Embed presentation
Downloaded 60 times


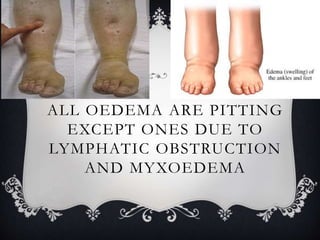




Oedema, also known as edema, is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitial spaces or body cavities. It can occur locally in specific areas like the lungs or abdomen, or systemically throughout the body. Oedema is classified as either transudative or exudative based on its fluid composition, and as pitting or non-pitting based on whether the fluid can be displaced by pressure. The main causes of oedema are increased hydrostatic pressure, reduced plasma oncotic pressure, lymphatic obstruction, and inflammation.






