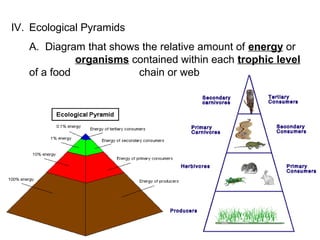
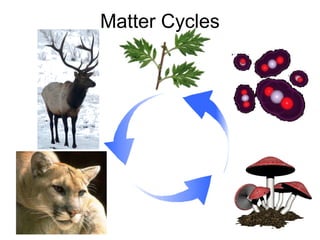
An ecosystem consists of biotic and abiotic components that interact with each other. Biotic factors include living organisms like plants, animals, and microbes, while abiotic factors refer to non-living physical and chemical elements like water, soil, sunlight, temperature, and minerals. Organisms depend on each other through food webs, with energy transferring between trophic levels from producers to primary, secondary and tertiary consumers. Ecosystems also cycle nutrients through the actions of decomposers which break down organic matter. Examples of ecosystems include forests, grasslands, freshwater and marine environments.