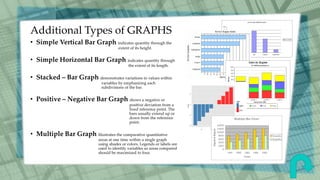
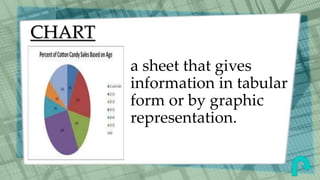
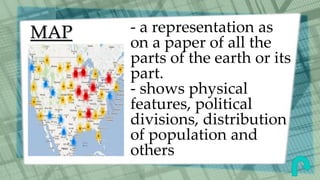
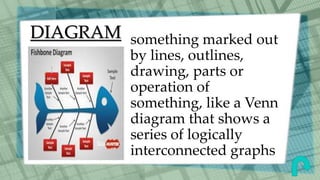
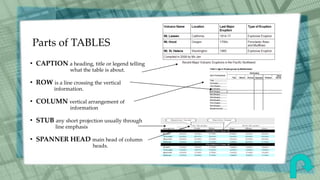
This document defines and provides examples of various graphic aids that can be used in reports to enhance textual information and understanding. It discusses figures, graphs, insets, charts, clip art, maps, diagrams, pictures, pictograms, side bars and tables. Specific types of graphs like vertical bar graphs, horizontal bar graphs and stacked bar graphs are described. The document also distinguishes between spot tables and reference tables and identifies the typical parts of tables like captions, rows, columns, stubs and spanner heads. The graphic aids aim to improve appreciation and comprehension of the topic being reported.