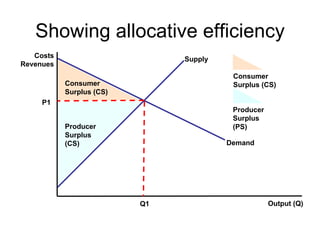
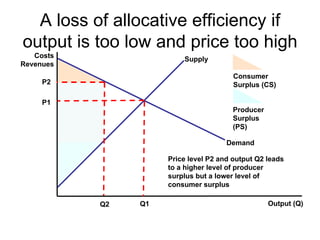
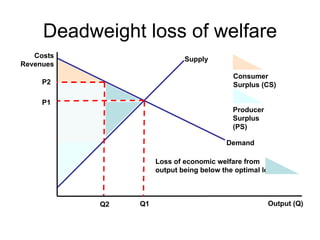
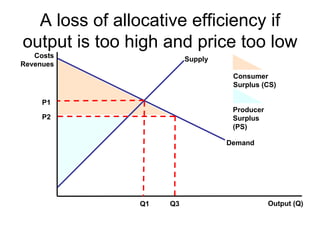
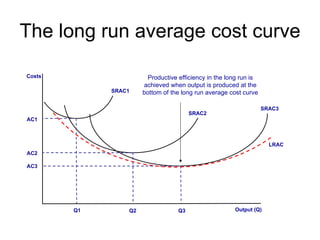
There are two types of economic efficiency: static and dynamic. Static efficiency looks at how efficiently a firm/economy uses its resources at a given point in time, while dynamic efficiency examines improvements in efficiency over time due to factors like technology and competition. Allocative efficiency occurs when the value consumers place on goods equals the cost of producing them, maximizing total welfare. It requires that price equals marginal cost. Productive efficiency means producing at minimum average total cost to minimize waste. Pareto efficiency is reached when resources cannot be reallocated to improve one person's situation without harming another's.