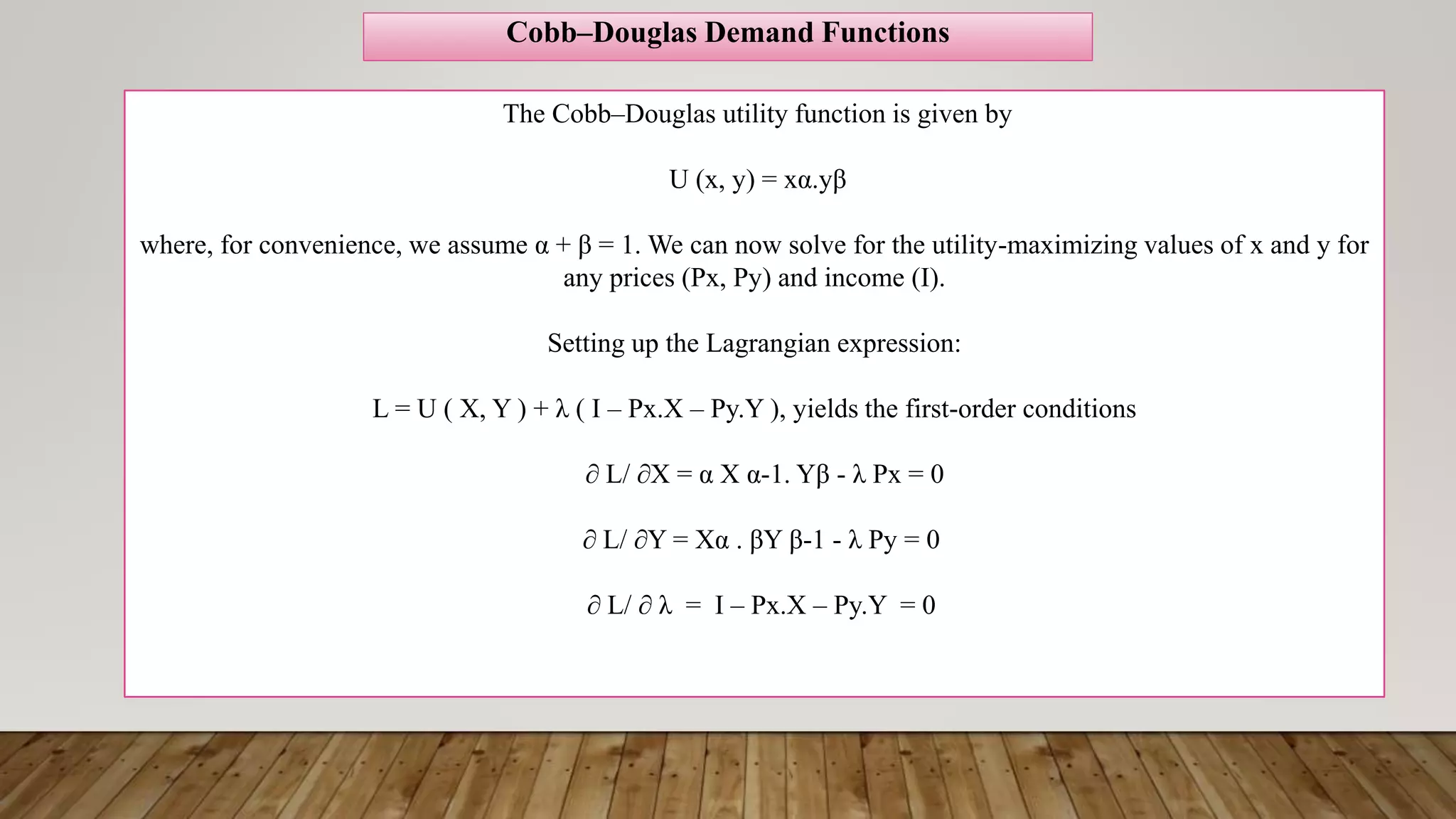
- Utility is a measure of satisfaction derived from consuming goods and services. Individuals seek to maximize their utility subject to a budget constraint.
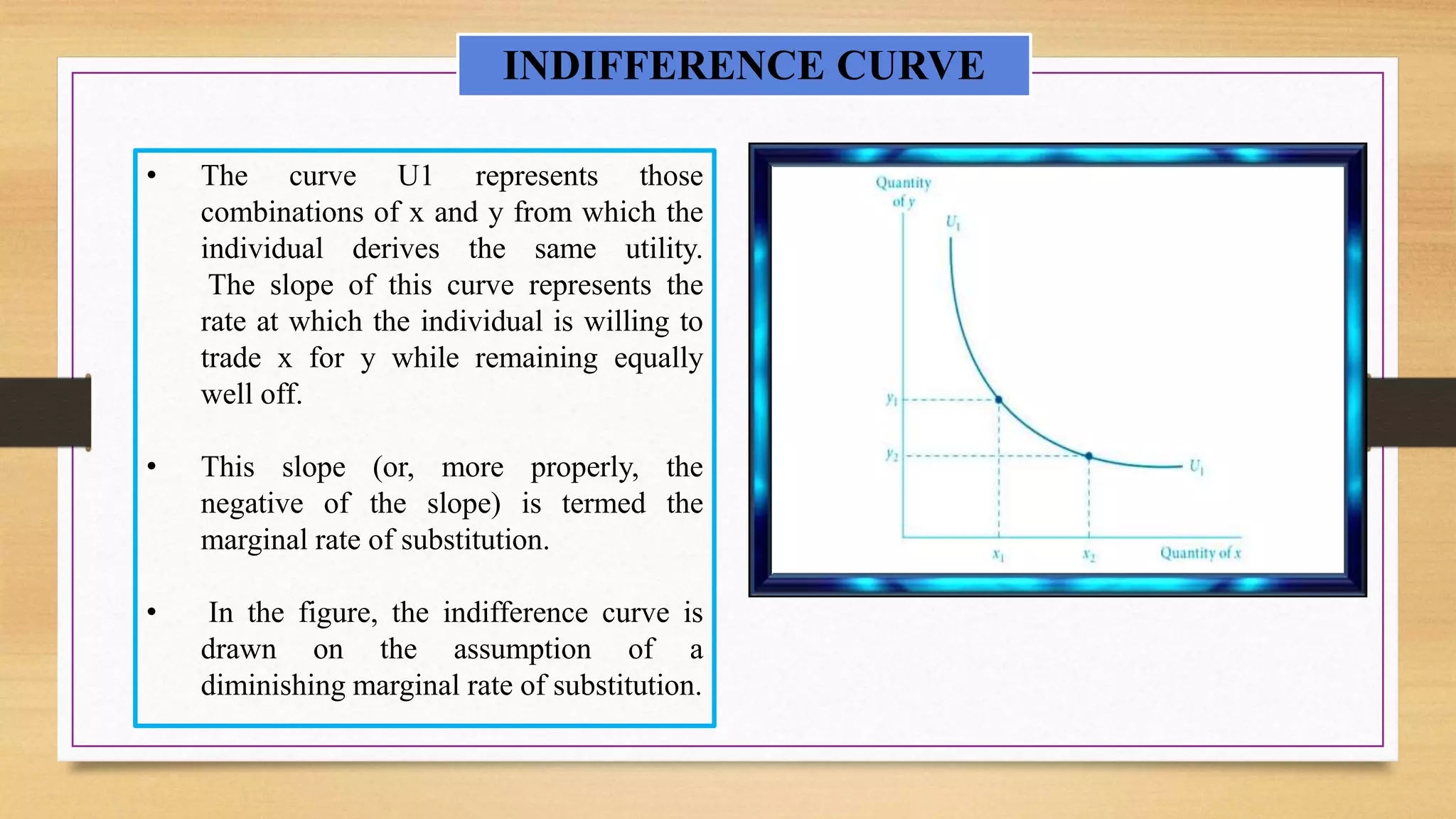
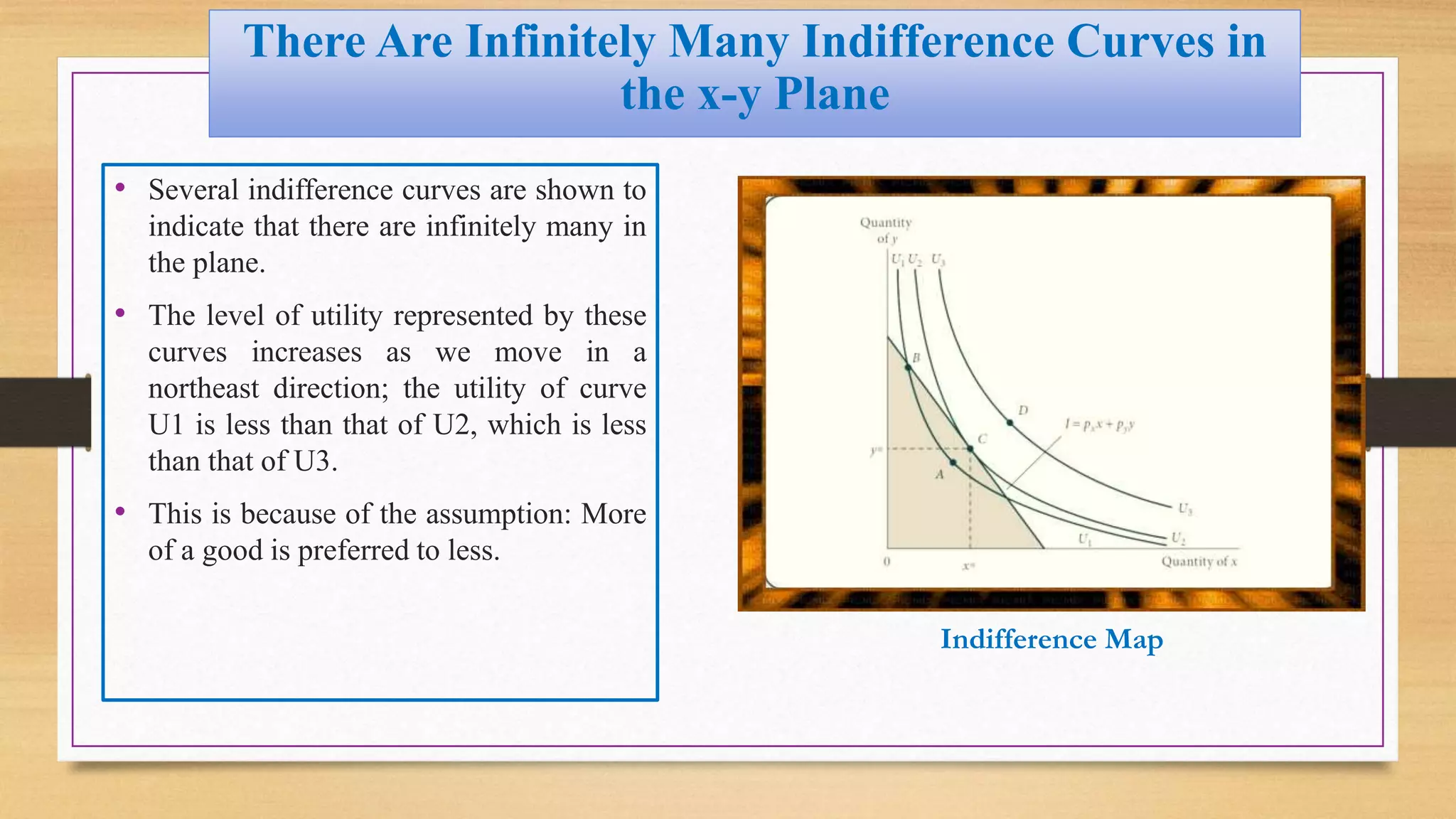
- Indifference curves represent combinations of goods that provide equal utility. The slope of the indifference curve is the marginal rate of substitution (MRS).
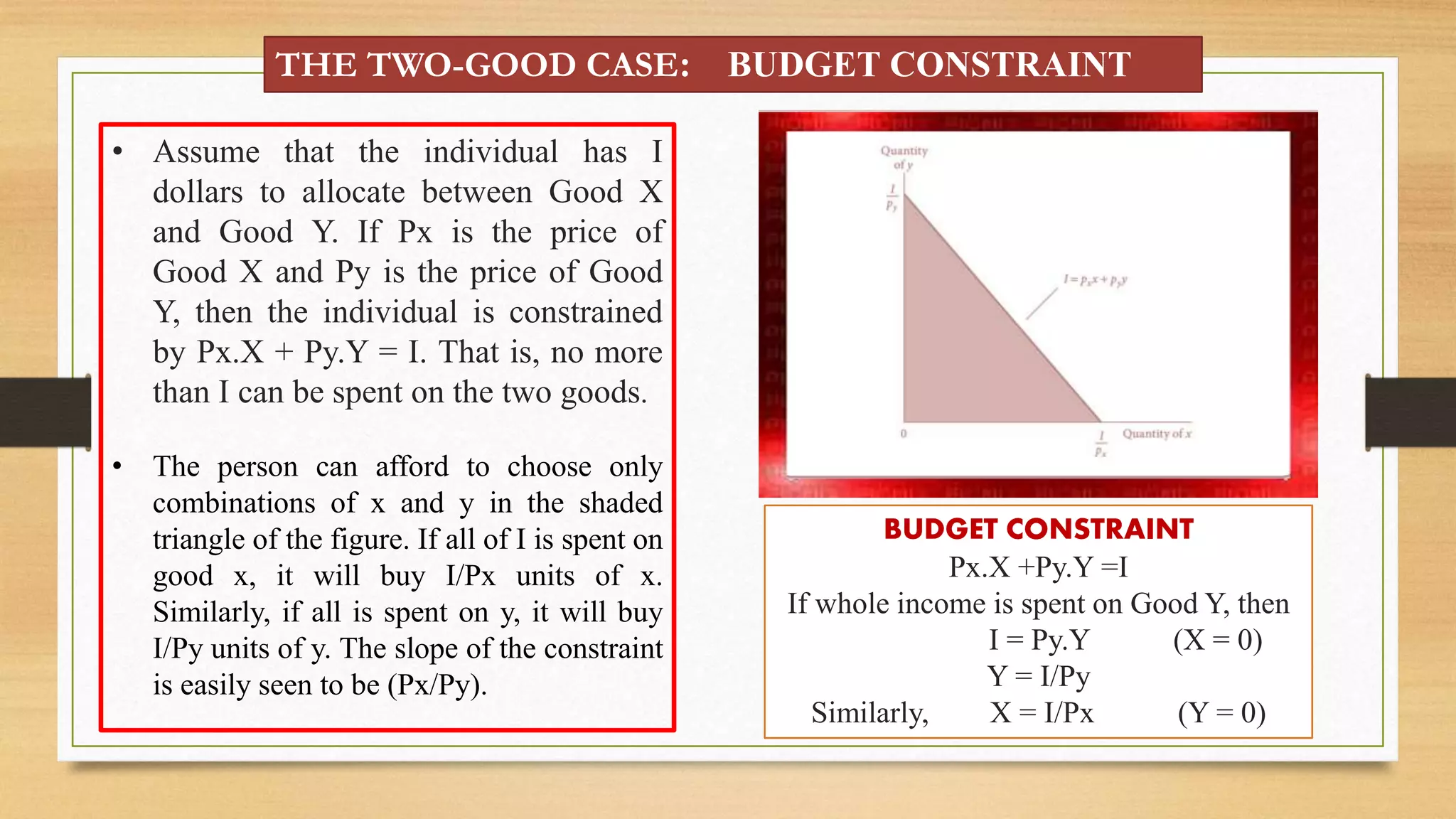
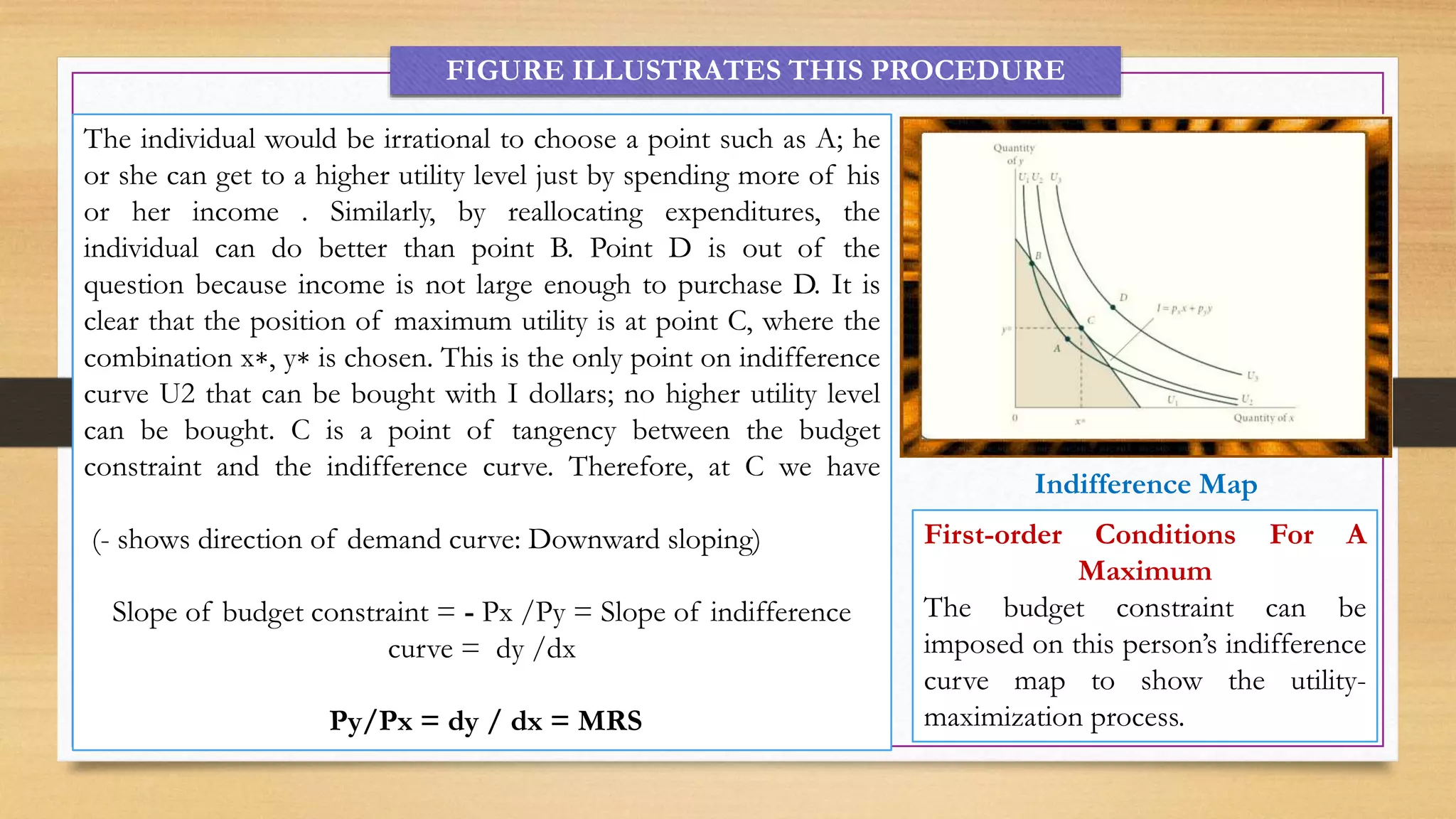
- The budget constraint shows affordable combinations given prices and income. Utility is maximized at the point where the MRS equals the price ratio, where the indifference curve is tangent to the budget constraint.
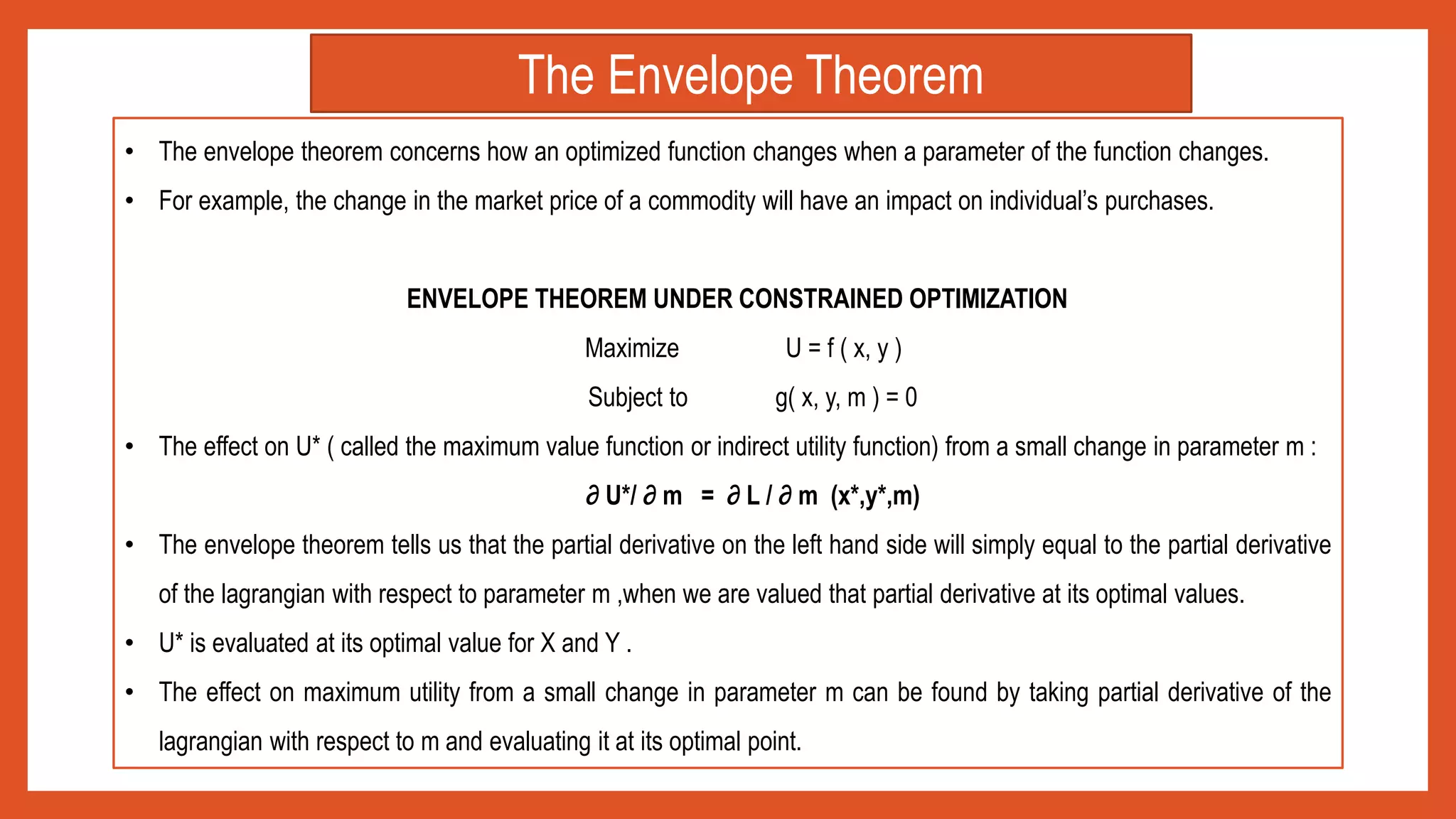
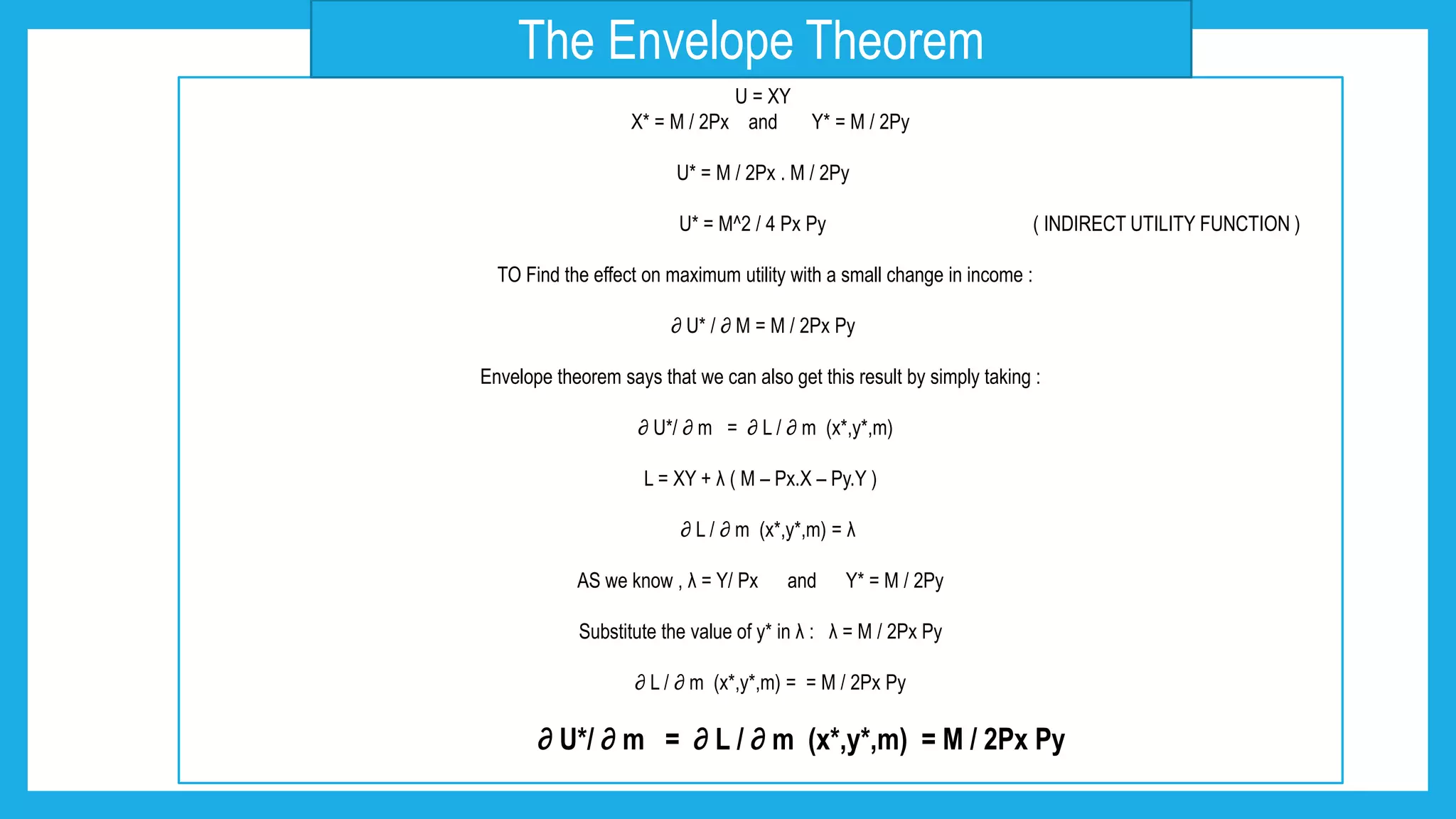
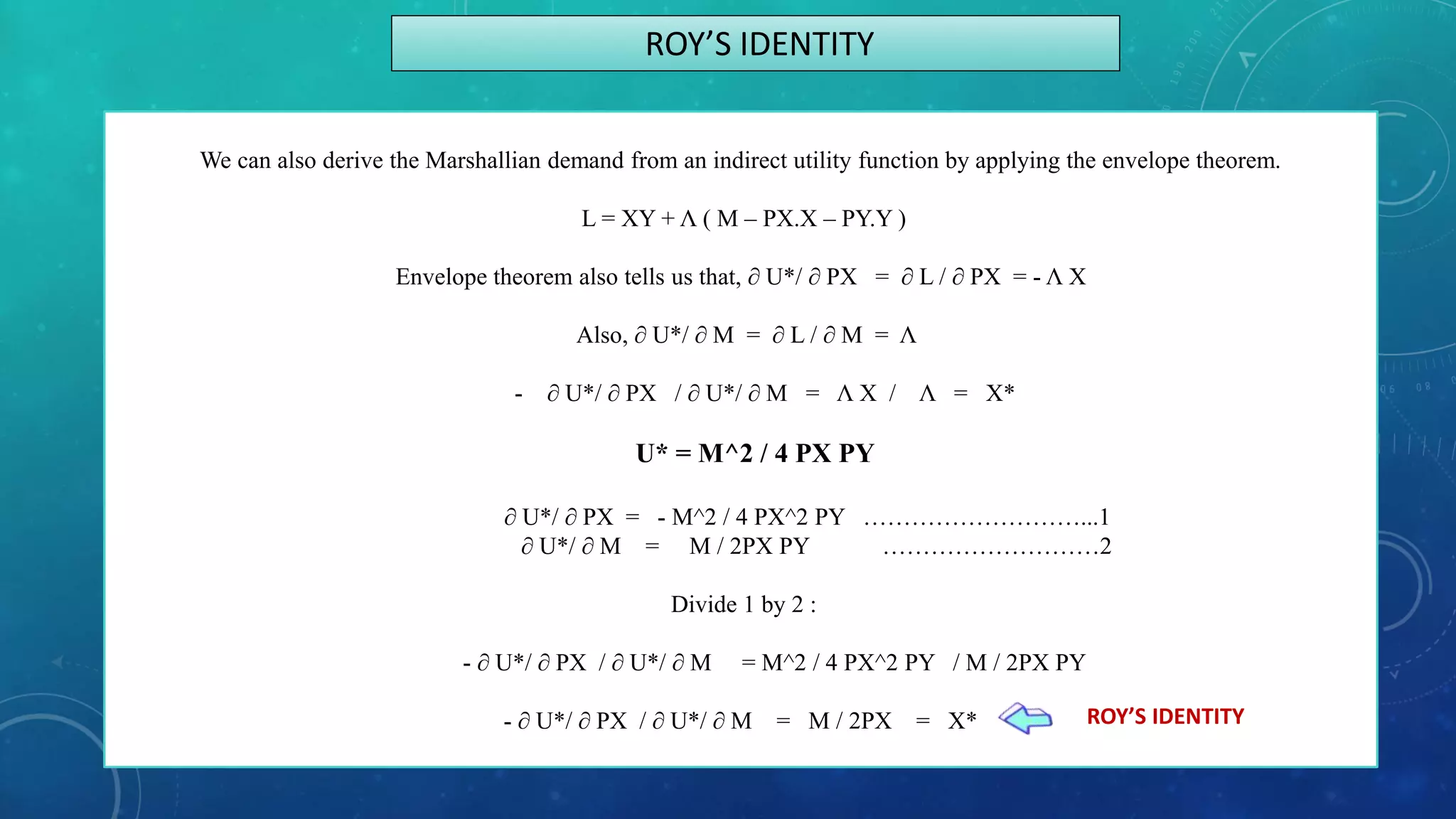
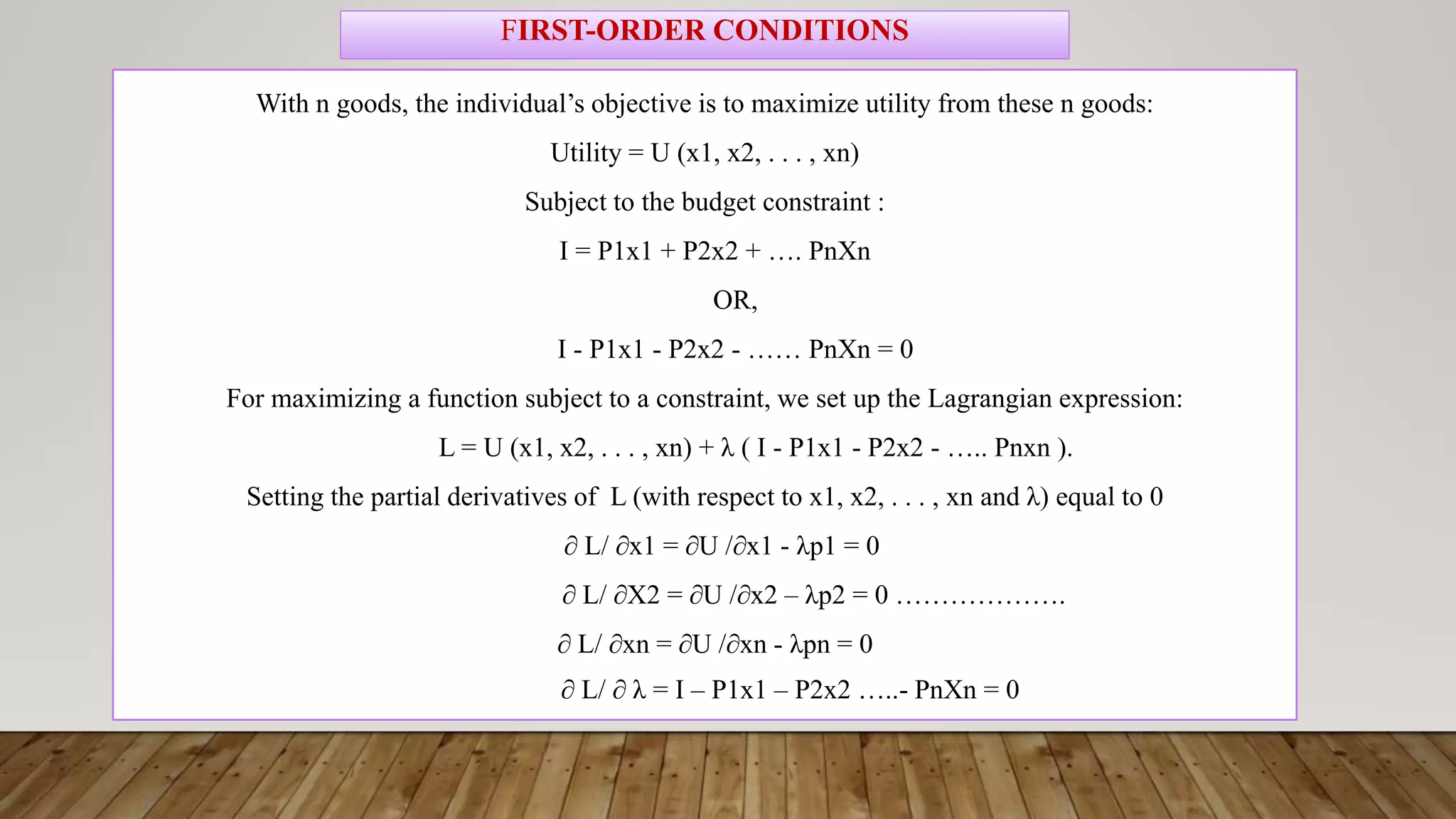
- Using tools like Lagrangian optimization and the envelope theorem, the amounts demanded of each good can be derived as functions of prices and income.

![In order to solve for the optimal values of x1, x2, . . . , xn.
These optimal values in general depends on the prices of all the goods and on the individual’s income. That is,
X1*= X1 (P1, P2, . . . , Pn, I ),
X2*= X2 (P1, P2, . . . , Pn, I ), ....
Xn*= Xn (P1, P2, . . . , Pn, I ),
These demand functions, shows the dependence of the quantity of each xi demanded on P1, P2, . . . , Pn and I.
Substitute the optimal values of the x’s to in the original utility function to yield maximum utility =
U [ X1* (P1, P2, . . . , Pn, I ), X2* (P1, P2, . . . , Pn, I ) ,… Xn* (P1, P2, . . . , Pn, I )] = V (P1, P2, . . . , Pn, I )
INDIRECT UTILITY FUNCTION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utilitypresentation-210903055912/75/INDIRECT-UTILITY-FUNCTION-AND-ROY-S-IDENTITIY-by-Maryam-Lone-11-2048.jpg)
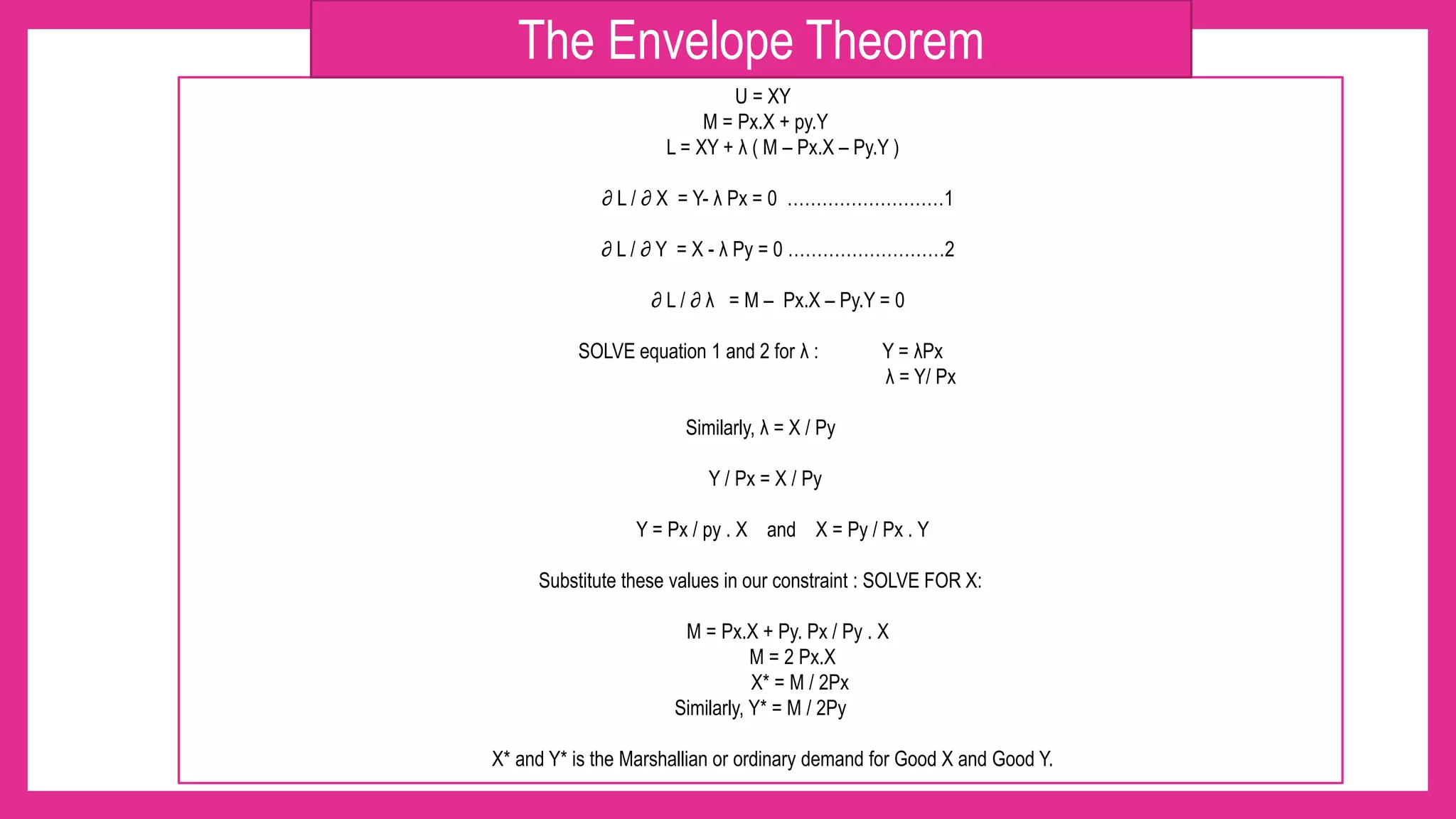
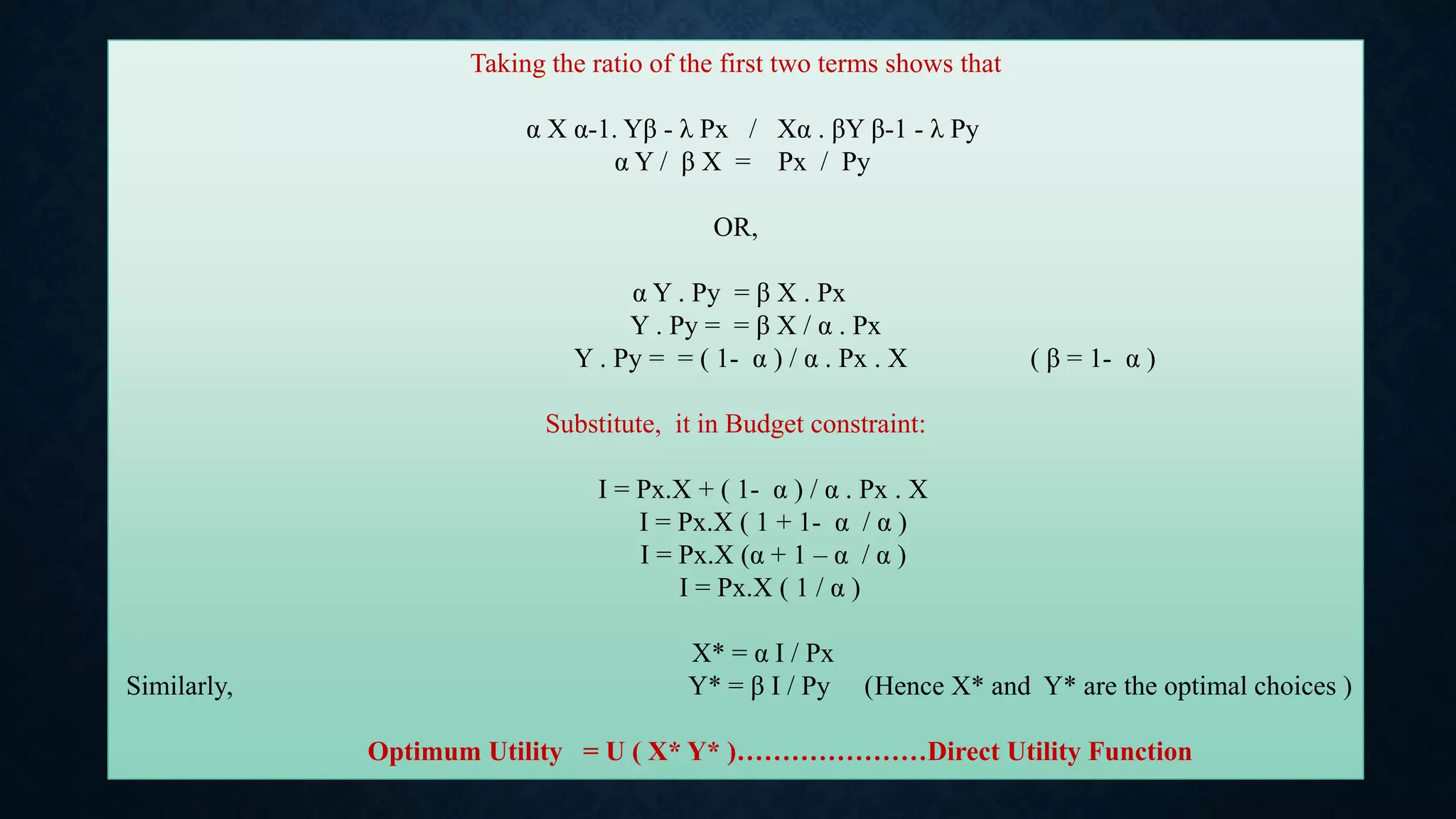
![Now as we know that :
X* = α I / Px
Y* = β I / Py
Putting these values in the original utility function, we get:
U (x*,y*) = xα.yβ = (α I / Px) α . (β I / Py ) β
If, I = 8 , Px = 1 , Py = 4 , α +β = 1 (constant returns to scale)
U ( x*,y*) = x^0.5 . y^0.5 = [ 0.5 (8) / 1 ]^0.5 . [ 0.5 (8) / 4 ]^0.5 =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utilitypresentation-210903055912/75/INDIRECT-UTILITY-FUNCTION-AND-ROY-S-IDENTITIY-by-Maryam-Lone-12-2048.jpg)
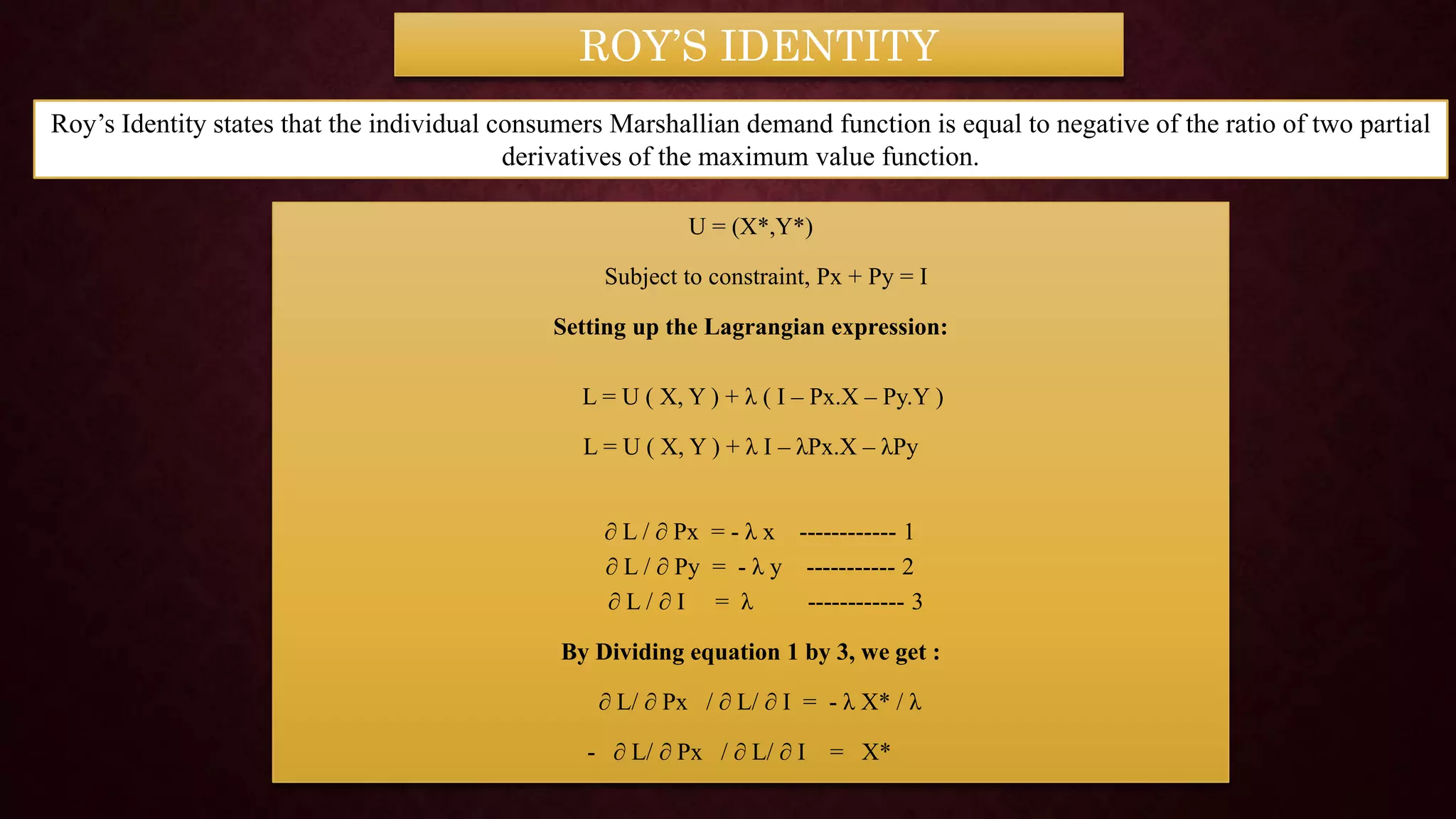

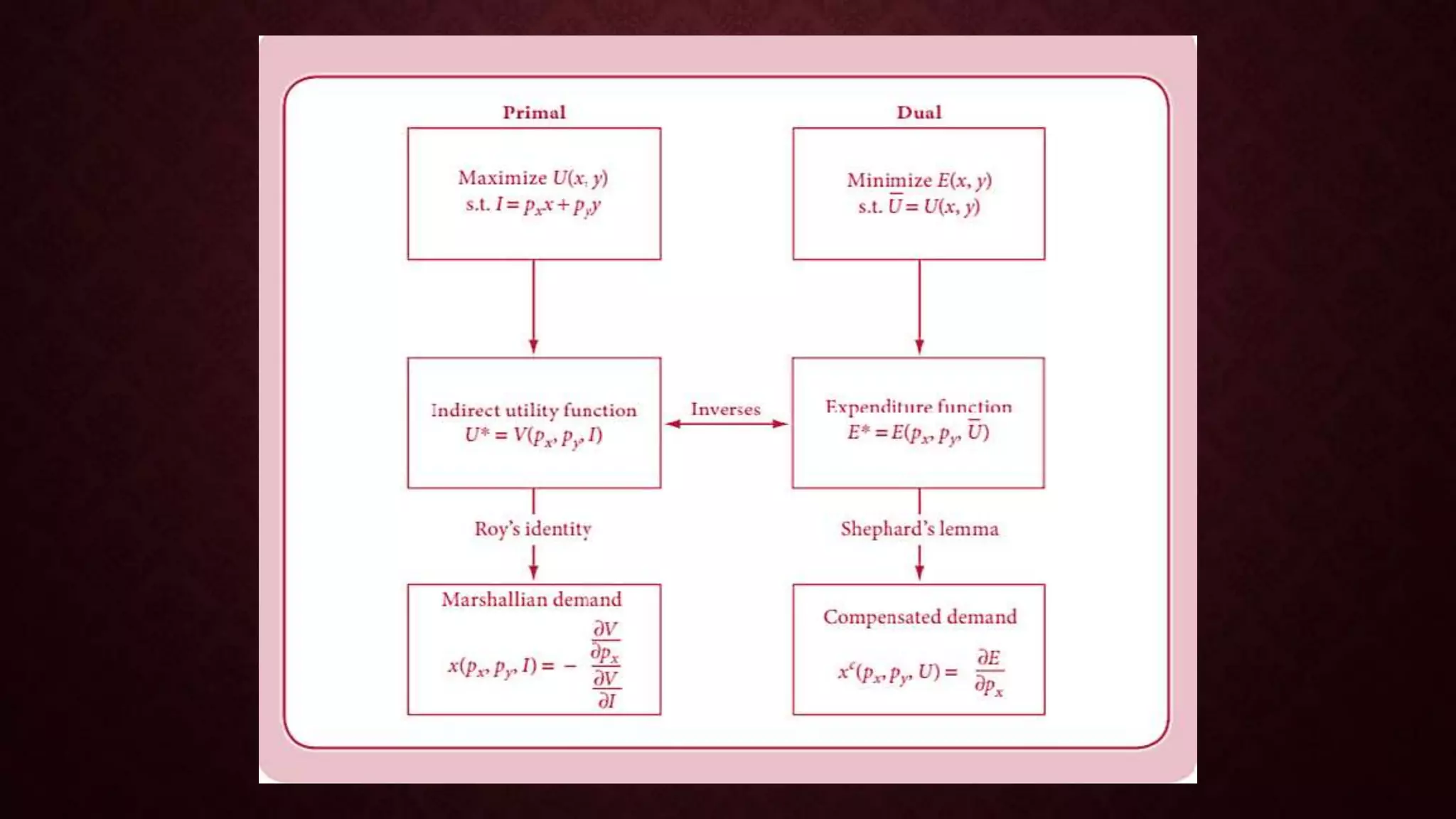
![Let U(x,y) be a utility function where x and y are
consumption goods. The consumer has a budget B and
faces market prices Px and Py for goods X and Y ,
respectively. The problem will be considered the primal
problem:
Maximize U = U (x,y)
subject to Px.X + Py.Y = B [ PRIMAL]
THE PRIMAL PROBLEM
A related dual problem for the consumer with the objective of
minimising the expenditure on X and Y while maintaining a fixed
utility level u* derived from the primal problem:
Minimise E = Px.X + Py.Y
subject to U (x,y) = U* [ Dual ]
THE DUAL PROBLEM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/utilitypresentation-210903055912/75/INDIRECT-UTILITY-FUNCTION-AND-ROY-S-IDENTITIY-by-Maryam-Lone-15-2048.jpg)