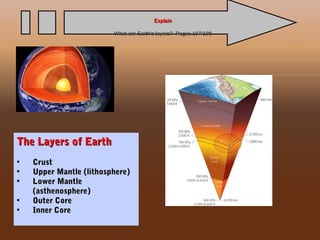
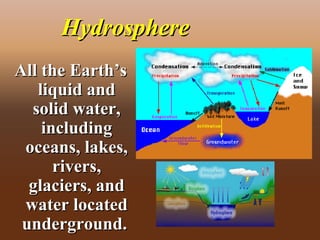
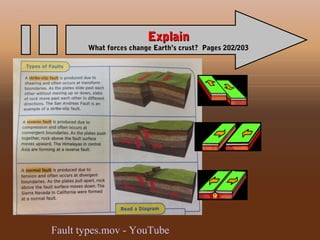
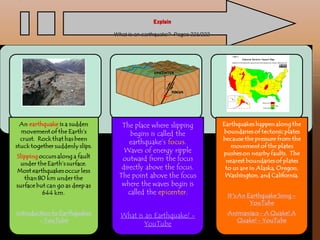
This document provides an overview of chapter 4 from an Earth Science textbook. It discusses key topics like the layers of Earth's interior including the core, mantle and crust. It defines important vocabulary like fault, magma, and hydrosphere. It explains how geological features like mountains form from processes such as volcanic eruptions, pressure changes below Earth's surface, and the movement of tectonic plates. It also summarizes how earthquakes occur along boundaries between tectonic plates when built-up pressure is released through sudden movements along faults.