Effect Of Bonus And Shift Tolerances On Stack Up Analysis By Arash Vakily
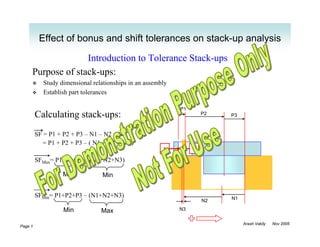
- 1. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Introduction to Tolerance Stack-ups Purpose of stack-ups: Study dimensional relationships in an assembly Establish part tolerances P1 Calculating stack-ups: P2 P3 SF = P1 + P2 + P3 – N1 – N2 – N3 = P1 + P2 + P3 – ( N1 + N2 + N3 ) S F SFMax= P1+P2+P3 – (N1+N2+N3) Max Min SFMin= P1+P2+P3 – (N1+N2+N3) N1 N2 Min Max N3 Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 1
- 2. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Advantages of using a stack-up study form: First step towards automation (using excel or other computer programs) Organized, verifiable, easy to review (especially for bonus and shift calculations) Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 2
- 3. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Stack-up Study Example Using the Form: To find Min. distance between points S and F: 1 2 7 S F 5 6 4 3 X- 389 Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 3
- 4. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Virtual Condition Virtual condition is used to evaluate mating and assembly of the parts All types of GD&T affect virtual condition as shown in the above example Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 4
- 5. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Example of Virtual Condition With Positional Tolerance Note radial versus diametrical values when calculating tolerance stack-ups / 10 ± 0.2 VC = 10 + 0.2 + 0.3 VC + / 0.3 A = 10.5 MM C R 0.15 VCRad = 5 + 0.1 + 0.15 Nominal = 5.25 C LM 0.1 0.1 0.15 Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 5
- 6. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Bonus Tolerance / 10 ± 0.2 .) ad + / 0.3 M A (R s nu VC Bo At Bonus Value MMC MMC No Bonus 0 LMC MMC – LMC = 0.4 Total size tolerance Any MMC - D 0 < B < 0.4 Diameter D Radial values are half of the values in the above table + Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 6
- 7. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Shift Tolerance MMC = 5 + 0.4 = 5.4 / 10 ± 0.2 + / 0.3 M M LMC = 5 – 0.4 = 4.6 A M M C VC = 5.4 + 0.5 = 5.9 or LM C At Shift Value MMC MMC – VC 0.5 (Min Shift) VC Sh LMC LMC – VC 1.3 ift (R (Max Shift) ad .) Shift for the feature is calculated from values of the Datum / 5 ± 0.4 Absolute values are used (no sign) + / 0.5 M B C D A Radial values are half of the values in the above table Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 7
- 8. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Example of Bonus and Shift Tolerances Max. Bonus = 8.6 – 8.3 = 0.3 Max. Radial Bonus = 0.3 / 2 = 0.15 Max. Shift = 12.6 – 12.4 = 0.2 Max. Radial Shift = 0.2 / 2 = 0.1 For calculations using stack-up study form, always Radial bonus and shift are used Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 8
- 9. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis How To Calculate Bonus and Shift Using Stack-up Study Form Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 9
- 10. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Stack-up Study Example With Bonus and Shift: To find Min. distance between points S and F: 2 2b 1 7 2s S F 5 6 6b 6s 4 3 X- 389 Page Arash Vakily Nov 2005 10
- 11. Effect of bonus and shift tolerances on stack-up analysis Examples of Special Considerations for Shift Tolerance Radial Shift 1 2 Max.: 0.25 Min.: 0 3 Radial Shift Max.: (LMC-VC) / 2 = 0.4 4 Min.: (MMC-VC) / 2 = 0.15 1. Shift (and bonus) calculations are valid for non-circular features that are symmetrical, such as slots and grooves 2. When there is no MMC for the datum(s) used in stack-up, shift is zero. In this example, datums are planar. For round datums that are regardless of feature size, same applies. 3. For features that are gauged simultaneously, such as two holes from the same pattern, shift is zero. 4. Example of shift tolerance where datum D itself has a positional tolerance. Arash Vakily Nov 2005 Page 11
