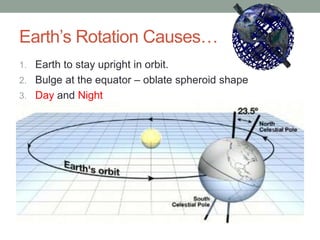
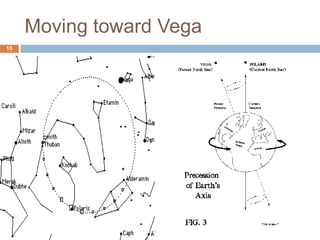
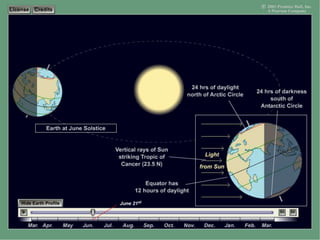
Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night. It also revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit, completing one revolution in 365.25 days. Earth's axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees, resulting in seasons. Earth's rotation causes it to bulge at the equator and precess slowly over thousands of years.