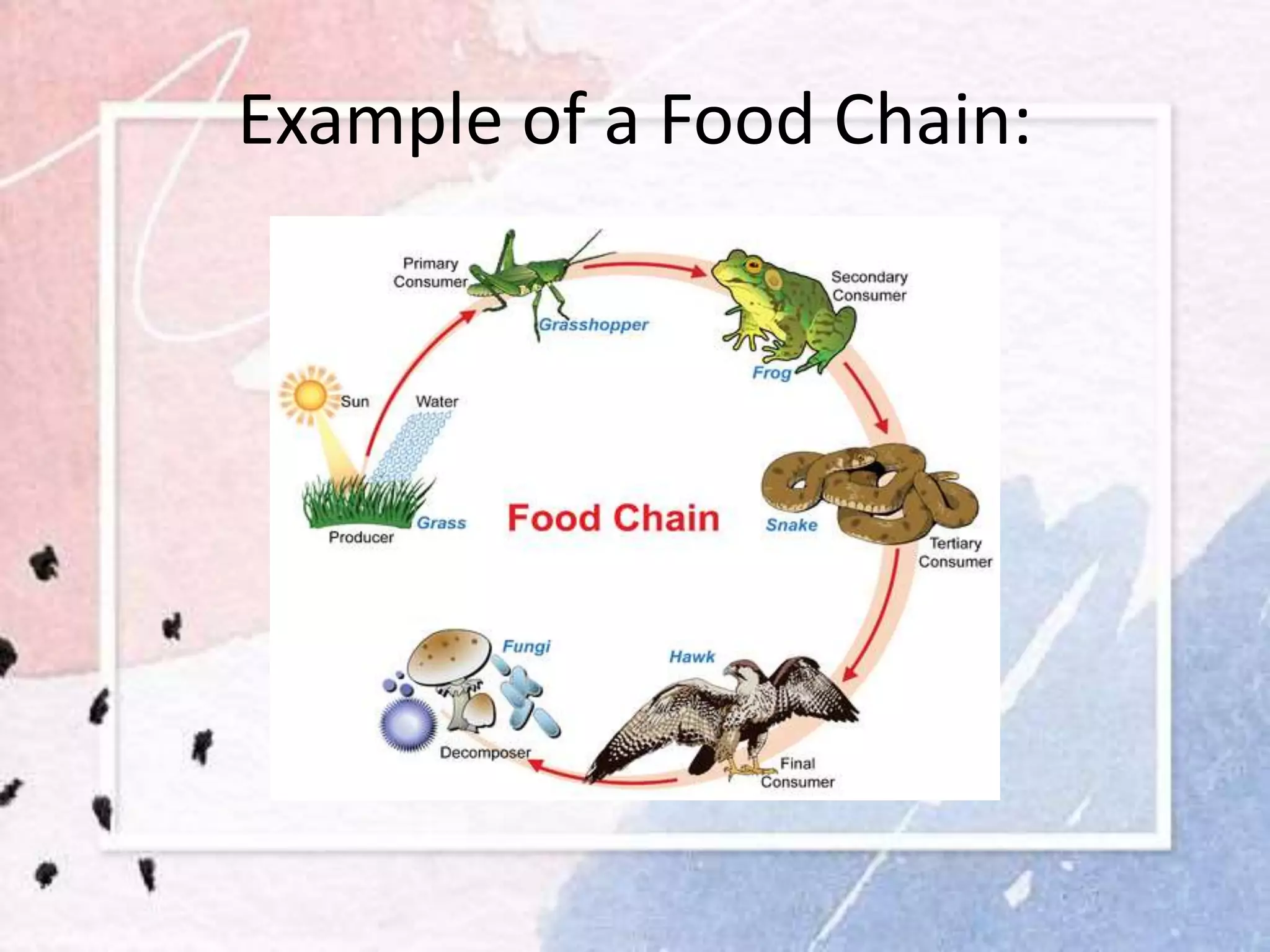
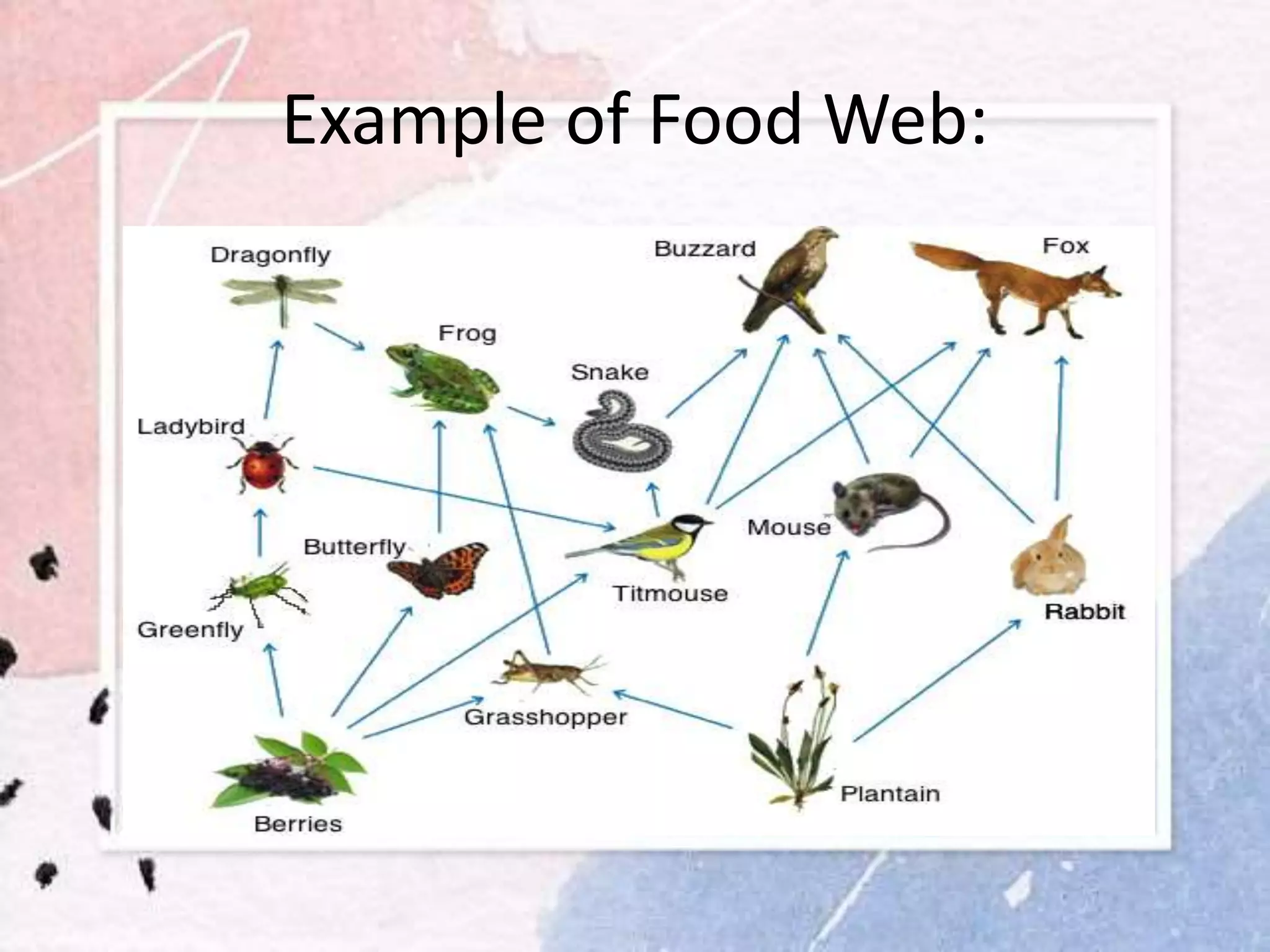
This document discusses food chains and food webs. It defines a food chain as the transfer of matter and energy from one organism to another through eating relationships. A food chain has producers, consumers, and decomposers. Producers make their own food, consumers eat other organisms, and decomposers break down dead organisms. A food web shows the interconnected food chains in an ecosystem and how different species interact with and depend on one another. Understanding food chains and food webs is important for appreciating ecosystem dynamics and biodiversity.