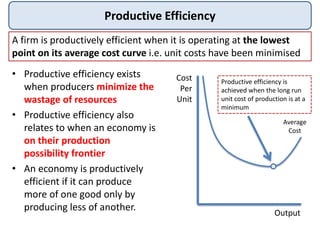
This document discusses different types of economic efficiency in markets: allocative efficiency, productive efficiency, and social efficiency. It also discusses dynamic efficiency through innovation. Allocative efficiency occurs when resources are allocated optimally to maximize total welfare. Productive efficiency means producers minimize waste. Social efficiency means marginal social costs equal marginal social benefits. Dynamic efficiency refers to innovation through new products, processes, and business models. The document concludes by defining market failure as an inefficient allocation of resources that results in a deadweight loss, which can be caused by externalities, public goods, monopolies, and other factors.