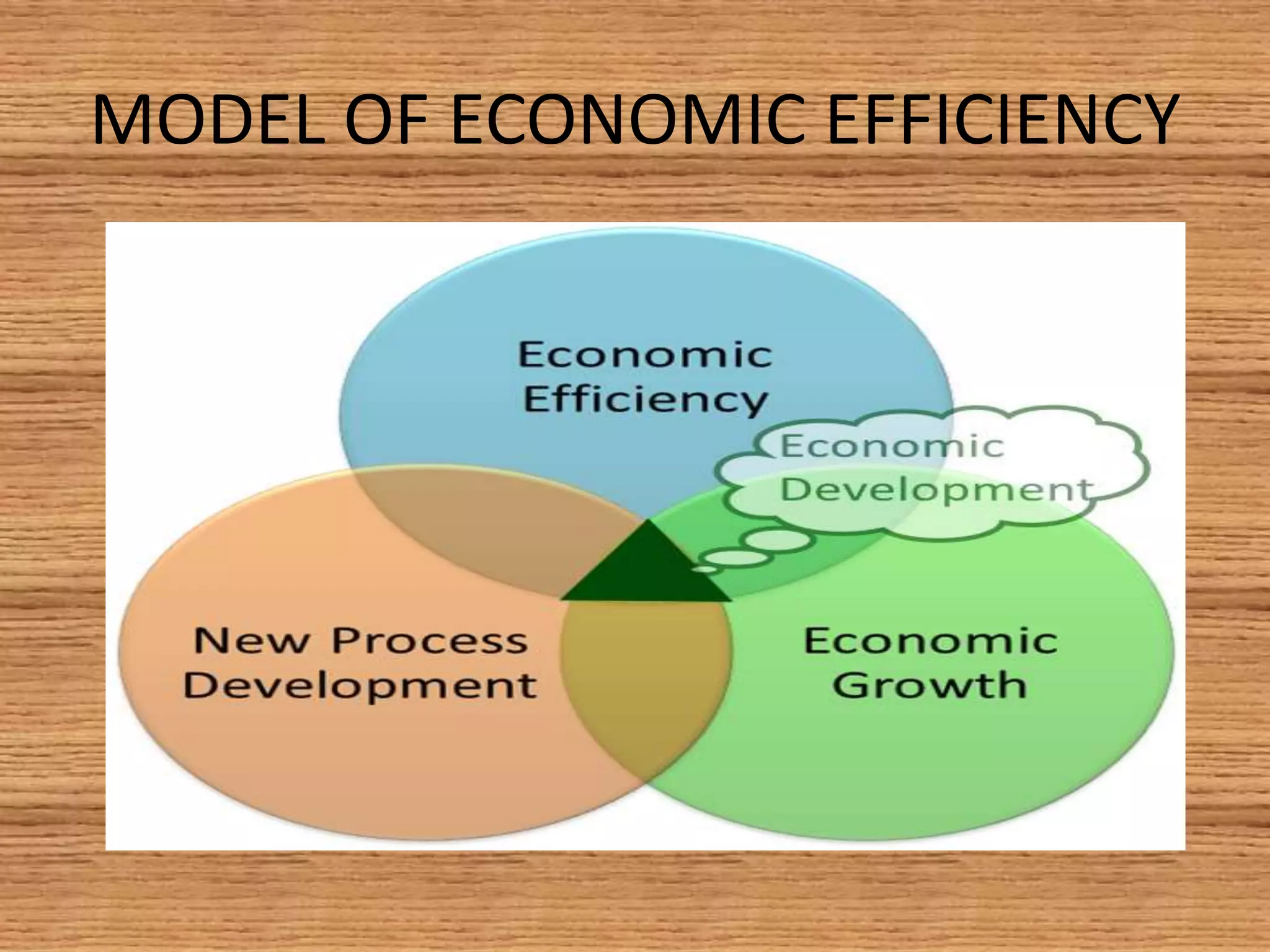
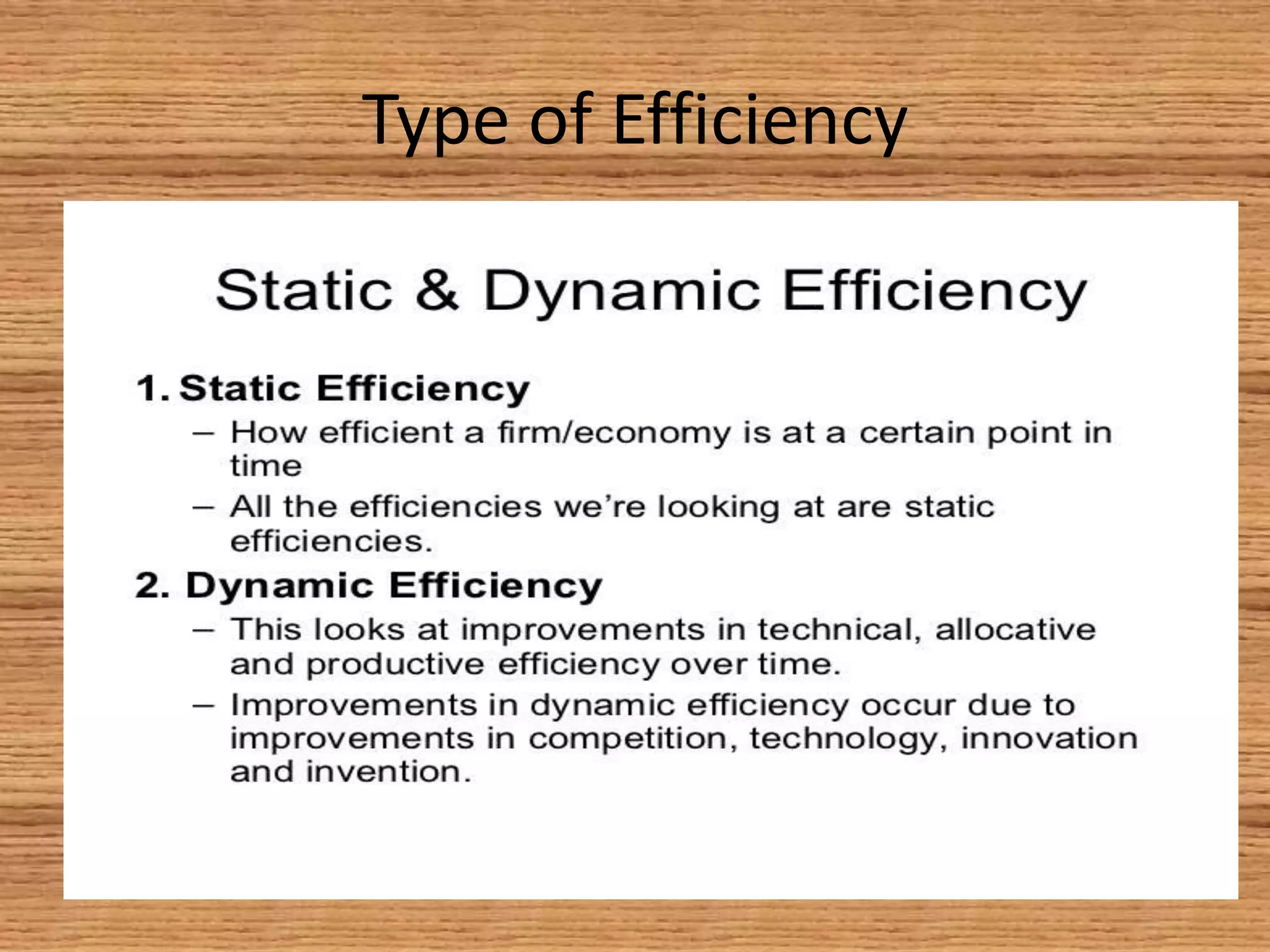
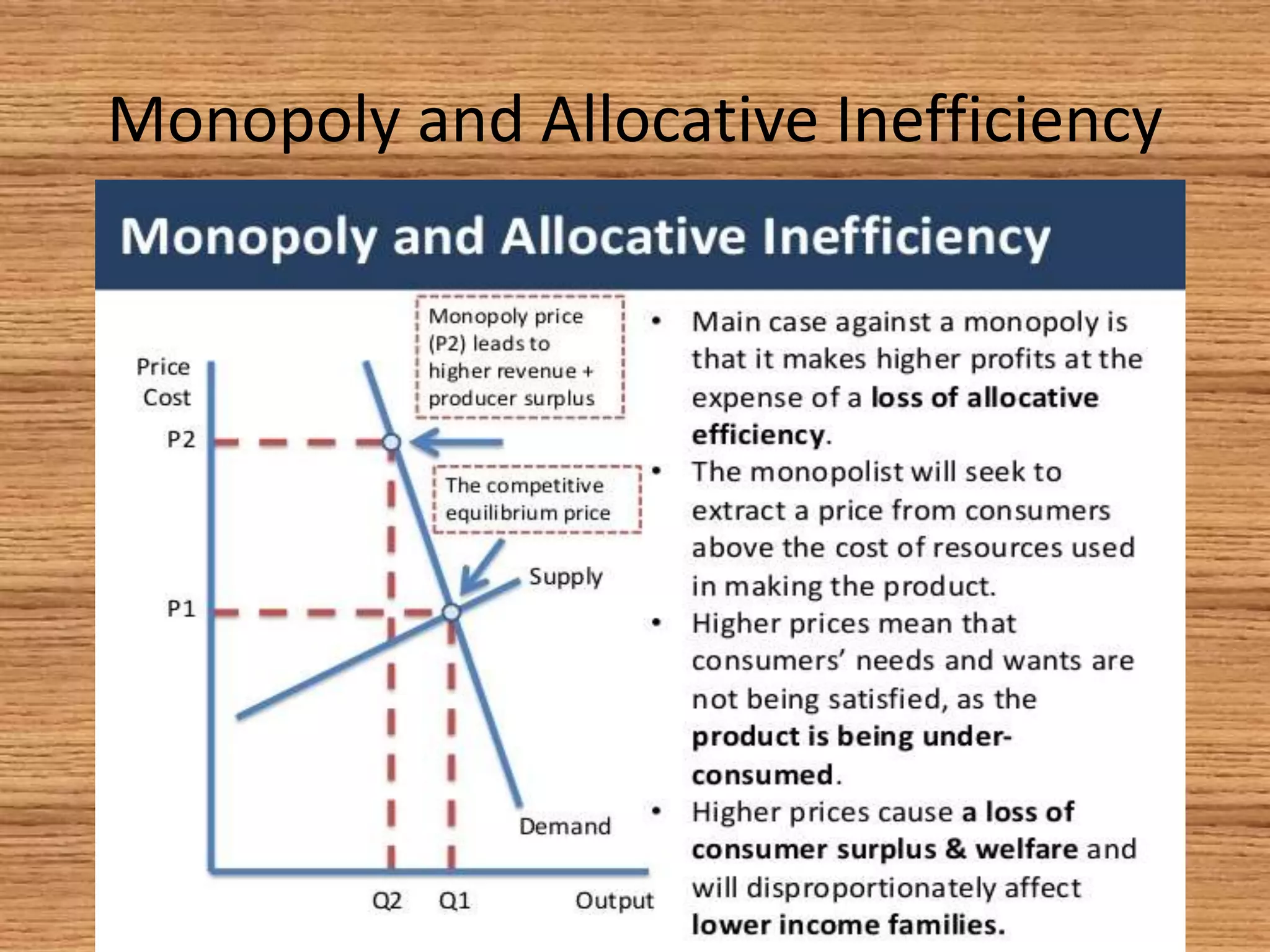
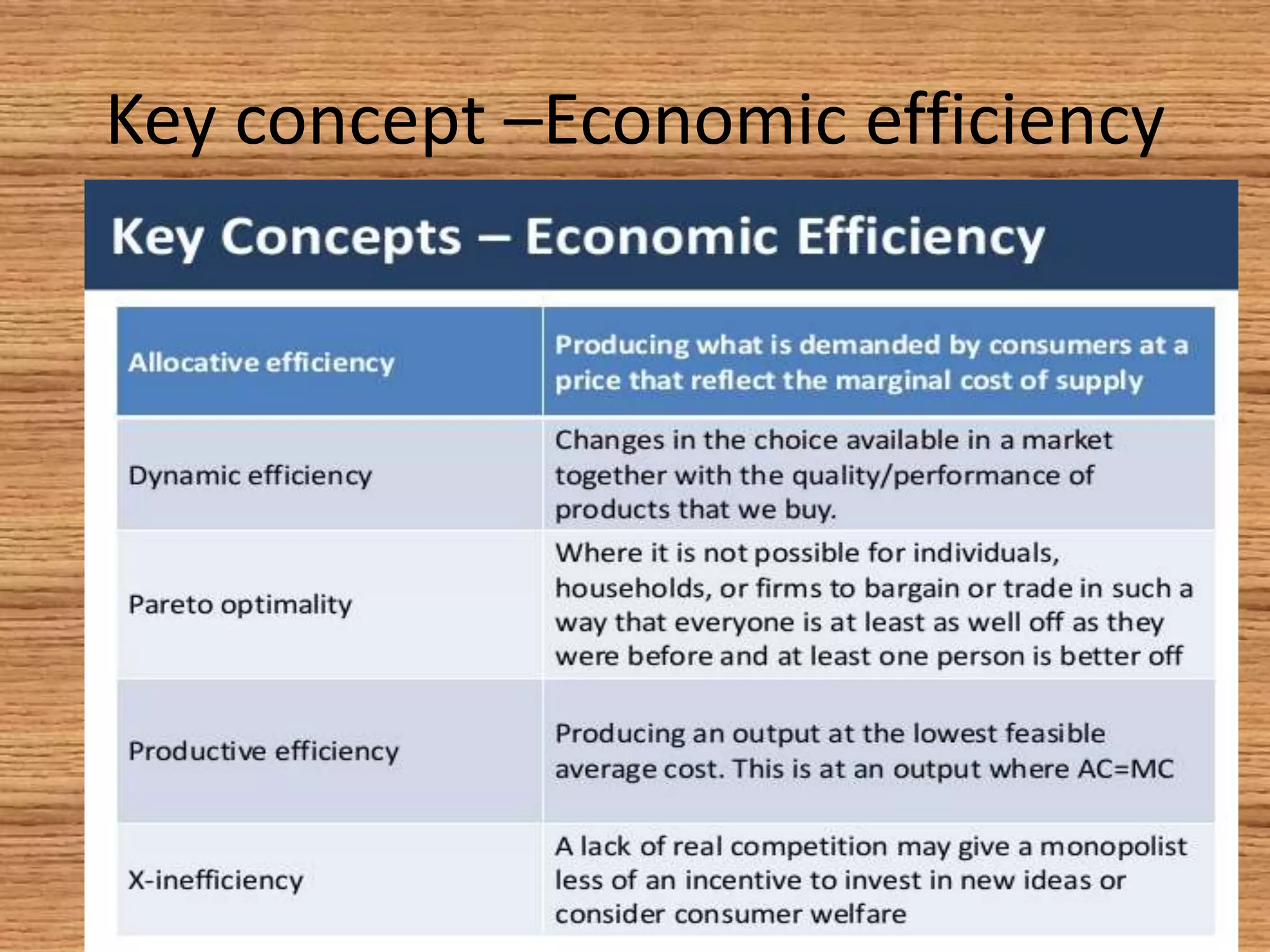
The document provides an overview of efficiency and economic valuation, detailing types such as allocative, productive, social, and dynamic efficiency. It defines key concepts like economic efficiency, monopoly, and market failure while emphasizing the importance of avoiding waste in resource allocation. The summary concludes that economic efficiency is a condition rather than a measurable quantity, with potential indicators having both advantages and disadvantages.