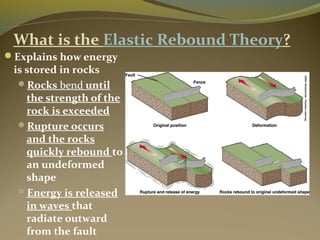
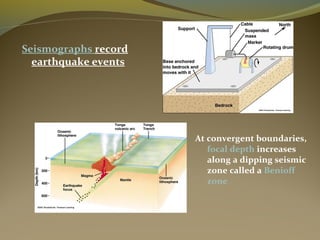
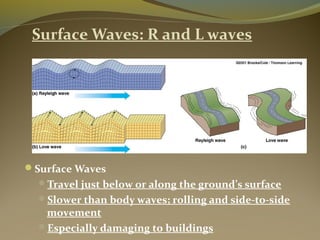
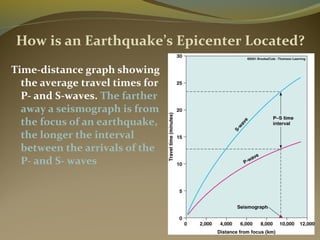
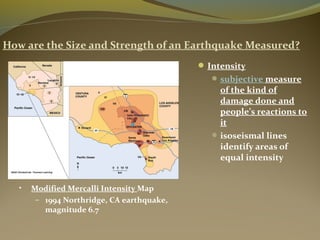
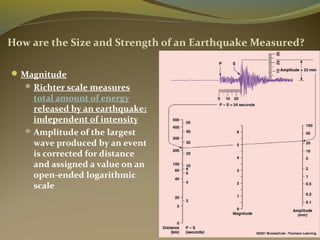
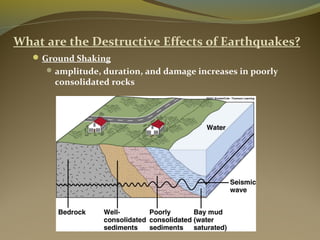
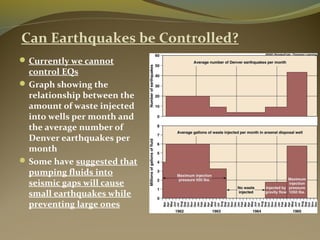
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy from movements of tectonic plates or breaking of rocks. The focus is the point where faulting begins underground, and the epicenter is the point directly above on the surface. Most earthquakes occur along plate boundaries and are measured using magnitude and intensity scales. Seismic waves, including P, S, and surface waves, are used to locate the epicenter based on their travel times to different seismograph stations. While some precursors and patterns in seismic activity can help assess earthquake risks, earthquakes currently cannot be predicted or controlled.