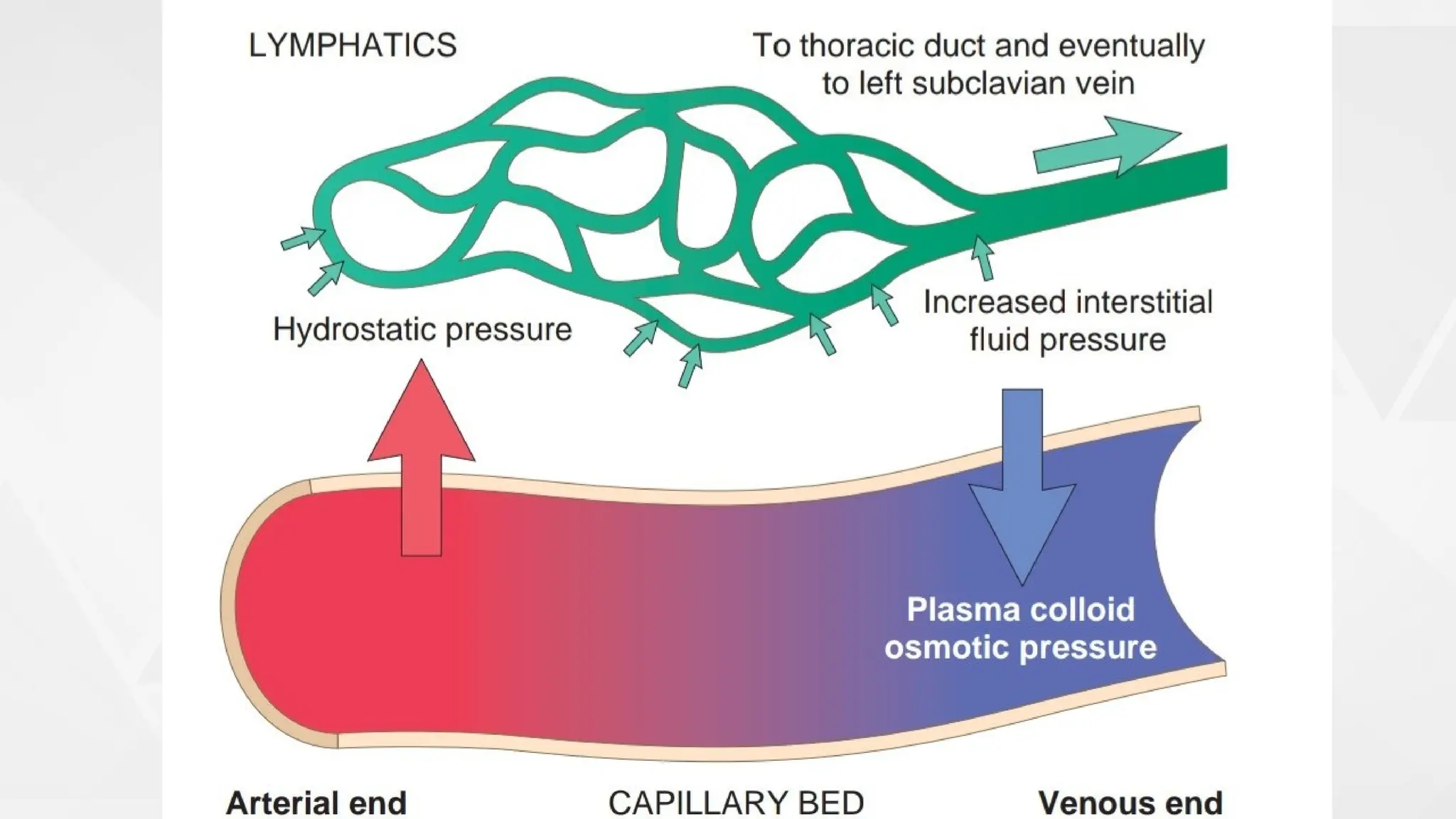
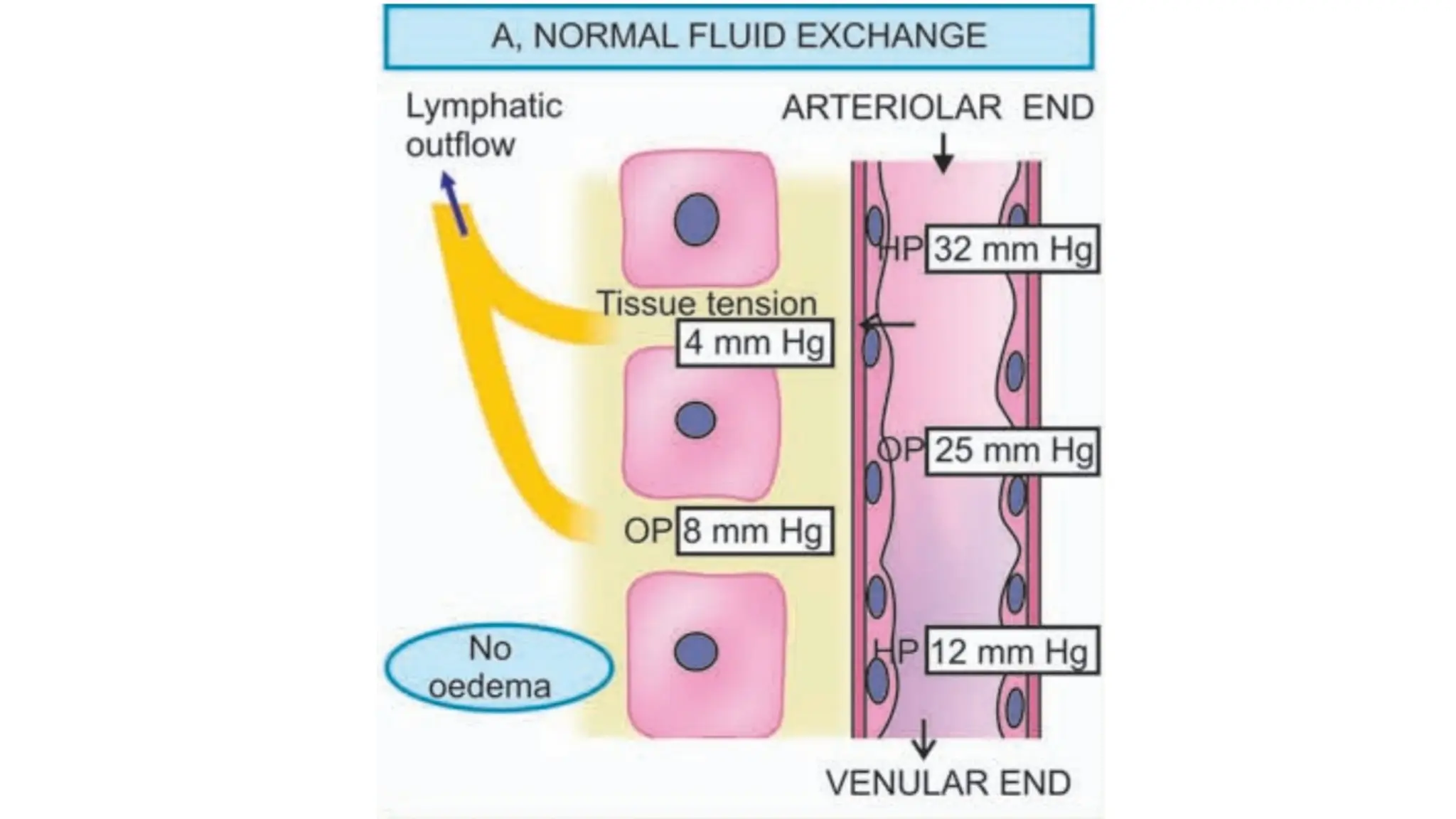
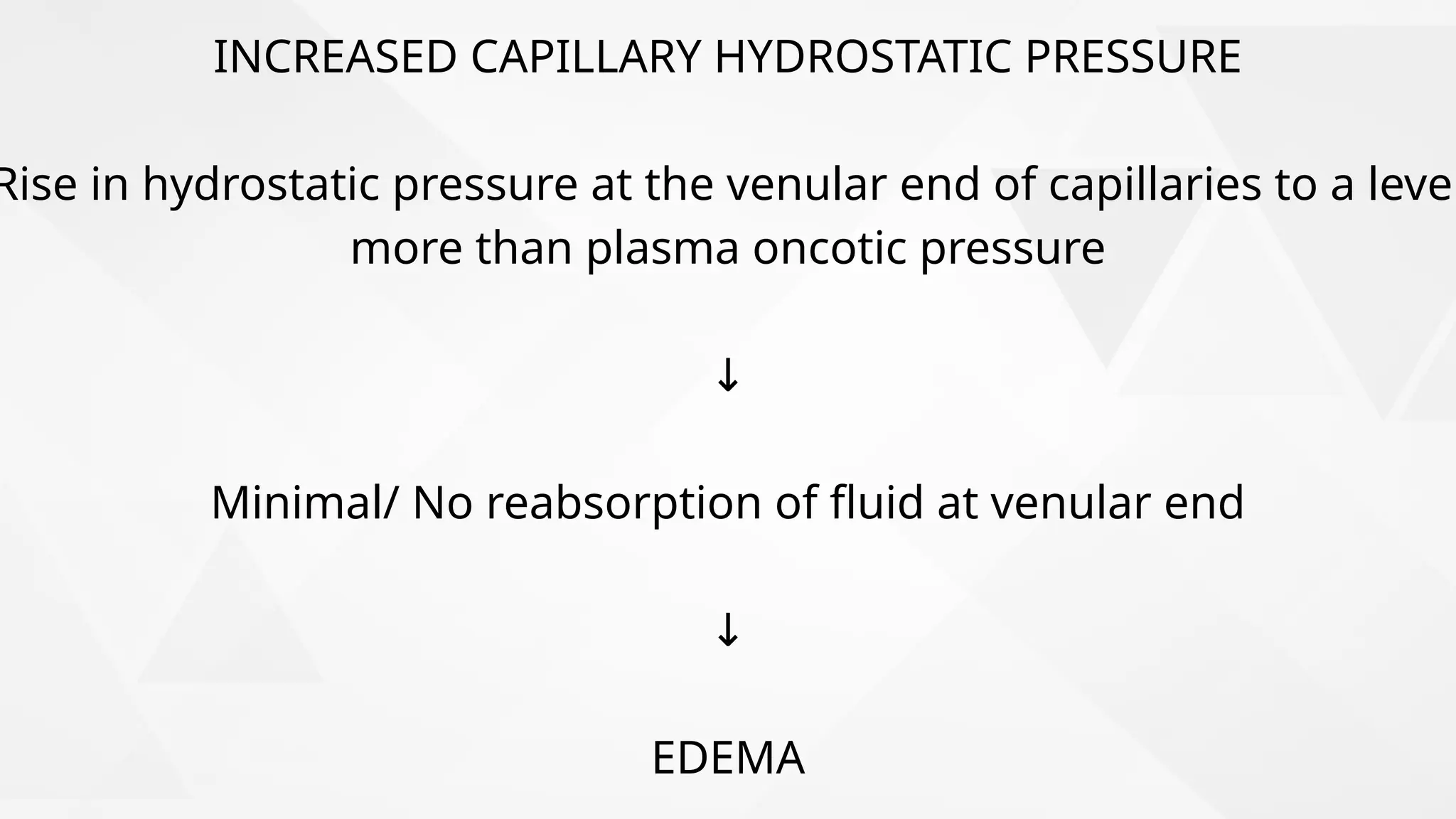
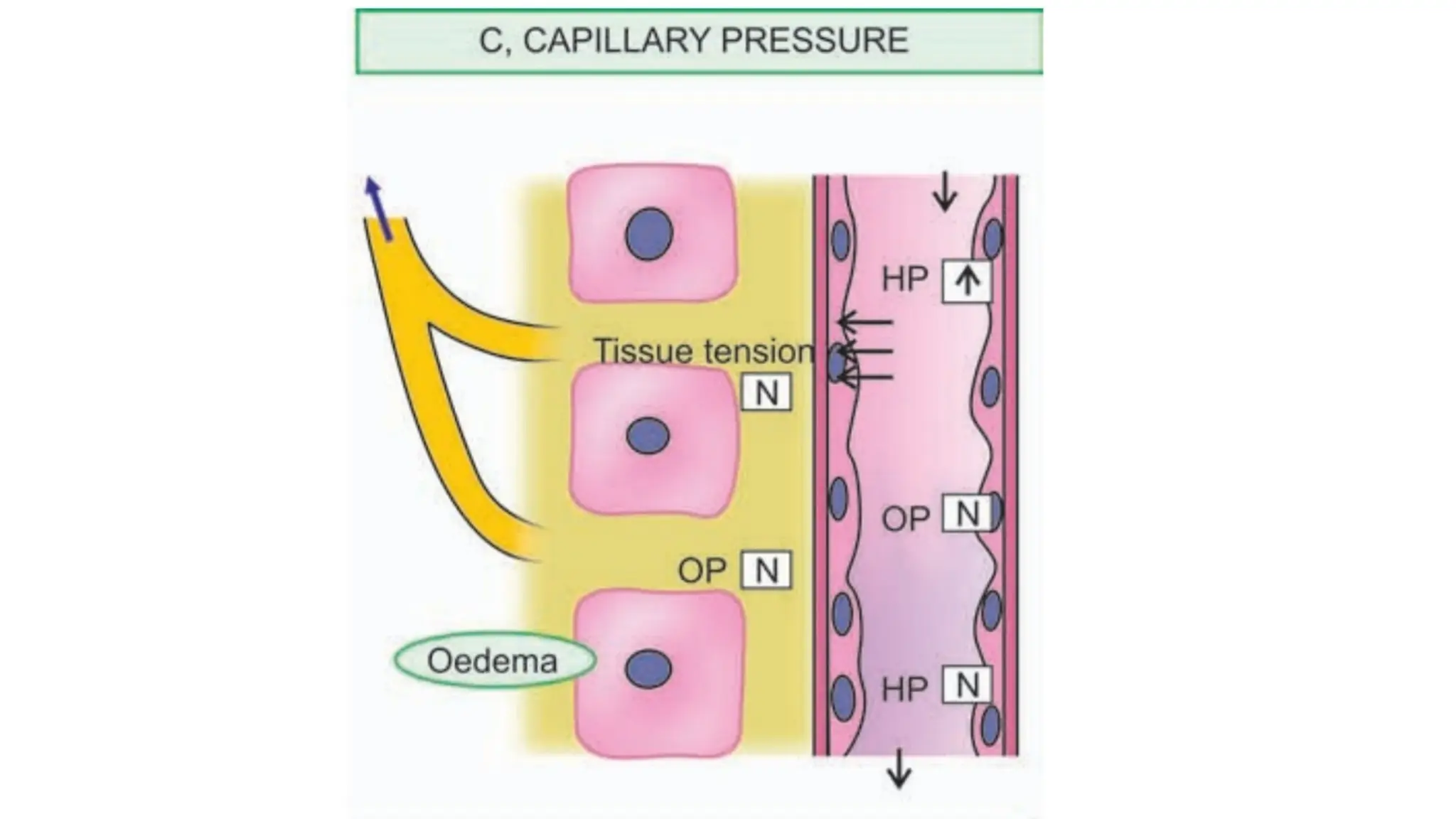
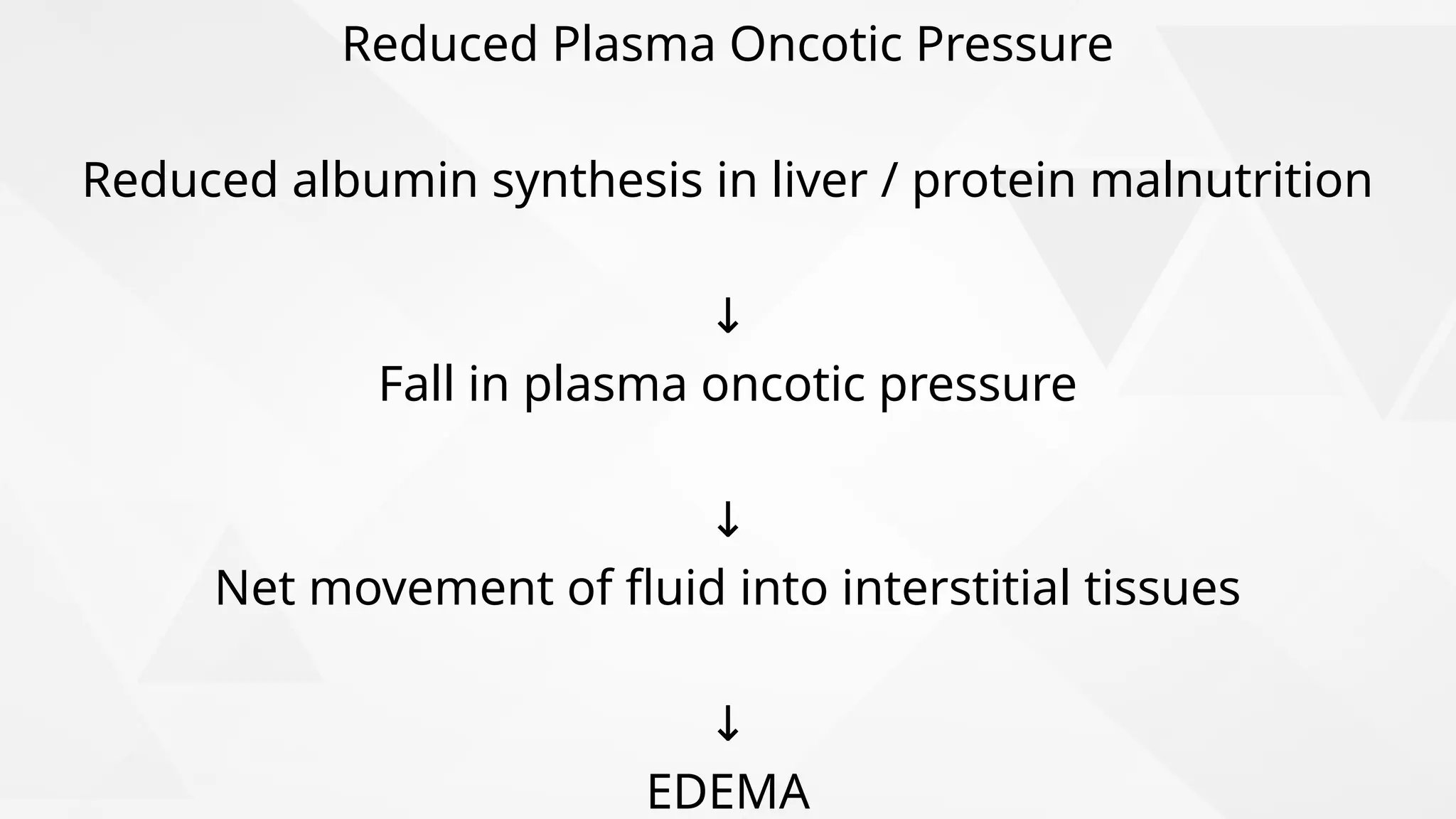
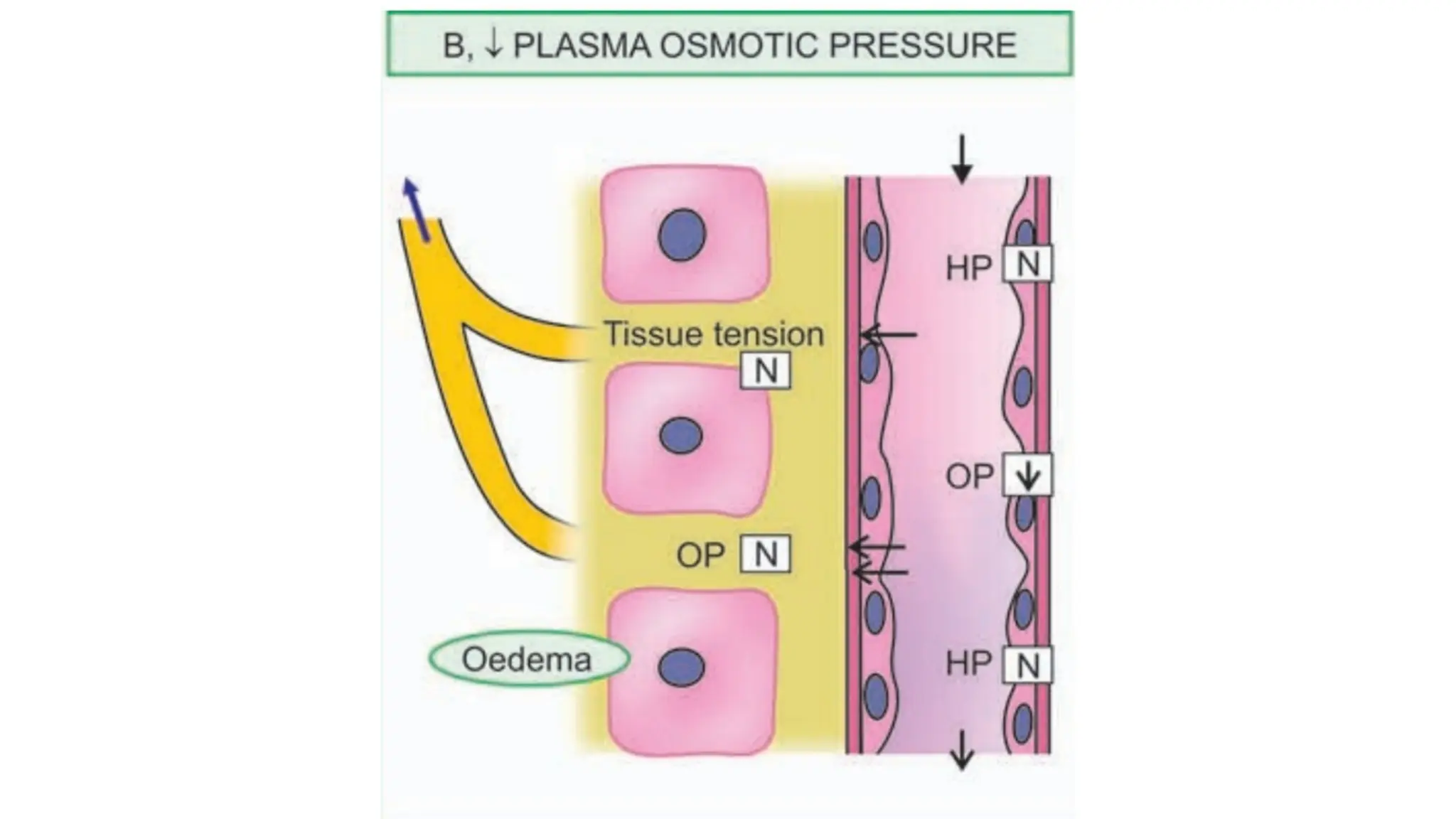
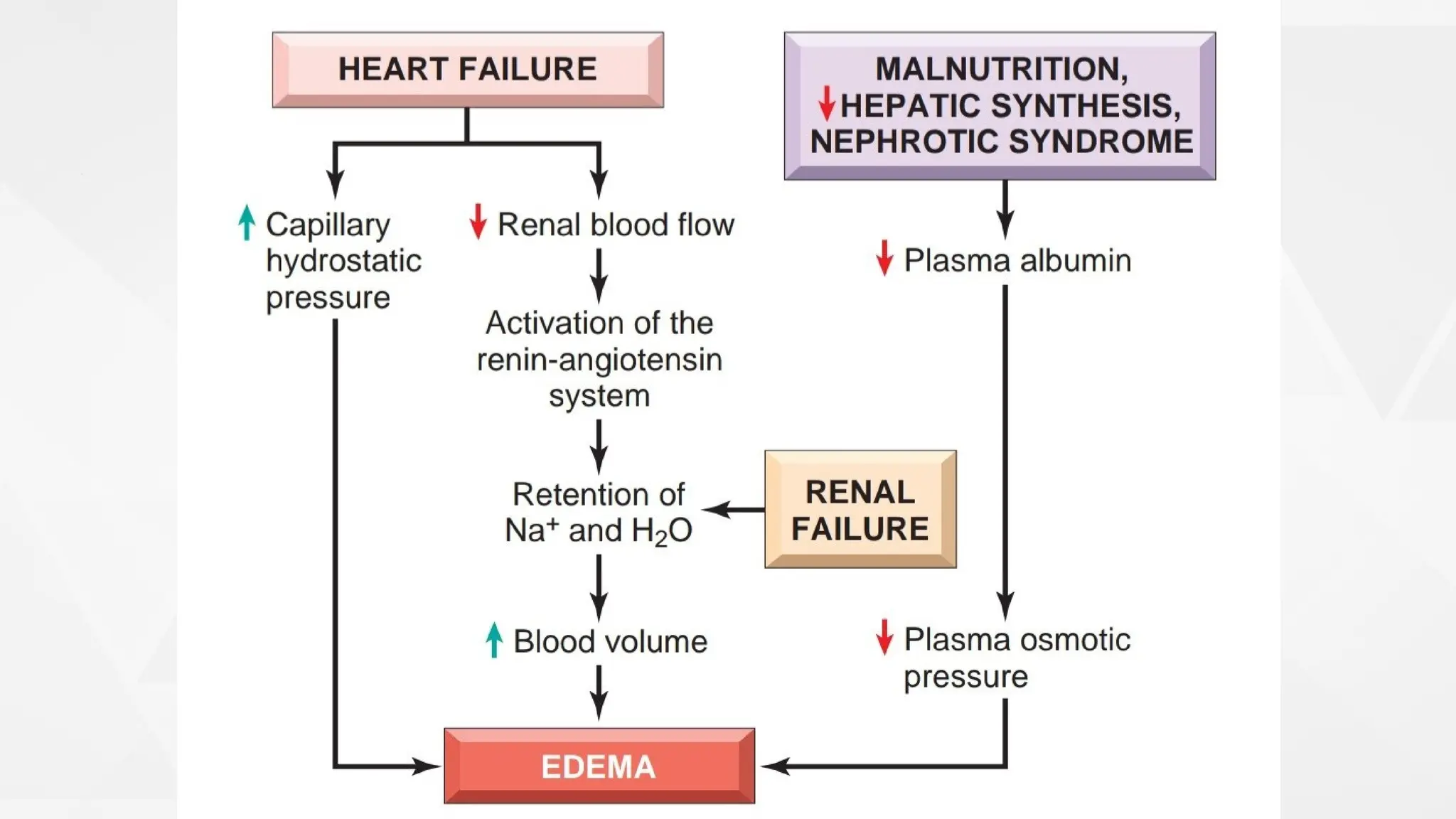
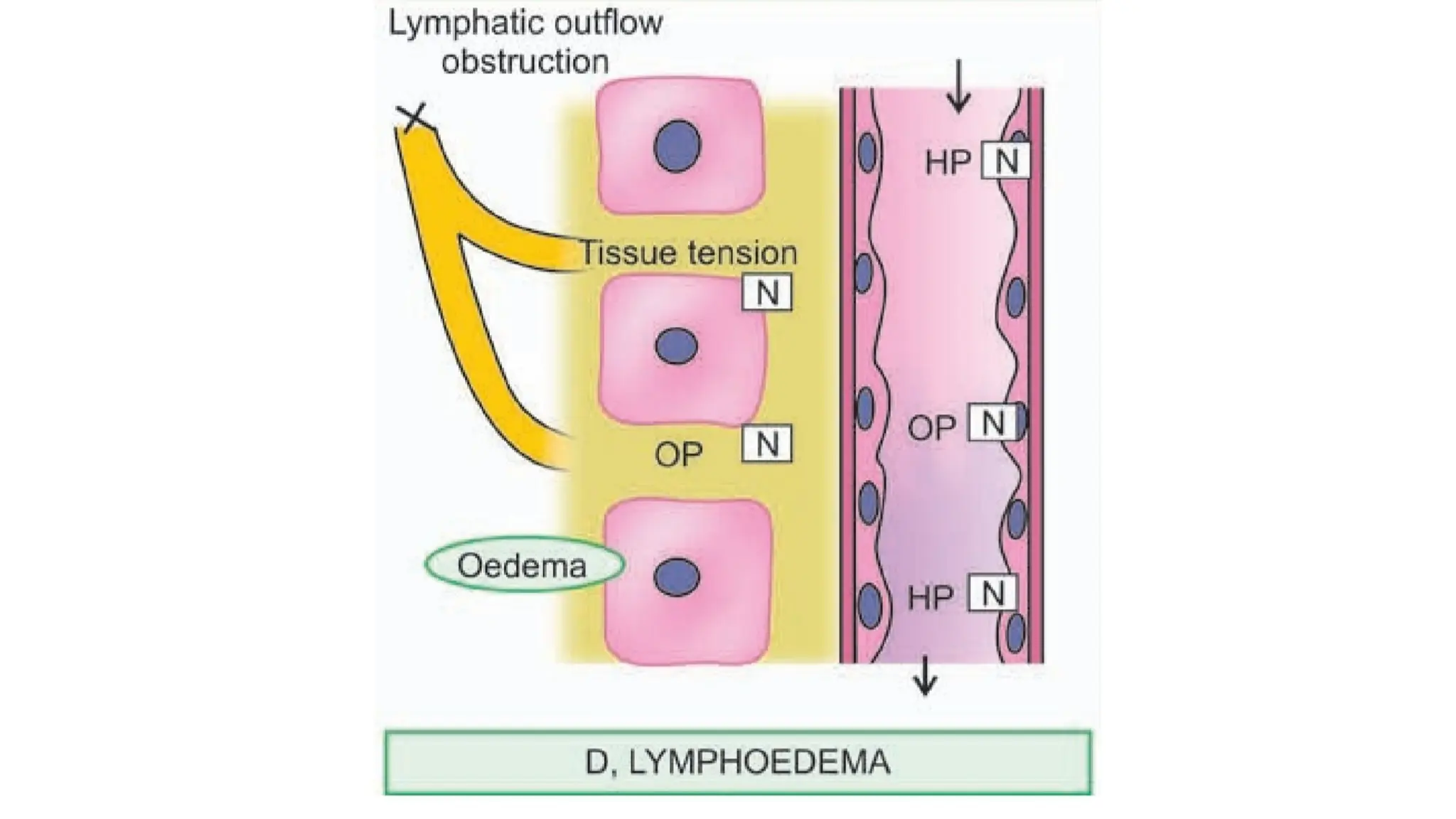
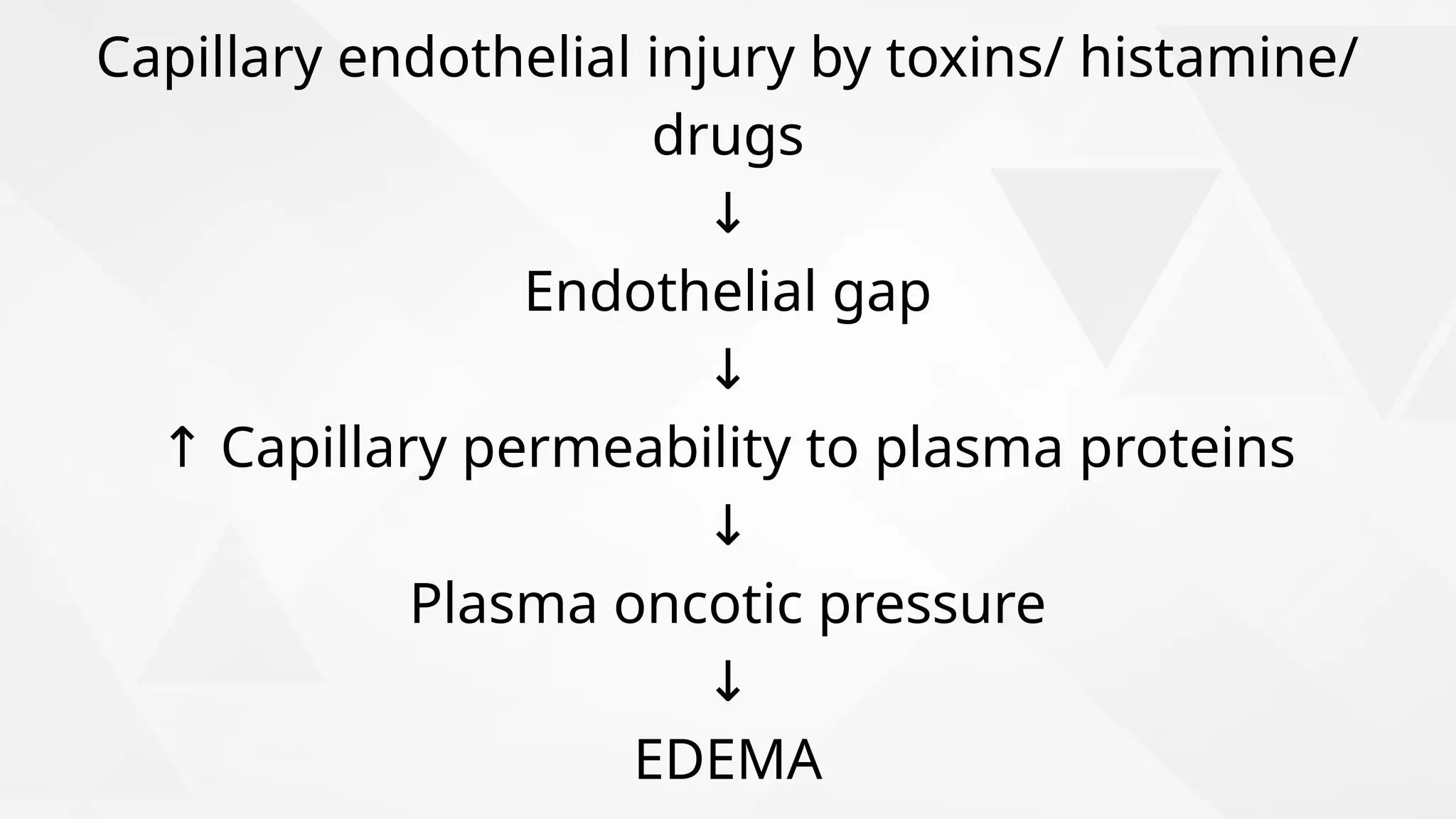
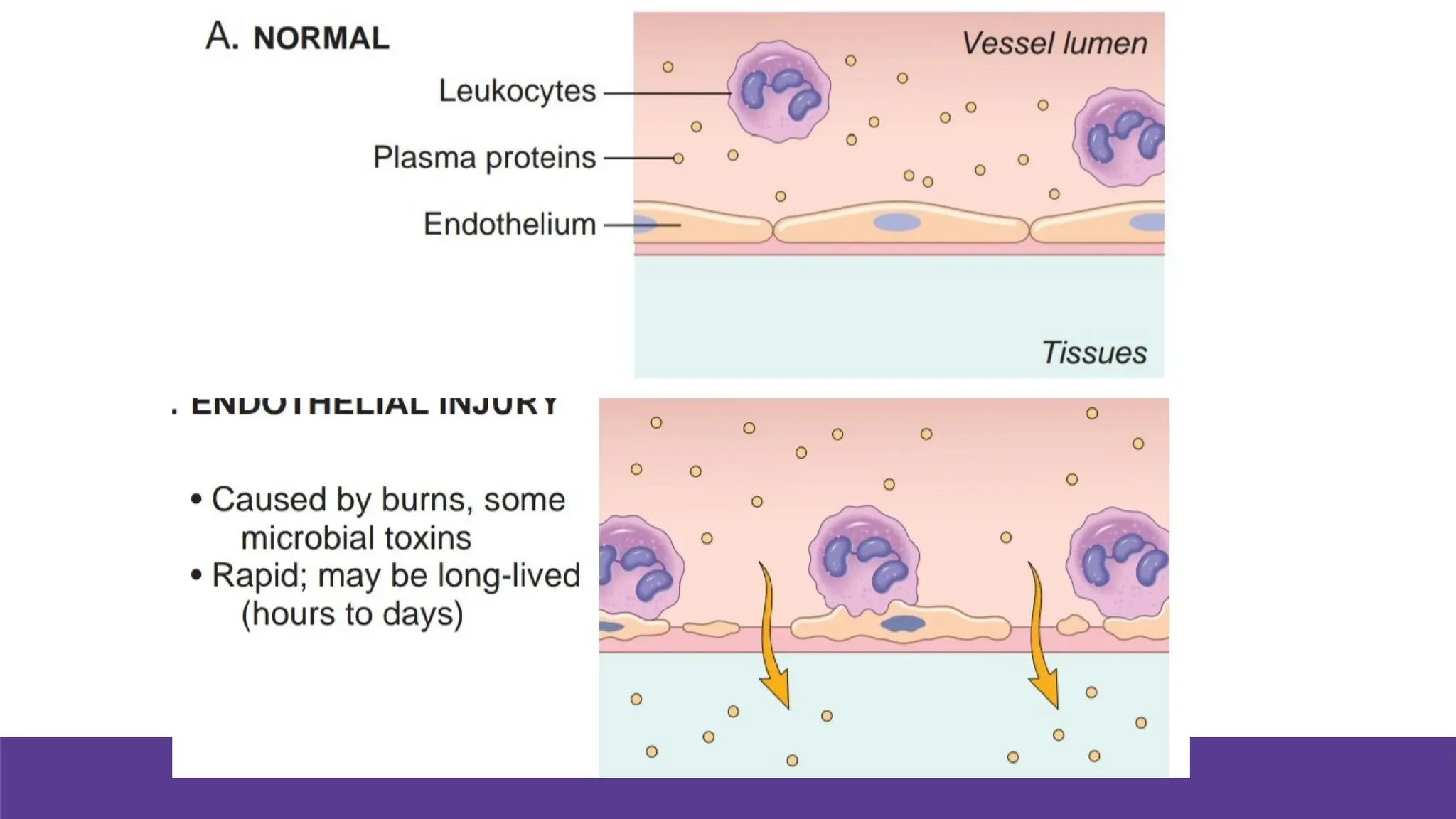
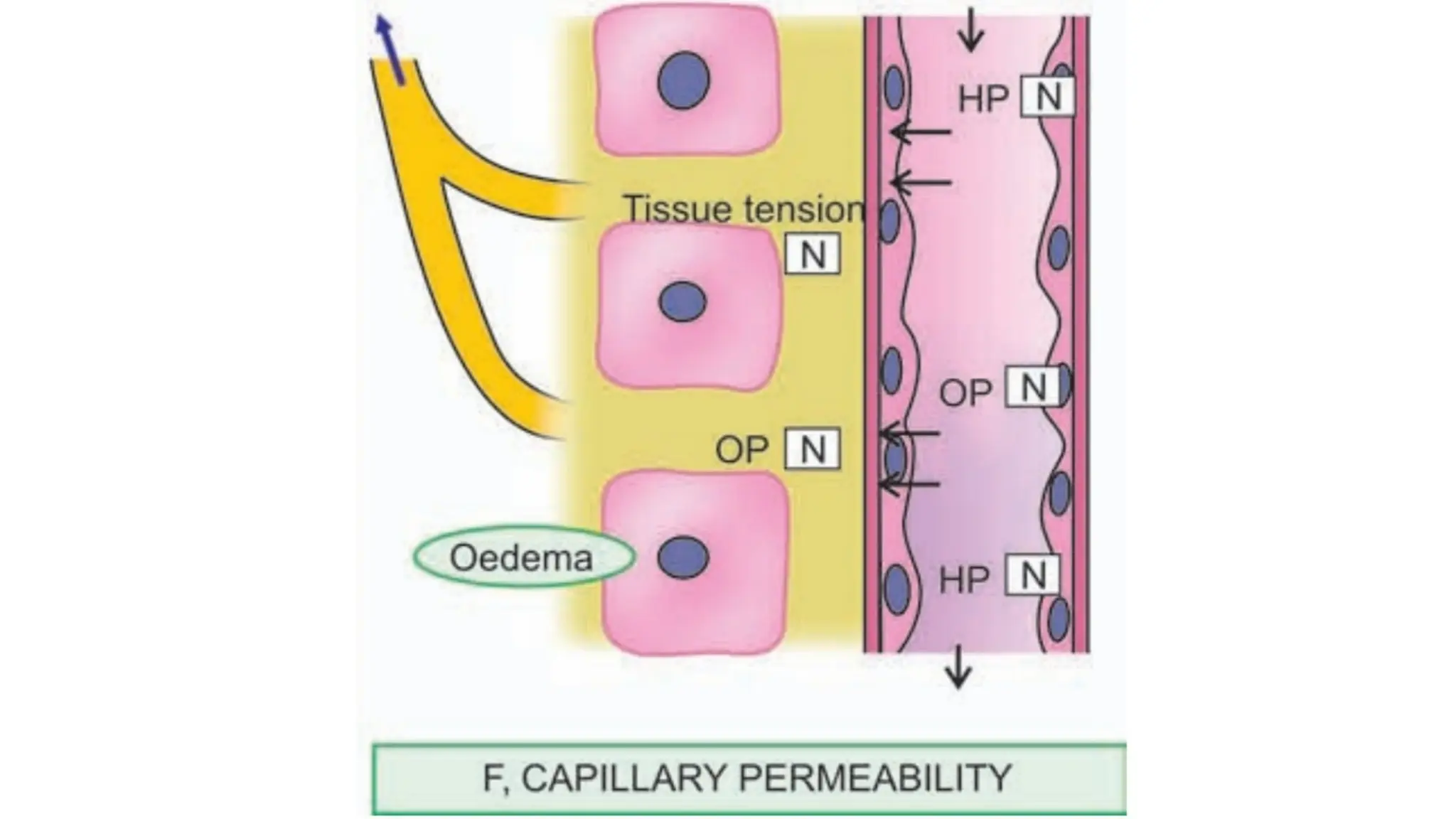
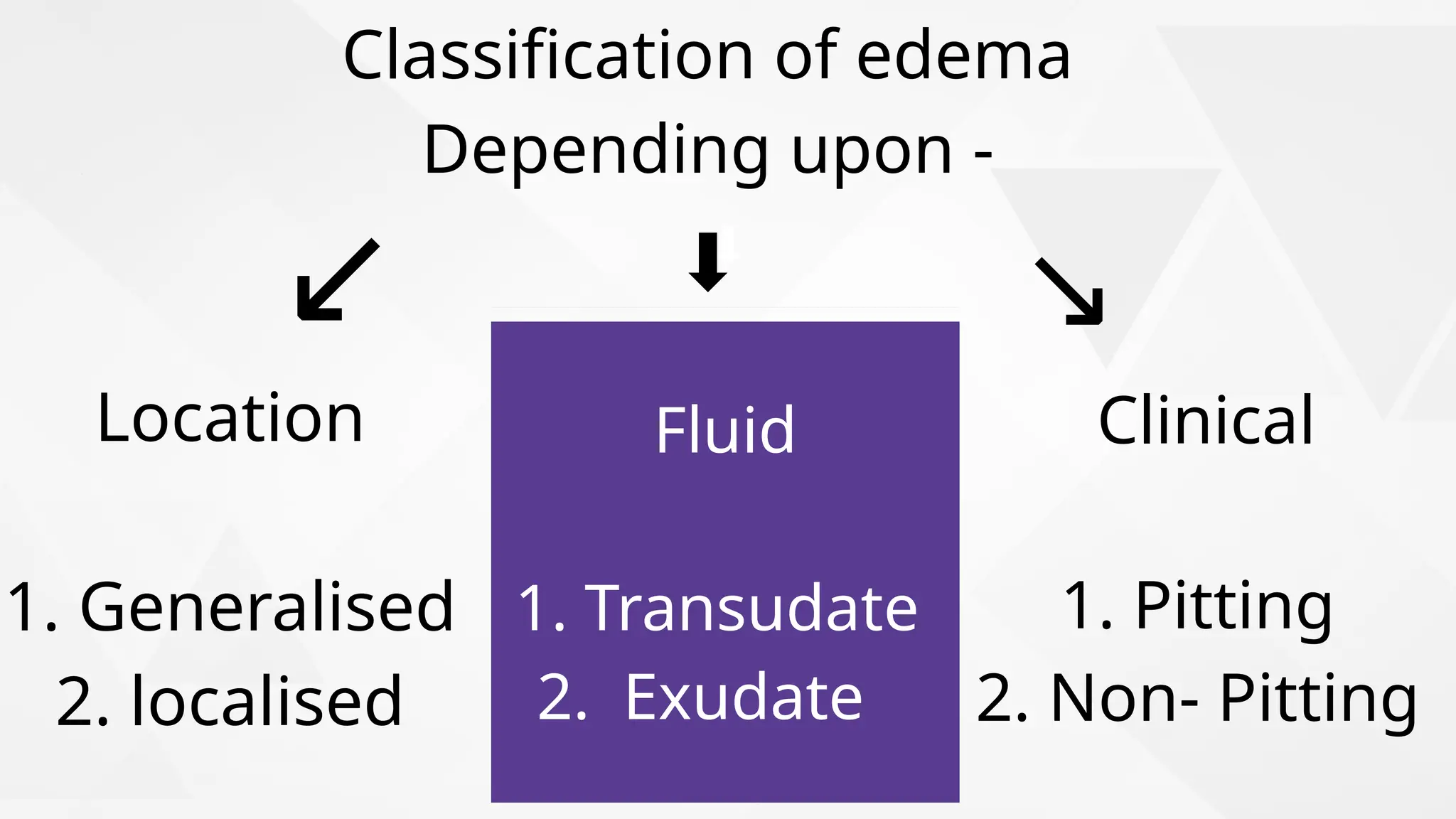
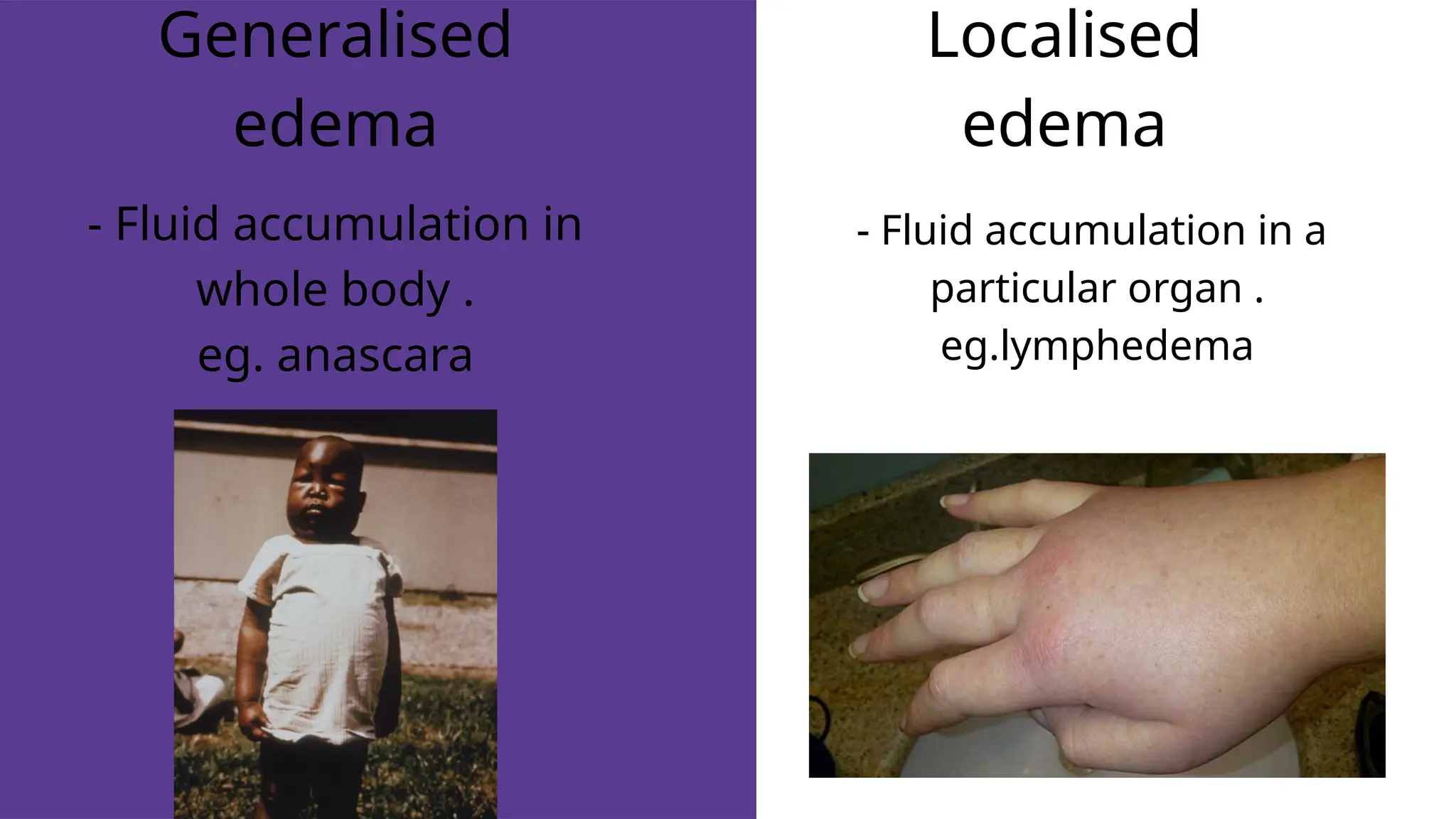
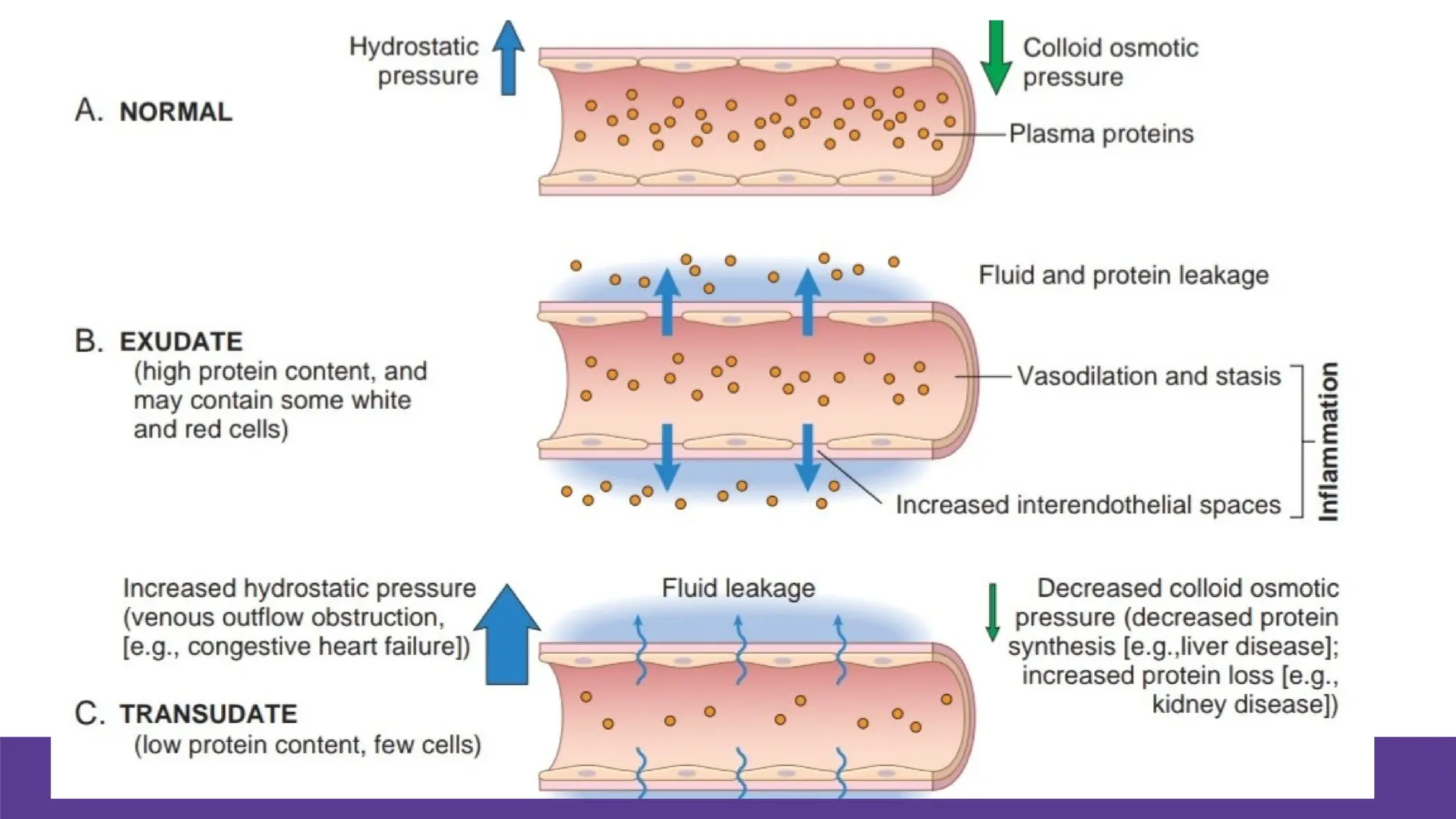
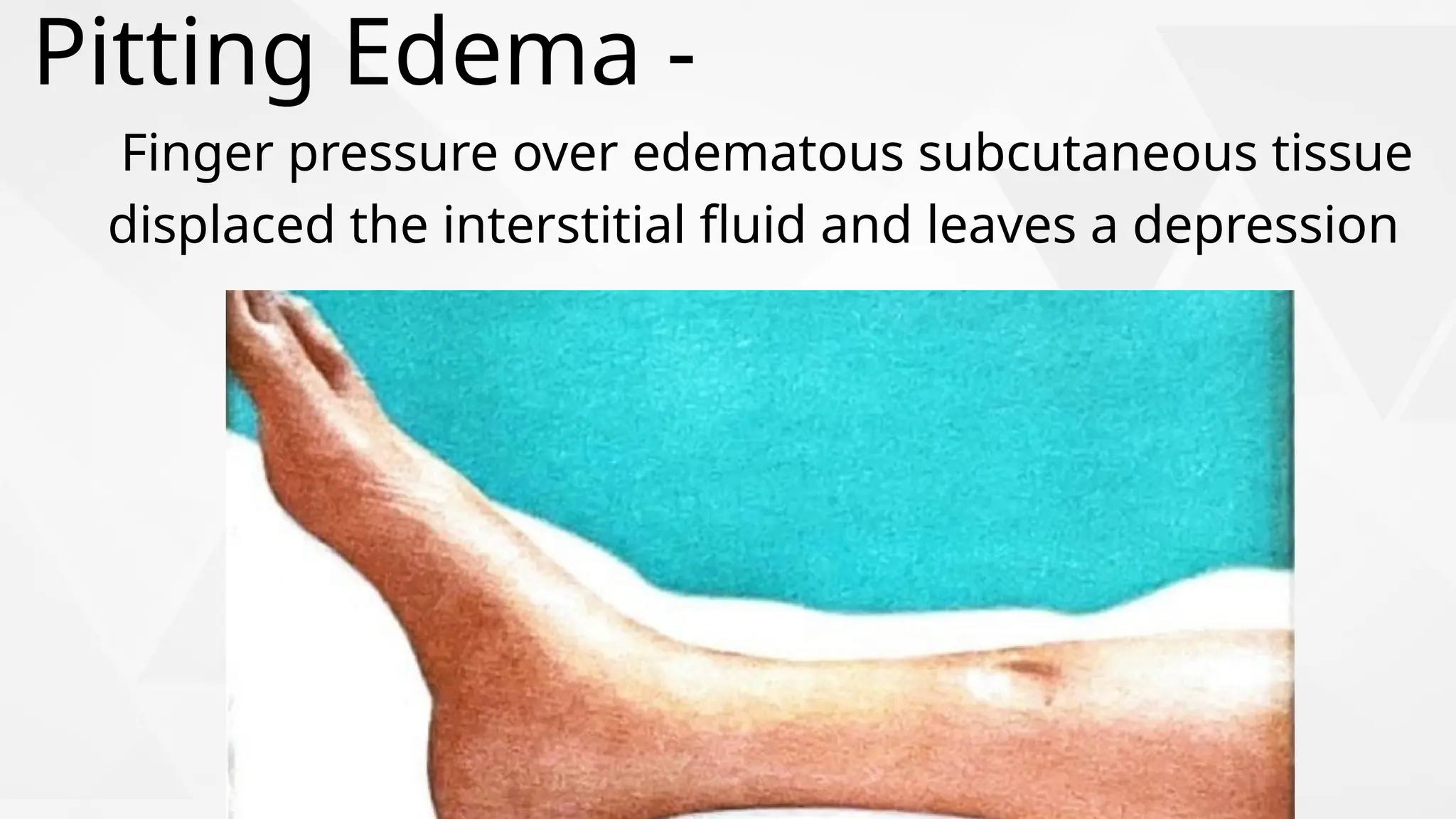
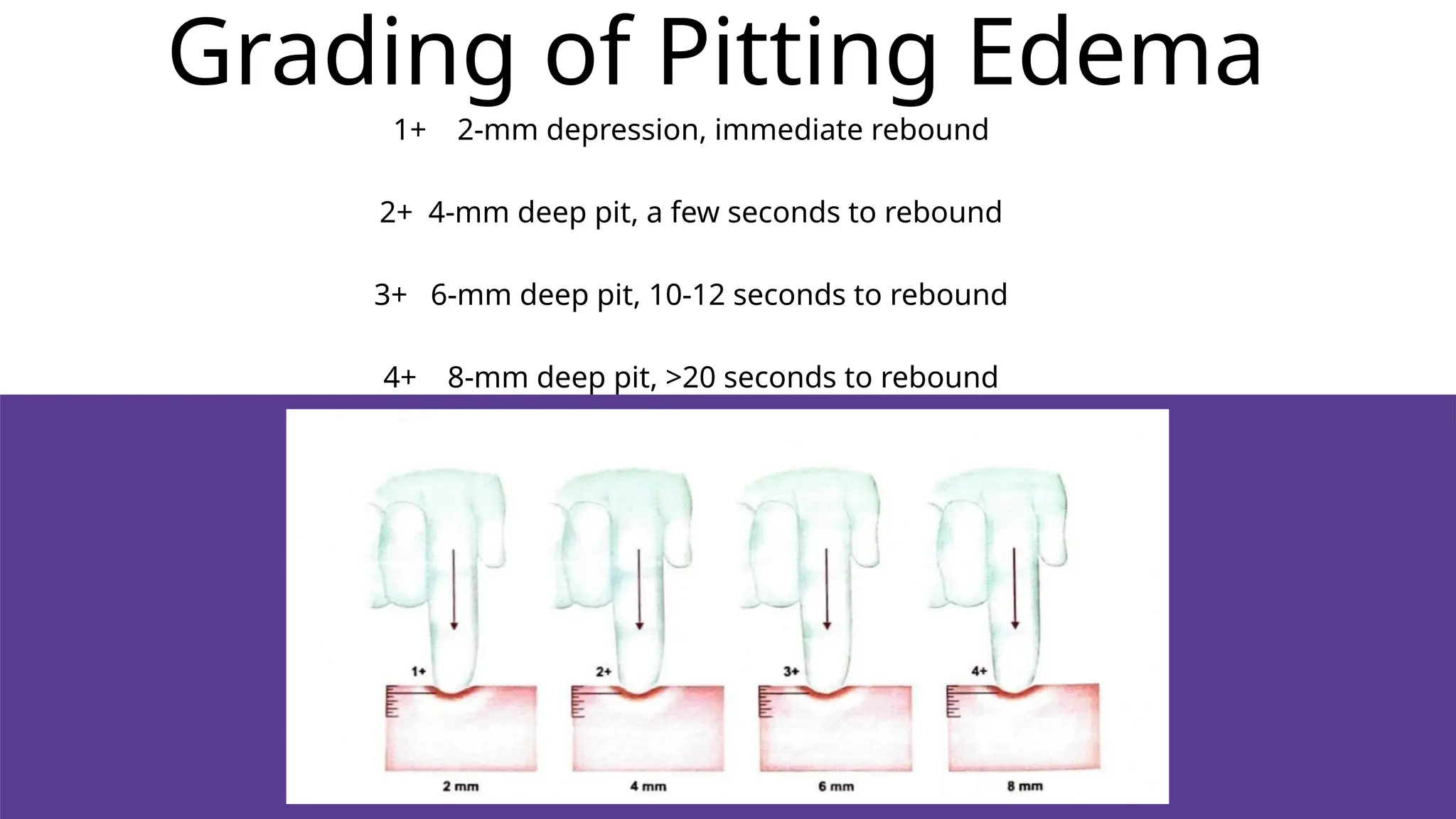
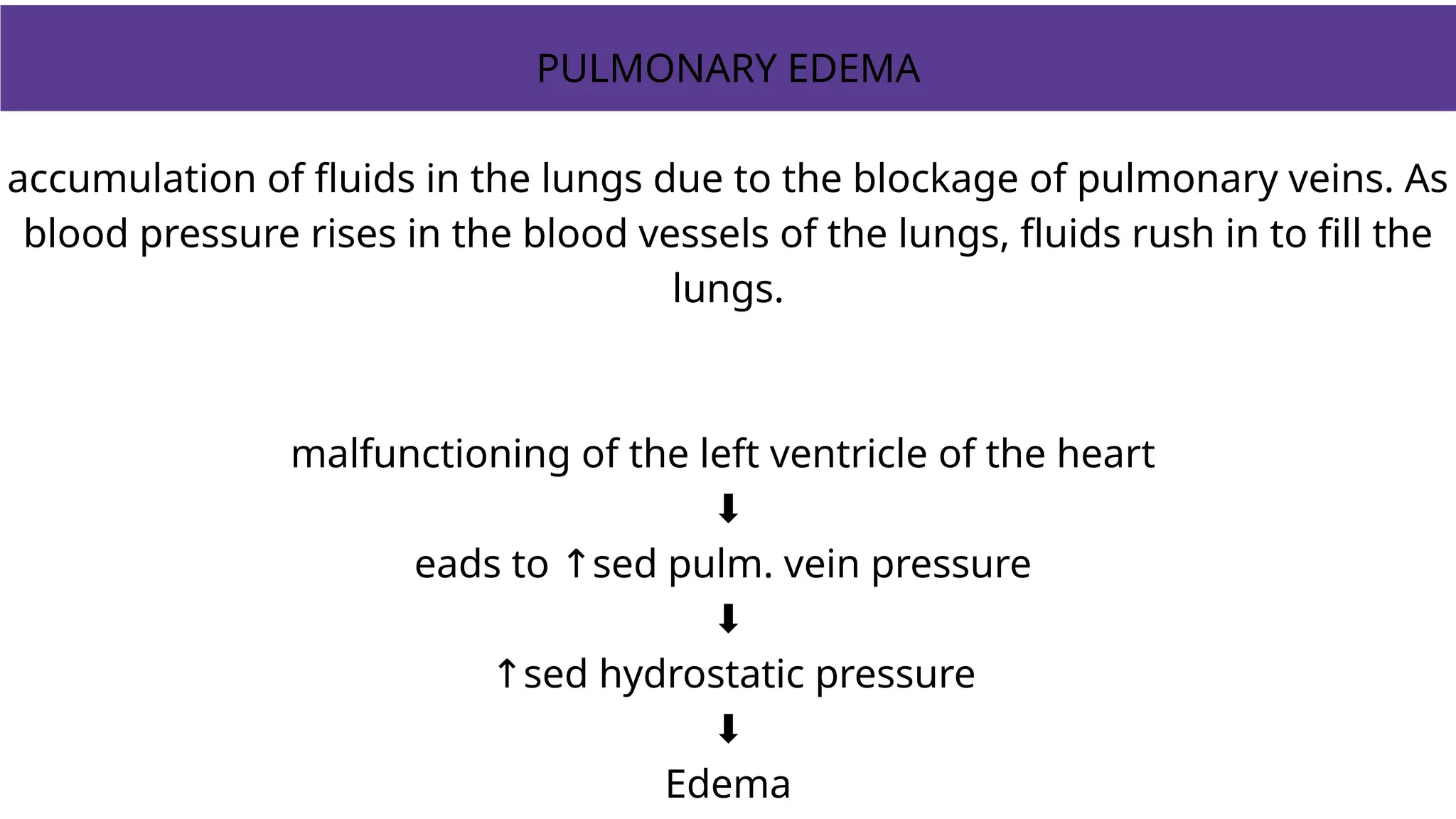
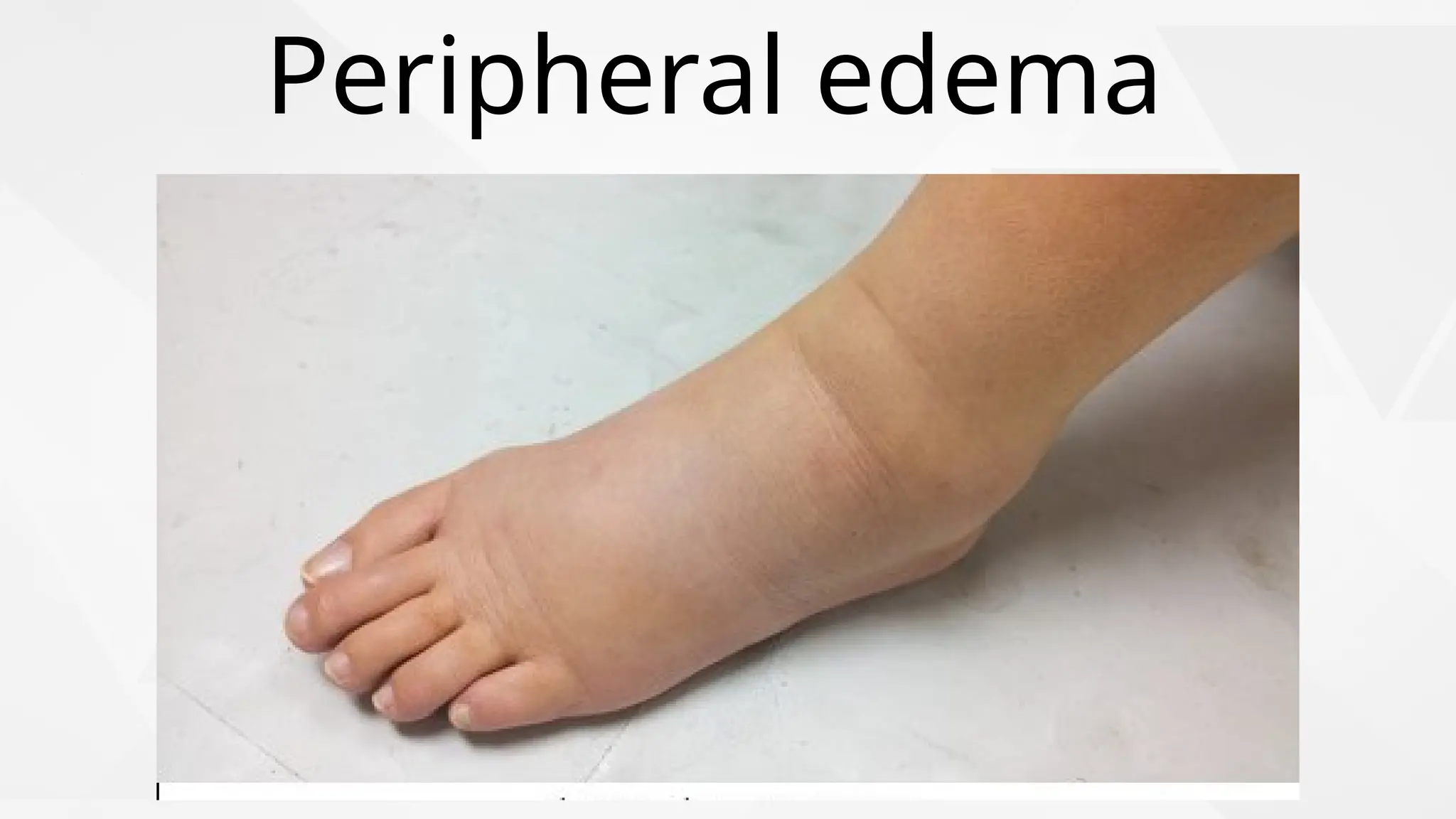
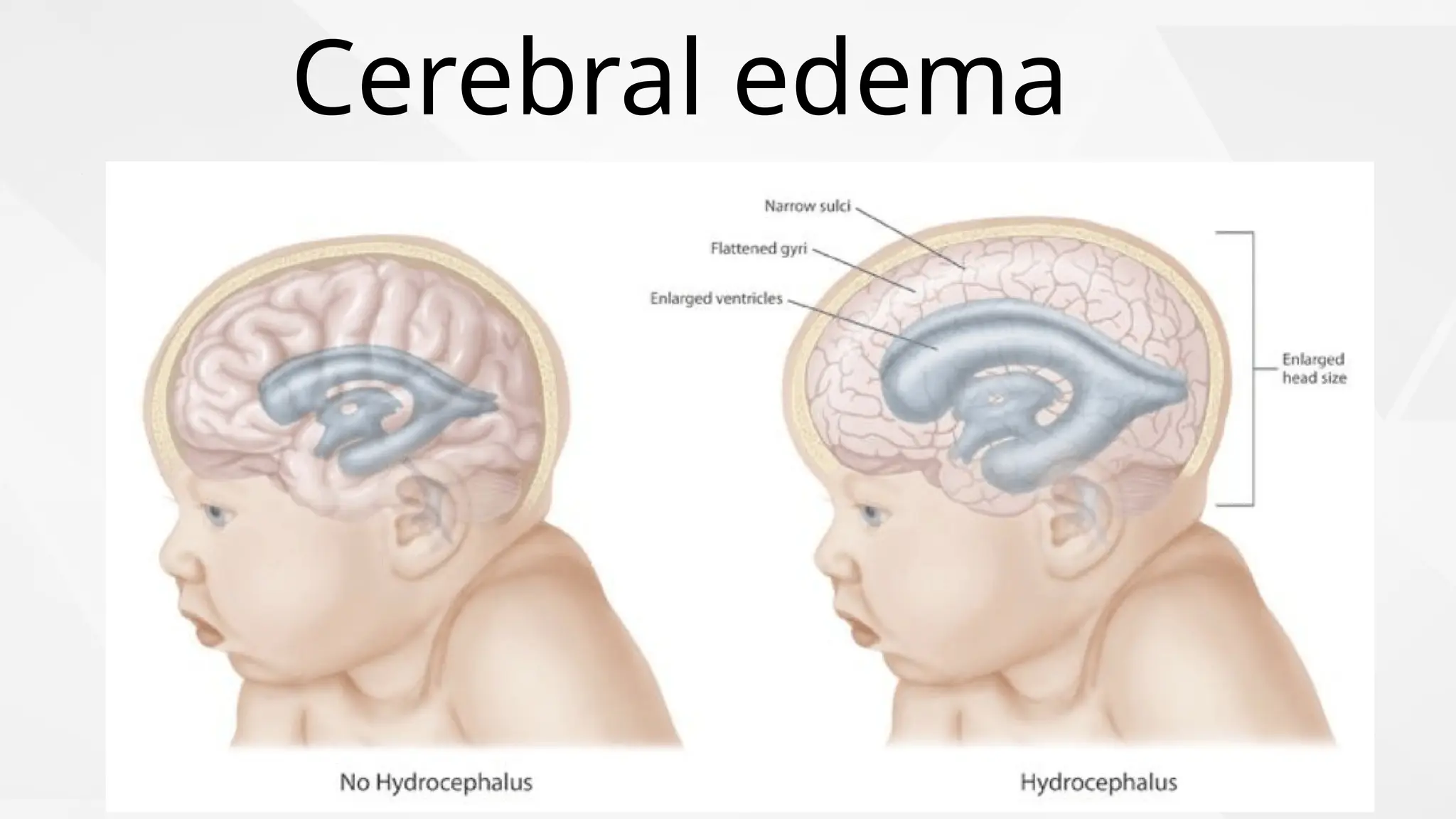
Edema is the abnormal accumulation of excess fluid in body tissues and cavities, categorized by location (generalized or localized) and fluid type (transudate or exudate). It can arise from factors such as increased hydrostatic pressure, reduced plasma osmotic pressure, sodium-water retention, or lymphatic obstruction and presents as either pitting or non-pitting edema. Major types include pulmonary edema affecting the lungs, peripheral edema in the legs and ankles, and cerebral edema impacting the brain, each associated with specific causes and health conditions.