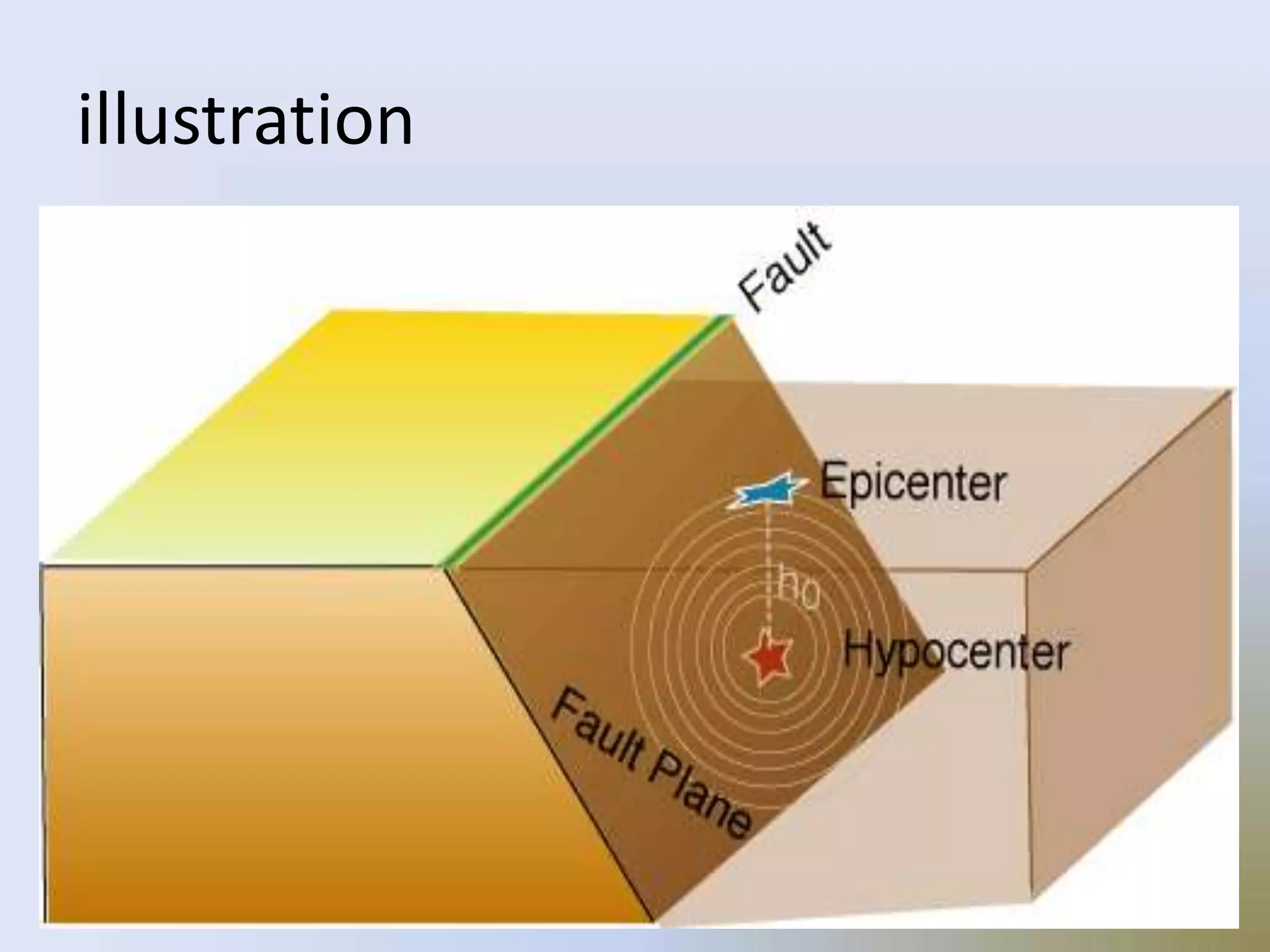
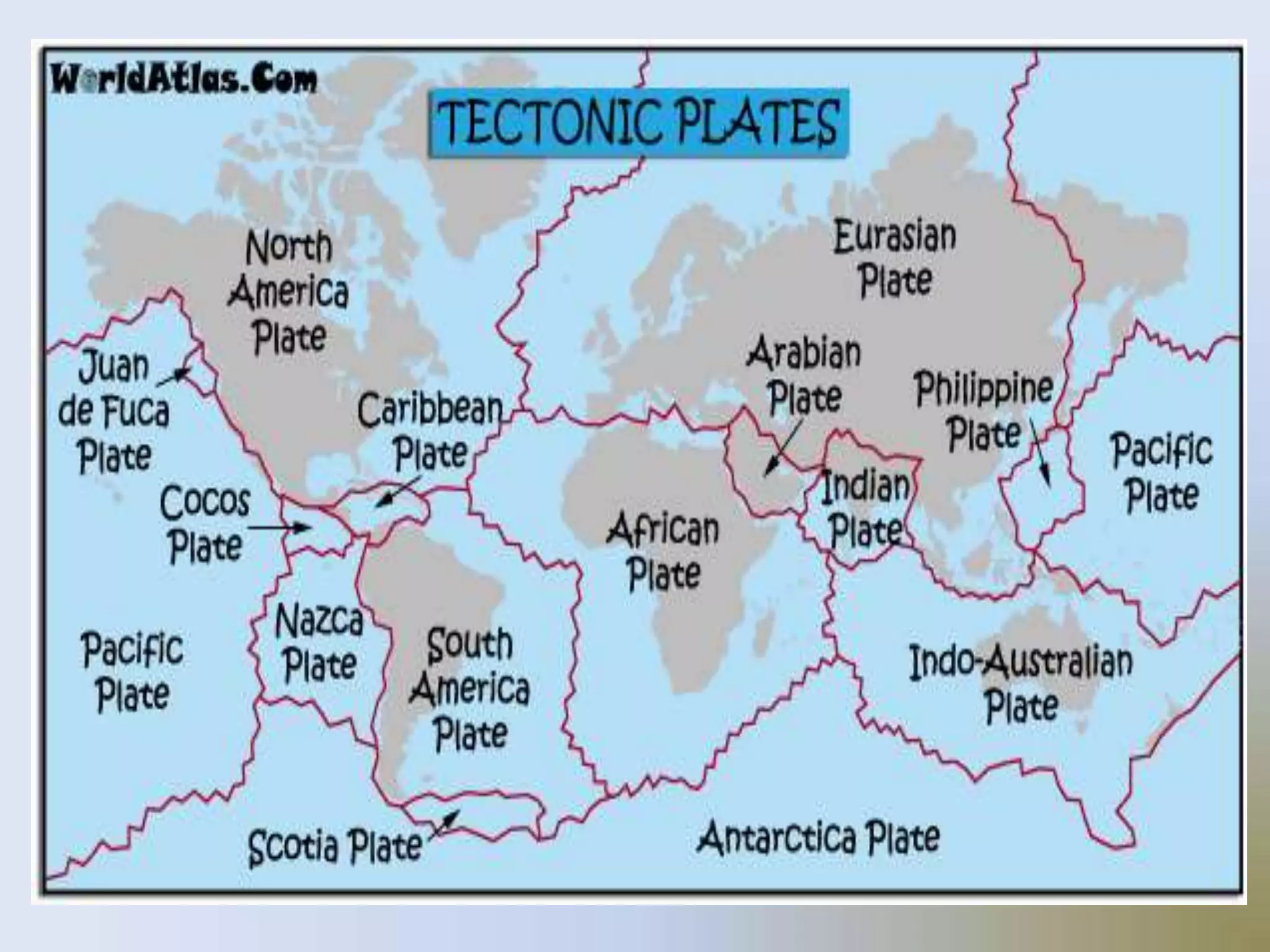
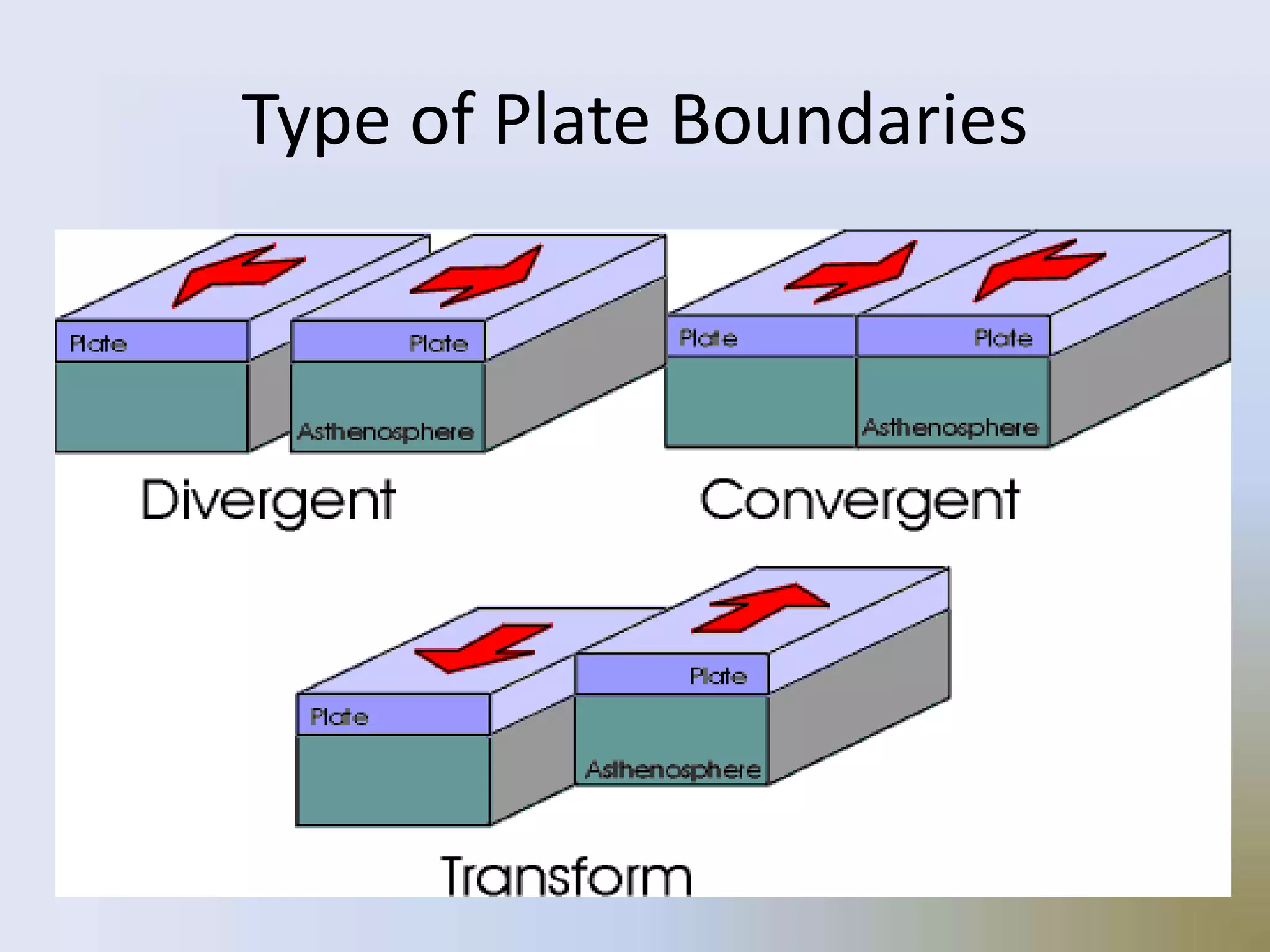
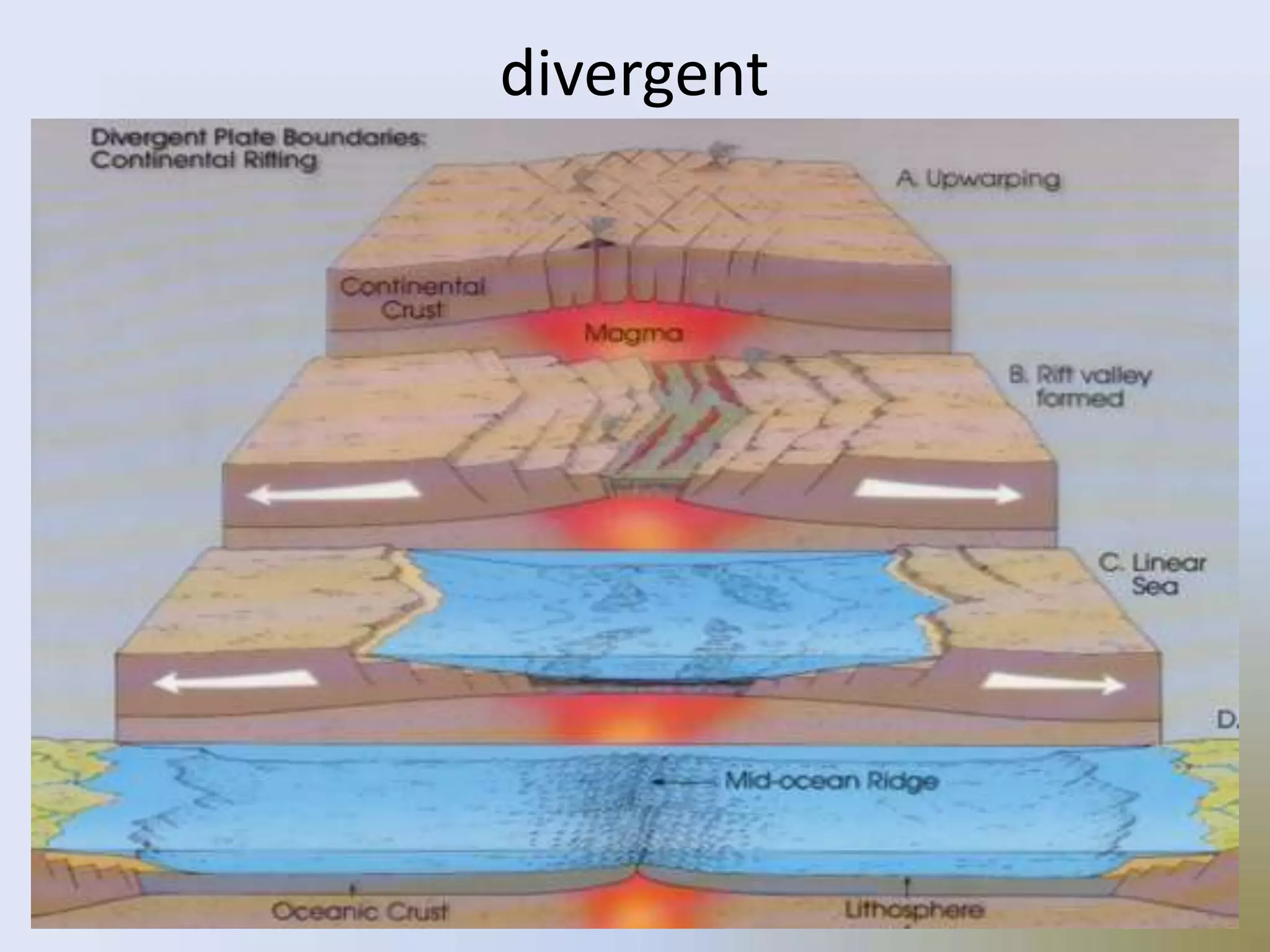
On January 17, 1995, a magnitude 7.2 earthquake struck Kobe, Japan, the second most populated area after Tokyo. Over 5,000 people were killed, more than 300,000 became homeless, and $100 billion in damage was caused during the brief 20 second shaking. The earthquake was caused by two blocks of the earth suddenly slipping past one another along a fault line.