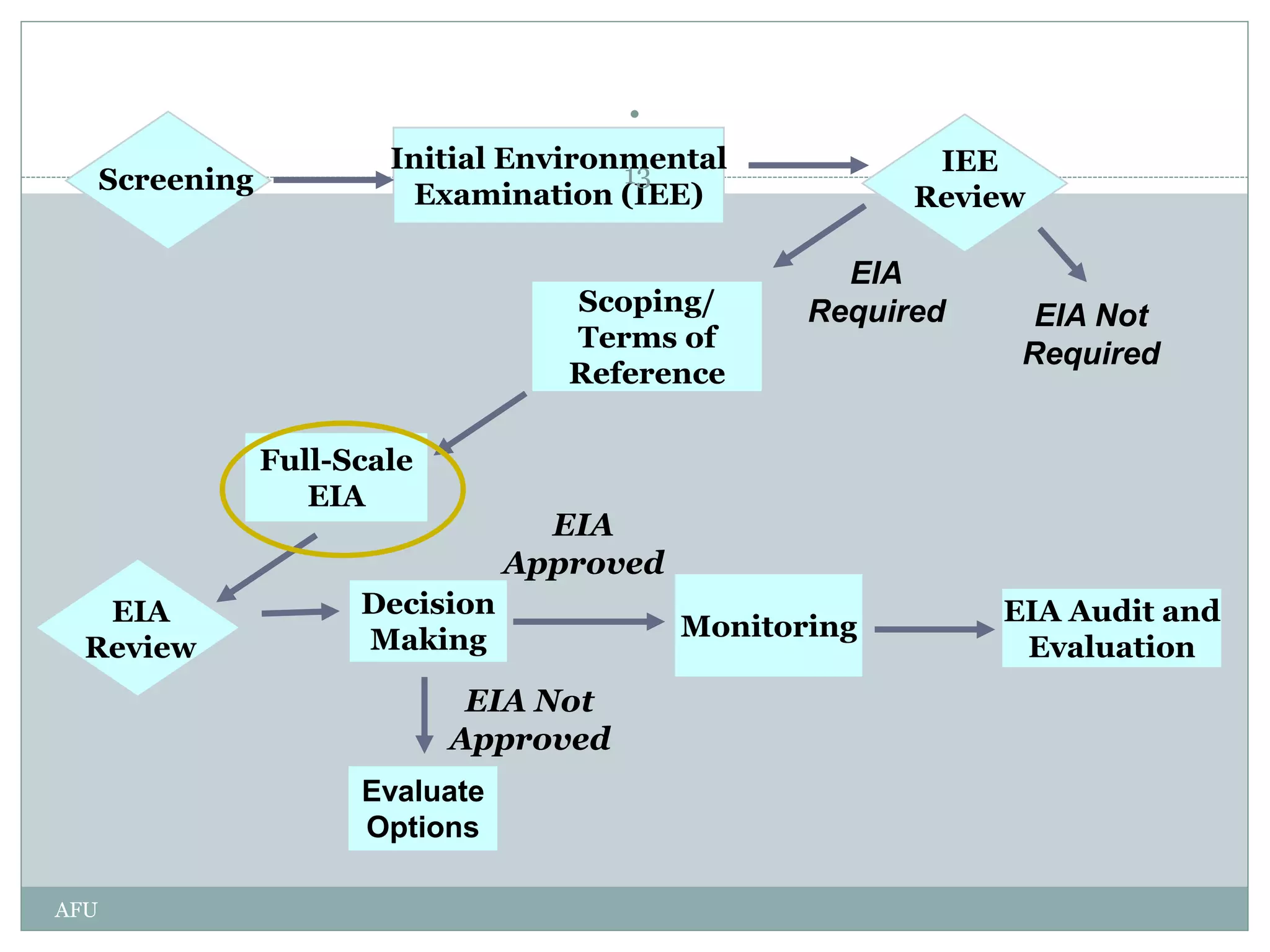
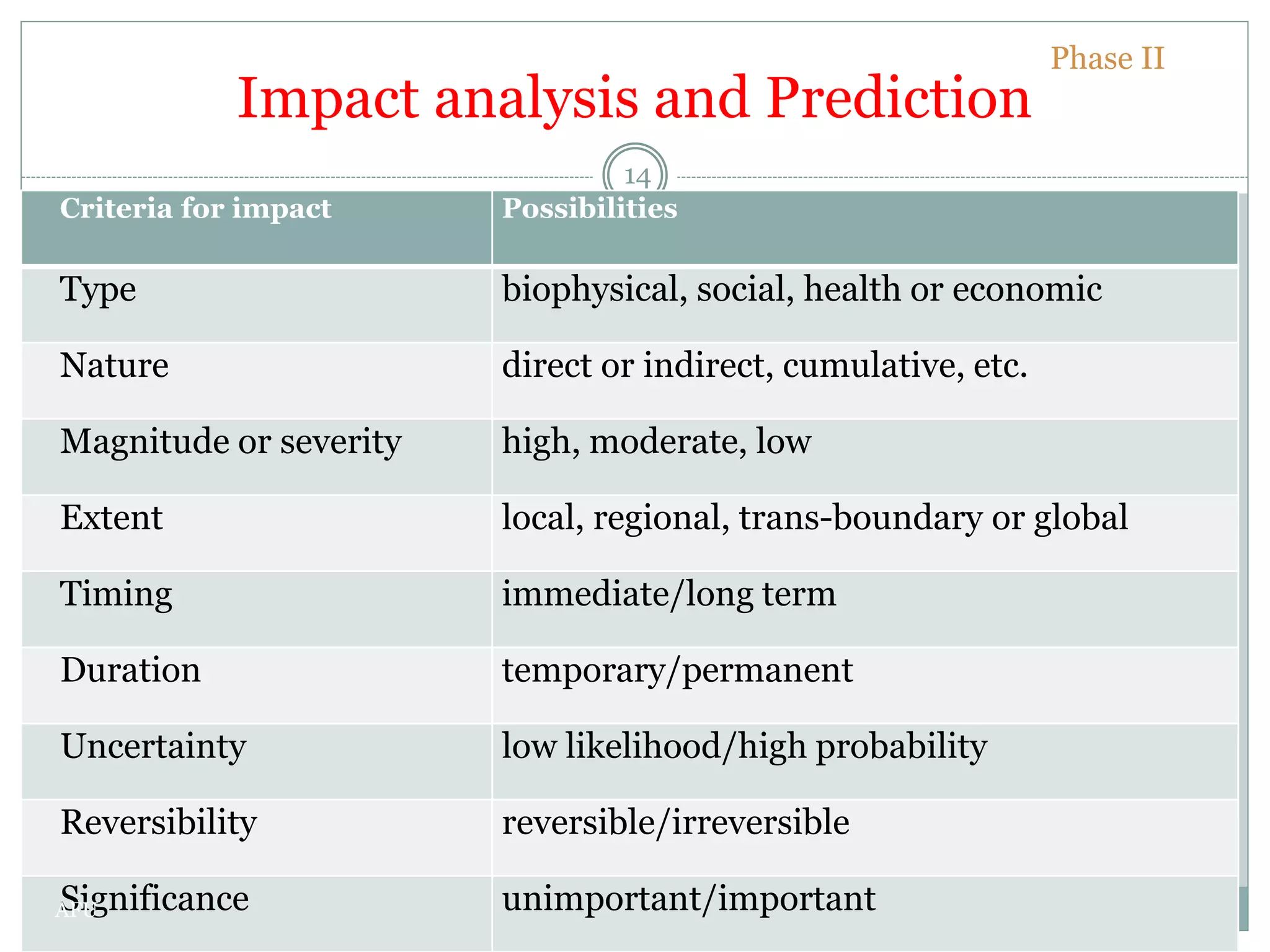
EIA is an assessment of the environmental consequences of a proposed project prior to major decisions. The EIA process involves screening, scoping, impact analysis and prediction, mitigation, reporting, review, decision making, monitoring and audit. Screening determines if an EIA is required. Scoping identifies key issues. Impact analysis predicts and evaluates effects. Mitigation proposes impact management. Reporting communicates findings. Review evaluates sufficiency. Decision making approves or rejects projects. Monitoring checks implementation. Audit evaluates accuracy and lessons learned. The goal of EIA is to integrate environmental considerations into development planning for sustainable development.