This document discusses key concepts about ecosystems, including:
- An ecosystem consists of interacting organisms and their environment. It defines the basic types of ecosystems as aquatic, terrestrial, and marine.
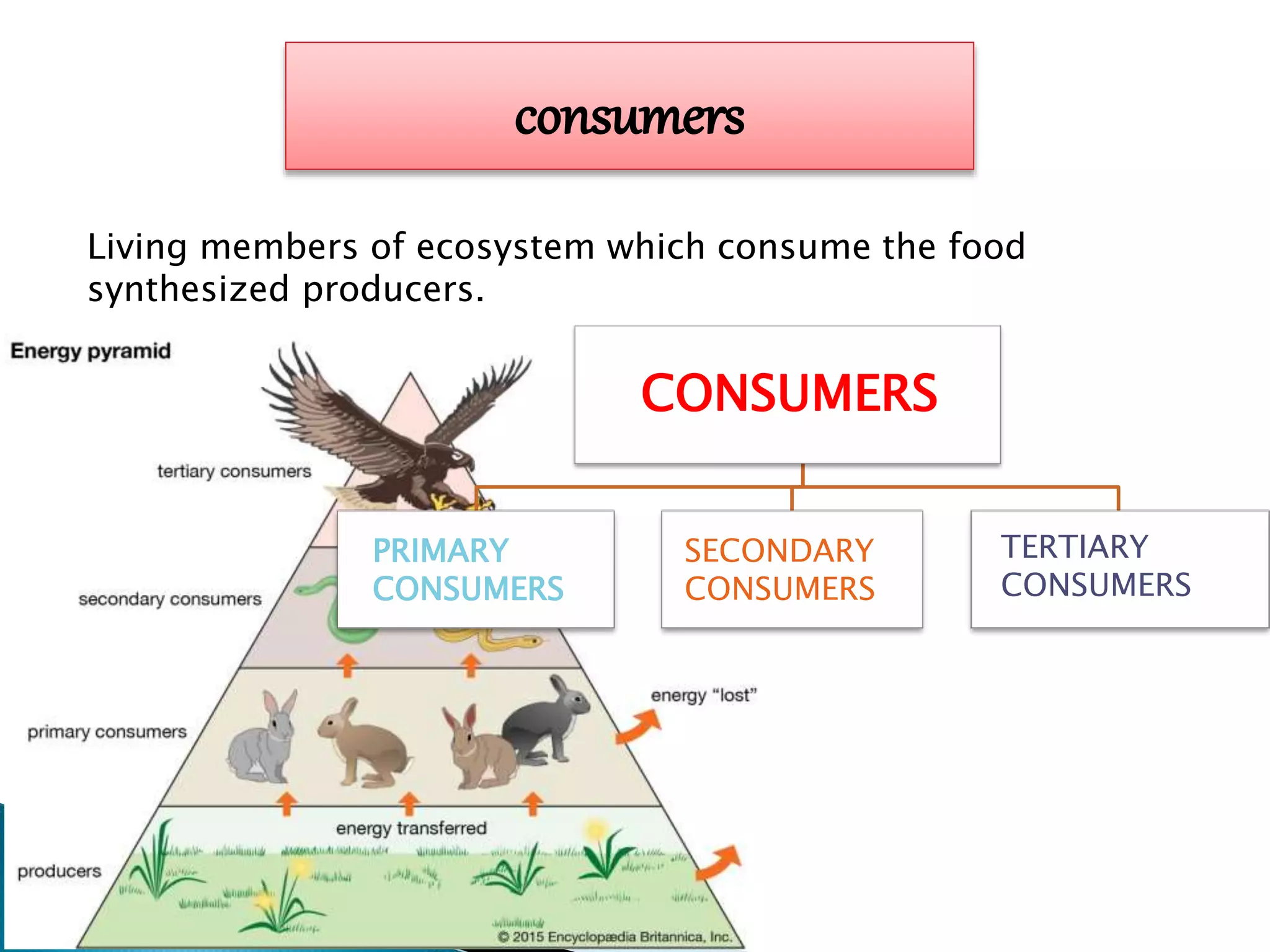
- Ecosystems contain biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components. Biotic components are divided into producers, consumers, and decomposers.
- Producers perform photosynthesis, consumers feed on producers or other consumers, and decomposers break down dead organic matter. Consumers are further divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers.
- Ecosystems have functions like productivity, decomposition, energy flow, and nutrient cycling to maintain interactions between components.